一、电话号码的字母组合
题目链接
思路:回溯三部曲。
确定回溯函数参数:题目中给的 digits,还要有一个参数就是int型的index(记录遍历第几个数字,就是用来遍历digits的,同时也代表了递归的深度),第三个参数numString(数字和字母映射)。
确定终止条件:如果index 等于 输入的数字个数(digits.size)了,就return。
确定单层遍历逻辑:首先要取index指向的数字,并找到对应的字符集;然后for循环来处理这个字符集
注意:
(1)解决三个问题
数字和字母如何映射 (使用map或者定义一个二维数组)
两个字母就两个for循环,三个字符我就三个for循环,以此类推,然后发现代码根本写不出来
输入1 * #按键等等异常情况
(2)区别于普通的组合问题,本题是多个集合求组合,因为本题每一个数字代表的是不同集合,也就是求不同集合之间的组合。
(3)全局变量:一个字符串sb来收集叶子节点的结果,一个字符串数组result保存sb。
解法:
class Solution {
// 最终结果字符数组和单次符合条件结果
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits.length() == 0 || digits == null)
return res;
String[] numString = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
backTracking(digits, numString, 0);
return res;
}
public void backTracking(String digits, String[] numString ,int num) {
if (num == digits.length()){
res.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
// digits.charAt(num)能够获取到当前的号码数字,2-9
String t = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0'];
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
sb.append(t.charAt(i));
backTracking(digits, numString, num + 1);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1); //回溯
}
}
}二、组合总和
题目链接
思路:基本与组合总和III类似。区别有:
组合没有数量要求
元素可无限重复选取
注意:
如果是一个集合来求组合的话,就需要startIndex;(否则会出现重复情况)
如果是多个集合取组合,各个集合之间相互不影响,那么就不用startIndex。
解法(未剪枝):
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
// sum, startIndex是开始位置也是candidates的索引
back(candidates, target, 0,0);
return res;
}
private void back(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if (sum > target)
return;
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++){
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
back(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}剪枝优化:
1.对总集合排序之后,如果下一层的sum(就是本层的 sum + candidates[i])已经大于target,就可以结束本轮for循环的遍历。
解法:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先进行排序
back(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return res;
}
private void back(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if (sum > target)
return;
// 多一步判断
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++){
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
back(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}三、组合总和II
题目链接
思路:与组合总和类似,但区别于
本题candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
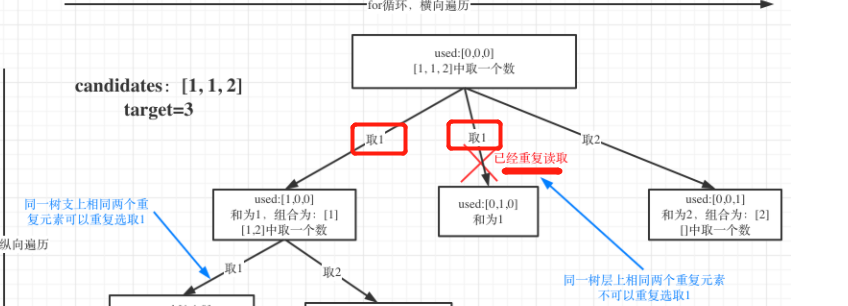
本题数组candidates的元素是有重复的,而39.组合总和 (opens new window)是无重复元素的数组candidates。也就是说组合里的元素可能有重复且只使用一次,但组合之间不能重复。
本题的难点在于区别2中:集合(数组candidates)有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合。
去重也去的是同一个树层上,重复的值。代码里就是判断i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1],直接continue
解法:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先进行排序
back(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return res;
}
private void back(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if (sum > target)
return;
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++){
// 碰到同一树层重复元素 直接continue
if ( i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] ) {
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
back(candidates, target, sum, i + 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}






![Python蓝桥杯训练:基本数据结构 [二叉树] 上](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9e5ba507238c42b088d44701239bb18e.png#pic_center)