目录
1.说明
2.怎样设置默认切片数
2.1 RDD默认切片设置
2.2 SparkSQL默认切片设置
3. makeRDD 切片原理
4. textFile 切片原理
4.1 切片规则
4.2 怎样设置切片大小
4.3 测试代码
5.hadoopFile 切片原理
5.1 说明
5.2 切片规则
5.3 怎样设置切片大小
5.4 代码测试
5.5 minPartitions 在 CombineTextInputFormat 中的作用?
5.6 重点关注
1.说明
在spark中为我们提供了用来读取数据的方法
比如 makeRDD、parallelize、textFile、hadoopFile等方法
这些方法按照数据源可以分为两类 文件系统、Driver内存中的集合数据
当我们使用指定的方法读取数据后,会按照指定的切片个数对文件进行切片
2.怎样设置默认切片数
在我们在使用RDD的算子时,经常会遇到可以显式的指定切片个数,或者隐式的使用默认切片个数,下面会告诉我们,怎样设置默认切片个数
2.1 RDD默认切片设置
1.驱动程序中设置
val sparkconf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("测试默认切片数")
.set("spark.default.parallelism","1000")
.setMaster("local[100]")
2.spark-shell或spark-submit 设置
spark-shell \
--master yarn \
--name "spark-shell-tmp" \
--conf spark.default.parallelism=1000 \
--driver-memory 40G \
--executor-memory 40G \
--num-executors 40 \
--executor-cores 6 \
3.不指定 spark.default.parallelism 参数时,将使用默认值
local模式:
local[100] : 100
local : 客户端机器核数
集群模式(yarn):
2 或者 核数总和源码:
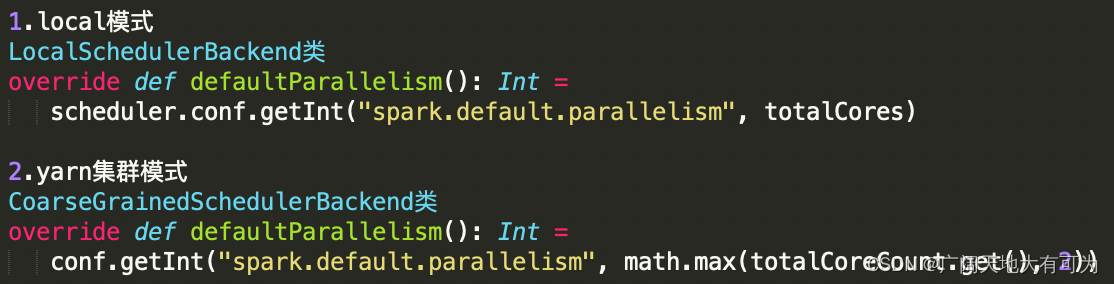
查看默认切片数:
// 获取默认切片数
val parallelism = sc.defaultParallelism2.2 SparkSQL默认切片设置
-- 设置默认切片数
set spark.sql.shuffle.partitions=1000;
默认值:
当不设置时,默认为200
注意:
spark.default.parallelism 只有在处理RDD时才会起作用,对SparkSQL的无效
spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 则是对sparks SQL专用的设置3. makeRDD 切片原理
可用通过 makeRDD算子 将Driver中序列集合中数据转换成RDD,在转换的过程中,会根据指定的切片个数 和 集合索引对集合切片
切片规则:
根据集合长度和切片数将集合切分成若干子集合(和集合元素内容无关)
示例代码:
test("makeRDD - 切片逻辑") {
// 初始化 spark配置实例
val sparkconf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName("")
// 初始化 spark环境对象
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkconf)
val rdd: RDD[(String, String)] = sc.makeRDD(List(
("张飞1", "张飞java scala spark")
, ("张飞2", "张飞java scala spark")
, ("刘备3", "刘备java spark")
, ("刘备4", "刘备java scala spark")
, ("刘备5", "刘备scala spark")
, ("关羽6", "关羽java scala spark")
, ("关羽7", "关羽java scala")
, ("关羽8", "关羽java scala spark")
, ("关羽9", "关羽java spark")))
// 查看每个分区的内容
rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex(
