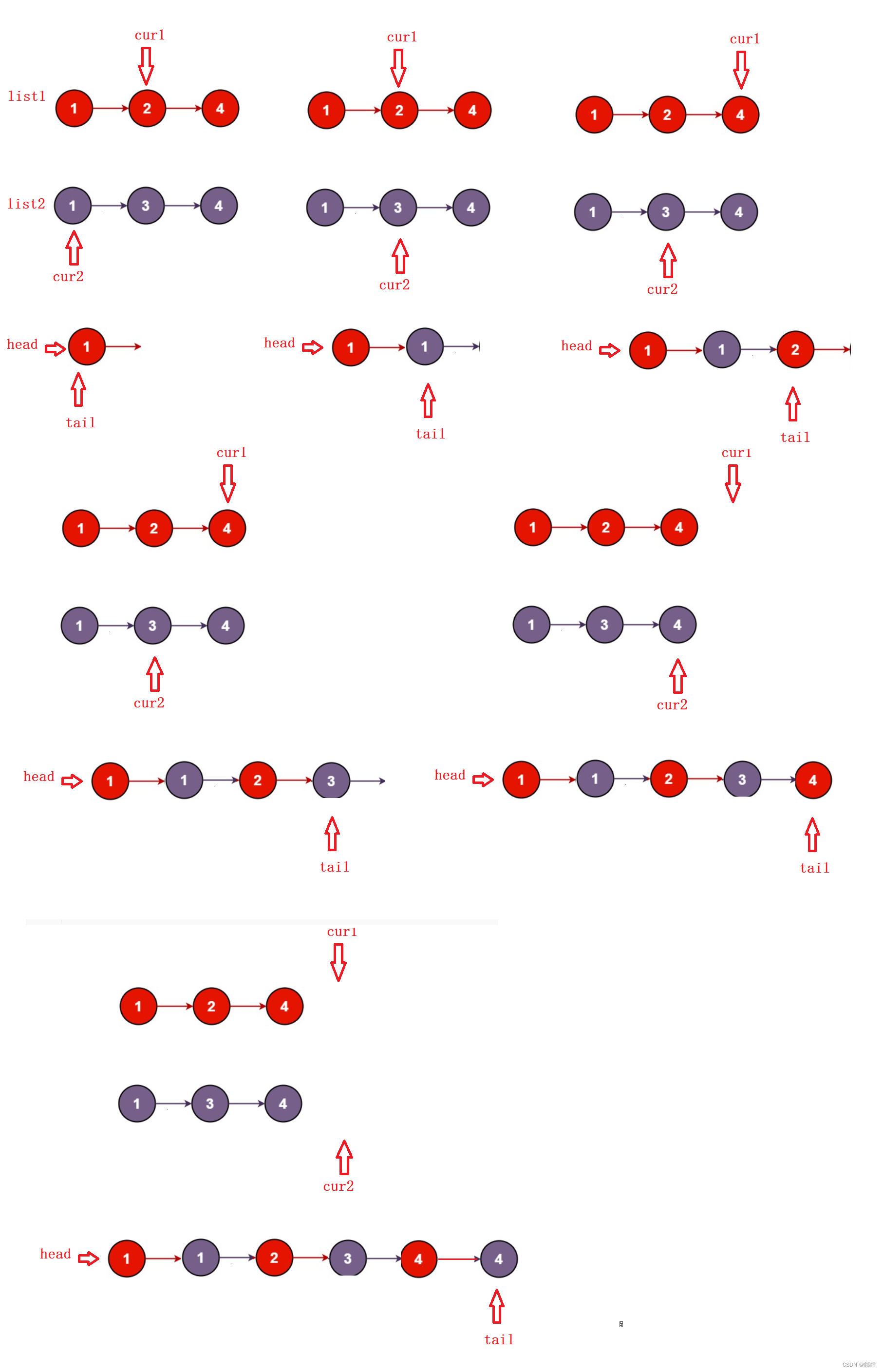
尾插
核心思路:依次比较 ,取经过比较后较小值进行尾插
cur1 指向list1 ,cur 2指向list2 ,当cur1走完list1 或者cur2 走完list2 后停止
如果cur1走完list1 ,可以将cur2 整个拿下来尾插
如果cur2走完list2 ,可以将cur1 整个拿下来尾插
特殊情况 : 如果list1 是空链表 返回 list2
如果list2 是空链表 返回 list1
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode*tail = NULL ;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1 ;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
//空链表
if(list1 ==NULL)
{
return list2 ;
}
if( list2 ==NULL)
{
return list1 ;
}
//非空链表
//依次比较
while ( cur1 && cur2) //其中一个链表走完了就结束循环
{
if( cur1->val < cur2->val) //list1 <list2
{
//尾插
if ( head == NULL)
{
head =tail =cur1 ;
}
else
{
tail->next= cur1 ;
tail =tail->next ;
}
cur1 =cur1->next ;
}
else
{
if ( head ==NULL)
{
head =tail =cur2 ;
}
else
{
tail->next= cur2 ;
tail =tail->next ;
}
cur2 =cur2->next ;
}
}
if( cur1) //cur2已经走完list2 ,直接将cur1整个拿下来尾插
{
tail->next =cur1 ;
}
if( cur2) //cur1已经走完list1 ,直接将cur2整个拿下来尾插
{
tail->next =cur2 ;
}
return head ;
}
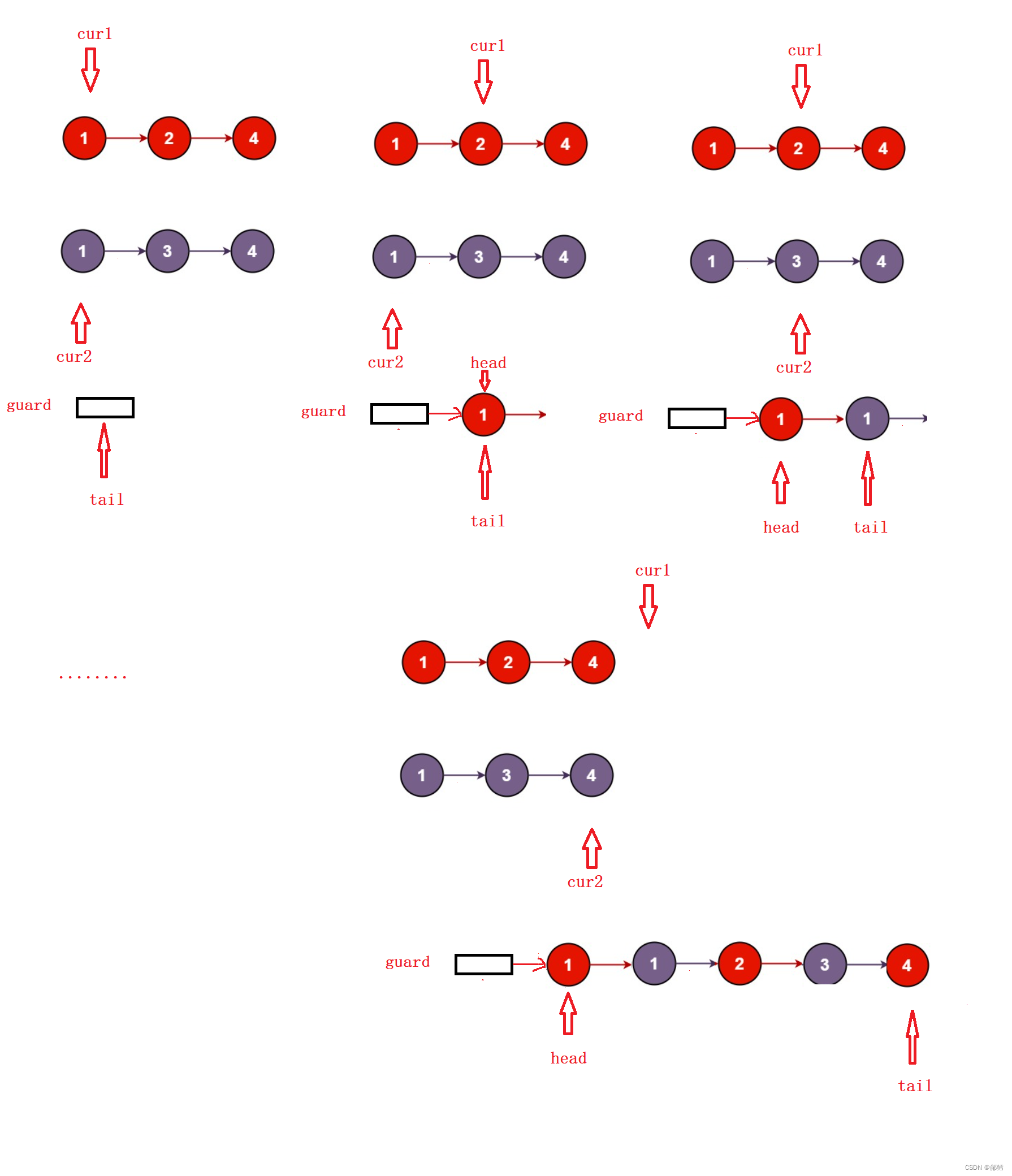
哨兵位头节点
哨兵位头节点 是一个附加的链表节点.该节点作为第一个节点,它的数据域不存储任何东西
只是为了操作的方便而引入的
