目录
- 0 专栏介绍
- 1 什么是D*算法?
- 2 D*算法核心概念一览
- 3 D*算法流程图
- 4 步步图解:算法实例
- 5 算法仿真与实现
- 5.1 ROS C++实现
- 5.2 Python实现
0 专栏介绍
🔥附C++/Python/Matlab全套代码🔥课程设计、毕业设计、创新竞赛必备!详细介绍全局规划(图搜索、采样法、智能算法等);局部规划(DWA、APF等);曲线优化(贝塞尔曲线、B样条曲线等)。
🚀详情:图解自动驾驶中的运动规划(Motion Planning),附几十种规划算法
1 什么是D*算法?
动态A*(Dynamic A*, D*)算法是一种增量式路径规划算法,与A*算法相比,它最大的优势是可以同时兼容静态环境和存在未知动态变化的场景,曾被美国用于火星探测器寻路。如果还不了解A*算法,可以看路径规划 | 图解A*、Dijkstra、GBFS算法的异同(附C++/Python/Matlab仿真)

这里有一个概念——增量式,什么是增量式呢?与启发式搜索利用启发函数指导高效搜索不同,增量式搜索对曾经的规划信息进行综合再利用以减少搜索范围和时间。
D*算法实现增量式规划采用从目标点向起始点的反向搜索策略:当既定路径被障碍阻塞时,障碍后各个节点到目标点的最短路径未被影响,只需在障碍附近重规划并更新起点到障碍处各节点的信息,当路径绕过障碍后即可重新利用曾经规划的到达目标位置的最短路径。
所以动态障碍越靠近起点,能重复利用的信息越多,规划效率越高。当动态障碍靠近终点时,仍要更新整张地图节点信息,相当于应用反向A*算法进行重规划。
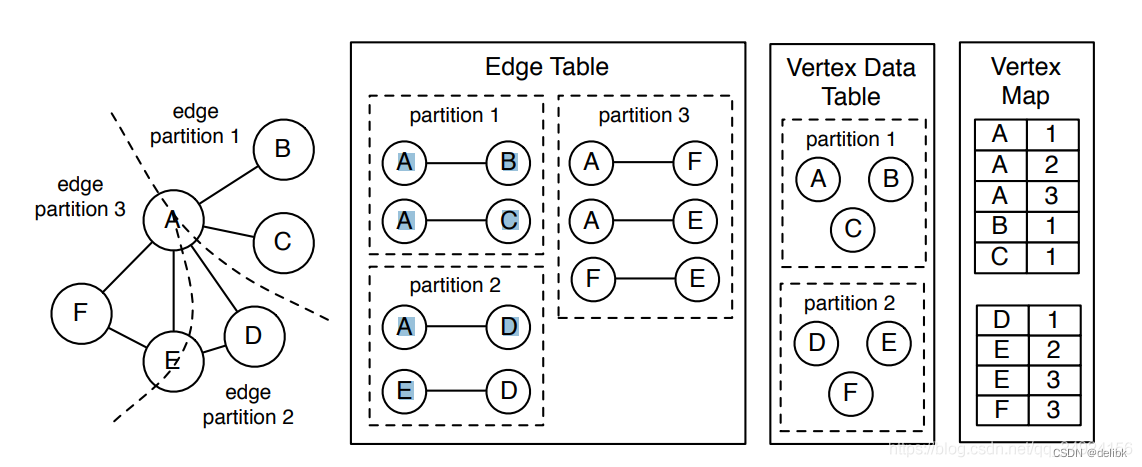
2 D*算法核心概念一览
D*算法的核心概念如下所示:
-
c ( x , y ) c\left( x,y \right) c(x,y):从节点 x x x移动到节点 y y y的代价,若 x x x、 y y y间存在障碍则 c ( x , y ) = i n f c\left( x,y \right) =\mathrm{inf} c(x,y)=inf;
-
t ( x ) t\left( x \right) t(x):节点 x x x的表状态。有
NEW——未被搜索过的点OPEN——正在搜索的待考察节点CLOSED——被搜索过的节点。
为了适应动态环境,D*算法的
OPEN与CLOSED状态允许相互转化,当节点扩展后从开节点表中移除时,状态从OPEN变为CLOSED;当节点传播动态障碍信息给邻域时,节点将再次加入开节点表,状态从CLOSED变为OPEN -
h ( x ) h\left( x \right) h(x):从节点 x x x到目标点的代价;
-
k ( x ) k\left( x \right) k(x):节点 x x x的历史最小 h ( x ) h\left( x \right) h(x)值,即
k ( x ) = { h ( x ) , t ( x ) = N E W min { k ( x ) , h ( x ) } , o t h e r w i s e k\left( x \right) =\begin{cases} h\left( x \right) \,\, , t\left( x \right) =\mathrm{NEW}\\ \min \left\{ k\left( x \right) ,h\left( x \right) \right\} , \mathrm{otherwise}\\\end{cases} k(x)={h(x),t(x)=NEWmin{k(x),h(x)},otherwise设置 k ( x ) k\left( x \right) k(x)的目的在于加快障碍处局部路径重规划的效率。当某个路径点变为障碍时,其 h ( x ) = i n f h\left( x \right) =\mathrm{inf} h(x)=inf而 k ( x ) k\left( x \right) k(x)不变。若从开节点表中首选 h ( x ) h\left( x \right) h(x)最小的点,则将最后考察障碍附近的点;而若从开节点表中首选 k ( x ) k\left( x \right) k(x)最小的点,则将率先考察障碍附近的点,符合实际情况;
-
节点 x x x的元状态:有
RAISED——此时 k ( x ) < h ( x ) k\left( x \right) <h\left( x \right) k(x)<h(x)说明节点 x x x受到障碍影响LOWER——此时 k ( x ) = h ( x ) k\left( x \right) =h\left( x \right) k(x)=h(x)说明节点 x x x未受障碍影响;
-
p r o c e s s _ s t a t e ( ) \mathrm{process}\_\mathrm{state}\left( \right) process_state():核心函数,静态环境下可以更新各节点到达目标点的最短路径及节点连接关系,动态环境下可以传播受障碍影响后节点 h ( x ) h\left( x \right) h(x)的变更信息到邻域;
-
i n s e r t ( x , v a l ) \mathrm{insert}\left( x,val \right) insert(x,val):将节点 x x x插入开节点表,并令其 h ( x ) = v a l h\left( x \right) =val h(x)=val,更新 k ( x ) k\left( x \right) k(x);
-
m o d i f y _ cos t ( x ) \mathrm{modify}\_\cos\mathrm{t}\left( x \right) modify_cost(x):通过 i n s e r t ( x , h ( x ) + c ( x , x . p a r e n t ) ) \mathrm{insert}\left( x,h\left( x \right) +c\left( x,x.\mathrm{parent} \right) \right) insert(x,h(x)+c(x,x.parent))将处于
CLOSED状态的节点 x x x转换为OPEN状态
3 D*算法流程图
D*算法主函数流程如下所示