(i, iter) => {
println(s"分区编号$i :${iter.mkString(" ")}");
iter
}
).collect()
rdd.getNumPartitions
sc.stop()
}
结果: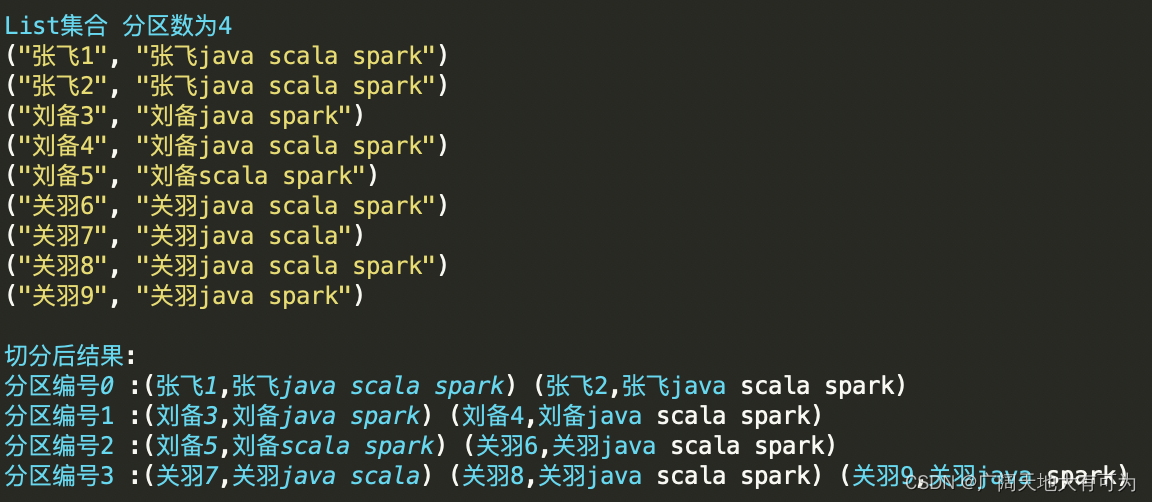
源码阅读:
1. 通过SparkContext创建rdd
def parallelize[T: ClassTag](
seq: Seq[T],
numSlices: Int = defaultParallelism): RDD[T] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
new ParallelCollectionRDD[T](this, seq, numSlices, Map[Int, Seq[String]]())
}
2. ParallelCollectionRDD类中的 getPartitions方法
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
val slices = ParallelCollectionRDD.slice(data, numSlices).toArray
slices.indices.map(i => new ParallelCollectionPartition(id, i, slices(i))).toArray
}
3. ParallelCollectionRDD对象的slice方法(核心切片逻辑)
def slice[T: ClassTag](seq: Seq[T], numSlices: Int): Seq[Seq[T]] = {
// 对切片数做合法性校验
if (numSlices < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Positive number of partitions required")
}
// TODO 通过 集合长度和切片数 获取每个切片的位置信息
// 从这可以得出 对集合的切片只和 集合索引和切片数相关,和集合内容无关
// 将 集合索引按照切片数 切分成若干元素
def positions(length: Long, numSlices: Int): Iterator[(Int, Int)] = {
(0 until numSlices).iterator.map { i =>
val start = ((i * length) / numSlices).toInt
val end = (((i + 1) * length) / numSlices).toInt
(start, end)
}
}
// 对集合类型做判断
seq match {
case r: Range =>
positions(r.length, numSlices).zipWithIndex.map { case ((start, end), index) =>
// If the range is inclusive, use inclusive range for the last slice
if (r.isInclusive && index == numSlices - 1) {
new Range.Inclusive(r.start + start * r.step, r.end, r.step)
} else {
new Range.Inclusive(r.start + start * r.step, r.start + (end - 1) * r.step, r.step)
}
}.toSeq.asInstanceOf[Seq[Seq[T]]]
case nr: NumericRange[T] =>
// For ranges of Long, Double, BigInteger, etc
val slices = new ArrayBuffer[Seq[T]](numSlices)
var r = nr
for ((start, end) <- positions(nr.length, numSlices)) {
val sliceSize = end - start
slices += r.take(sliceSize).asInstanceOf[Seq[T]]
r = r.drop(sliceSize)
}
slices.toSeq
case _ =>
val array = seq.toArray // To prevent O(n^2) operations for List etc