如果一个链表有哨兵节点的话,那么线性表的第一个元素应该是链表的第二个节点
也就是说返回这个链表,应该返回哨兵位的next,因为哨兵位的next才是有效的真实的头节点
要注意使用完哨兵位头节点后,对其进行释放,避免内存泄漏
哨兵位头节点相比较上面的解法 ,不需要判断tail是否为空 (tail 不会为空)
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc( sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* tail = guard ;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1 ;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2 ;
tail->next = NULL ;
while ( cur1 &&cur2) //两个链表都不为空
{
//尾插
if( cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
tail->next = cur1 ;
cur1 = cur1->next ;
tail = tail->next ;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2 ;
cur2 = cur2->next ;
tail = tail->next ;
}
}
// cur1 走完list1
if( cur2)
{
tail->next = cur2 ;
}
if( cur1) // cur2 走完list2
{
tail->next = cur1 ;
}
struct ListNode* head = guard->next ;
return head ;
free(guard);//要注意使用完哨兵位头节点后,对其进行释放,避免内存泄漏
}
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,不妨动动手指给点赞收藏加转发,给鄃鳕一个大大的关注
你们的每一次支持都将转化为我前进的动力!!!










![[2.2.1]进程管理——调度的概念、层次](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4badbeccc4a8bbc246d3baee80c81d5f.png)