positions(array.length, numSlices).map { case (start, end) =>
array.slice(start, end).toSeq
}.toSeq
}
}4. textFile 切片原理
textFile使用的MapReduce框架中TextInputFormat类完成对文件切片和读取切片中数据
4.1 切片规则
1.对job输入路径中的每个文件单独切片
2.判断每个文件是否支持切片
true : 按照指定切片大小对文件切片
false: 文件整体作为一个切片
4.2 怎样设置切片大小
// 切片大小计算规则
splitSize = Math.max(minSize, Math.min(goalSize, blockSize))
// 参数说明
1.minSize
set mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize=256000000 或
set mapred.min.split.size=256000000
默认值 minSize=1L
2.goalSize
goalSize=所有文件大小总和/指定的切片个数
3.blockSize
本地目录32M|HDFS目录128M或256M(看hdfs文件块具体配置)
// 需求
1.真实切片大小 < blockSize
goalSize=所有文件大小总和/指定的切片个数 < blockSize 即(创建rdd时调大切片个数)
2.真实切片大小 > blockSize
set mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minSize=大于blockSize值4.3 测试代码
test("textFile - 切片逻辑") {
// 初始化 spark配置实例
val sf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName("Test textFile")
// 初始化 spark环境对象
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sf)
sc.hadoopConfiguration.setInt("mapred.min.split.size", 469000000)
// sc.hadoopConfiguration.setInt("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize", 256000000)
// 读取目录下的所有文件
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/data/dir/dir3/LOL.map", 1000)
// 打印分区个数
println("切片个数:"+rdd.getNumPartitions)
sc.stop()
}
执行结果:

5.hadoopFile 切片原理
5.1 说明
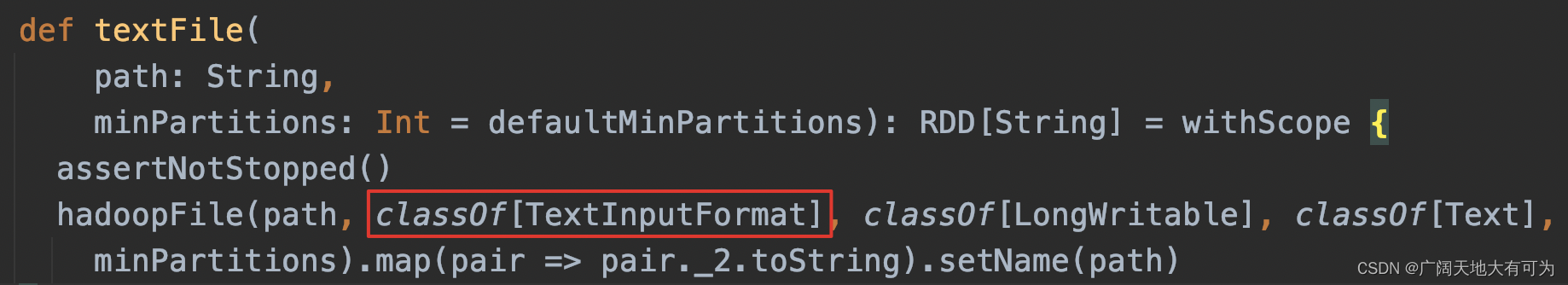
def hadoopFile[K, V](
path: String,
inputFormatClass: Class[_ <: InputFormat[K, V]],
keyClass: Class[K],
valueClass: Class[V],
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[(K, V)] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
功能:
读取HDFS文件或本地文件来创建RDD(使用MapReduce框架中InputFormat类)
参数:
path: 指定job的输入路径
inputFormatClass: 对输入文件切片和读取的实现类
keyClass: key的数据类型
valueClass: value的数据类型
minPartitions: 最小切片数5.2 切片规则
根据指定的切片大小进行切片,允许将多个文件合并成换一个切片对象
5.3 怎样设置切片大小
指定切片大小(默认值Long.MaxValue)
set mapred.max.split.size=切片大小 或
set mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize=切片大小5.4 代码测试
test("spark中使用 CombineTextInputFormat") {
// 初始化 spark配置实例
val sf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName("")
// 初始化 spark环境对象
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sf)
// 读取目录下的所有文件
val input = "src/main/resources/data/dir/dir3"
val combineRDD: RDD[(LongWritable, Text)] = sc.hadoopFile[LongWritable, Text
, org.apache.hadoop.mapred.lib.CombineTextInputFormat](input, 10000)
// val combineRDD: RDD[(LongWritable, Text)] = sc.hadoopFile[LongWritable, Text
// , org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat](input, 10000)
sc.hadoopConfiguration.setInt("mapred.max.split.size", 128000000)
//sc.hadoopConfiguration.setInt("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize", 128000000)
println("切片个数:" + combineRDD.getNumPartitions)
//combineRDD.map(_._2.toString).foreach(println(_))
//combineRDD.collect()
//combineRDD.had
sc.stop()
}
执行结果: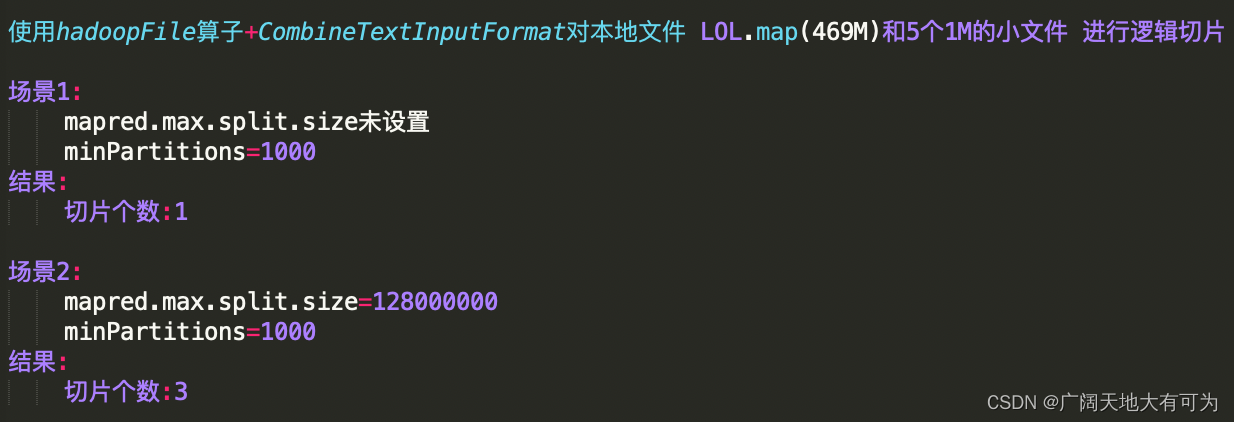
5.5 minPartitions 在 CombineTextInputFormat 中的作用?
CombineTextInputFormat切片逻辑和 最小切片数(minPartitions) 无关
查看 org.apache.hadoop.mapred.lib.CombineTextInputFormat类 getSplits方法
TODO: numSplits指定的切片个数,并没有使用
public InputSplit[] getSplits(JobConf job, int numSplits)
throws IOException {
List<org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit> newStyleSplits =
super.getSplits(Job.getInstance(job));
InputSplit[] ret = new InputSplit[newStyleSplits.size()];
for(int pos = 0; pos < newStyleSplits.size(); ++pos) {
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileSplit newStyleSplit =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.CombineFileSplit) newStyleSplits.get(pos);
ret[pos] = new CombineFileSplit(job, newStyleSplit.getPaths(),
newStyleSplit.getStartOffsets(), newStyleSplit.getLengths(),
newStyleSplit.getLocations());
}
return ret;
}5.6 重点关注
对计算任务而言,合并小文件是一把双刃剑,合并小文件后 就舍弃了数据本地化,则加了网络IO的开销,需要根据实际情况合理的选择 切片策略
CombineTextInputFormat源码参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wawmg/article/details/17095125