其中核心的
p
r
o
c
e
s
s
_
s
t
a
t
e
(
)
\mathrm{process}\_\mathrm{state}\left( \right)
process_state()算法流程如下

在将动态信息传播到邻域进行修正的过程中,分为两种情况讨论:
- 节点
x
x
x处于
LOWER态。考虑到障碍的出现只可能让路径不变或更曲折,即让节点 h ( x ) ⩾ k ( x ) h\left( x \right) \geqslant k\left( x \right) h(x)⩾k(x),所以对处在LOWER态的节点,不存在更优路径,此时只需将节点 的最优信息更新到邻域即可; - 节点
x
x
x处于
RAISED态。与LOWER态节点不同,此时节点 x x x处可能存在更优路径,即可能存在 y ∈ n e i g h b o r ( x ) y\in \mathrm{neighbor}\left( x \right) y∈neighbor(x)使 h ( x ) > h ( y ) + c ( x , y ) h\left( x \right) >h\left( y \right) +c\left( x,y \right) h(x)>h(y)+c(x,y)。对于 y . p a r e n t = x y.\mathrm{parent}=x y.parent=x的情形RAISED态与LOWER态更新情况相同,以保持联结节点信息的同步。对于 y . p a r e n t ≠ x y.\mathrm{parent}\ne x y.parent=x的情形,若 h ( y ) > h ( x ) + c ( x , y ) h\left( y \right) >h\left( x \right) +c\left( x,y \right) h(y)>h(x)+c(x,y)则重新将节点 x x x加入开节点表进行考察,因为 x x x可能可以用更优的代价值来更新邻域;若 h ( x ) > h ( y ) + c ( x , y ) h\left( x \right) >h\left( y \right) +c\left( x,y \right) h(x)>h(y)+c(x,y),考虑到 h ( y ) ⩽ k o l d h\left( y \right) \leqslant k_{\mathrm{old}} h(y)⩽kold的情形在S2处已考虑,因此只需包含 h ( y ) > k o l d h\left( y \right) >k_{\mathrm{old}} h(y)>kold,更进一步,由于节点 y y y处在CLOSED状态,所以通常 h ( y ) = k ( y ) ⩽ k o l d h\left( y \right) =k\left( y \right) \leqslant k_{\mathrm{old}} h(y)=k(y)⩽kold,但此处 h ( y ) > k o l d h\left( y \right) >k_{\mathrm{old}} h(y)>kold说明节点 y y y也受到了障碍影响导致价值升高,体现了将 y y y重新纳入开节点表的必要性。
4 步步图解:算法实例
以下面的栅格地图为例,红色栅格表示起点,蓝色栅格表示终点,黄色栅格表示开节点表中的节点,绿色栅格表示闭节点表中的栅格

D*算法的静态规划阶段如下图所示

D*算法动态路径修正阶段如下所示

5 算法仿真与实现
5.1 ROS C++实现
double DStar::processState()
{
if (open_list_.empty())
return -1;
double k_old = open_list_.begin()->first;
DNodePtr x = open_list_.begin()->second;
open_list_.erase(open_list_.begin());
x->t = CLOSED;
expand_.push_back(*x);
std::vector<DNodePtr> neigbours;
this->getNeighbours(x, neigbours);
// RAISE state, try to reduce k value by neibhbours
if (k_old < x->g_)
{
for (DNodePtr y : neigbours)
{
if (y->t != NEW && y->g_ <= k_old && x->g_ > y->g_ + this->getCost(y, x))
{
x->pid_ = y->id_;
x->g_ = y->g_ + this->getCost(y, x);
}
}
}
// LOWER state, cost reductions
if (k_old == x->g_)
{
for (DNodePtr y : neigbours)
{
if (y->t == NEW || ((y->pid_ == x->id_) && (y->g_ != x->g_ + this->getCost(x, y))) ||
((y->pid_ != x->id_) && (y->g_ > x->g_ + this->getCost(x, y))))
{
y->pid_ = x->id_;
this->insert(y, x->g_ + this->getCost(x, y));
}
}
}
else
{
// RAISE state
for (DNodePtr y : neigbours)
{
if (y->t == NEW || ((y->pid_ == x->id_) && (y->g_ != x->g_ + this->getCost(x, y))))
{
y->pid_ = x->id_;
this->insert(y, x->g_ + this->getCost(x, y));
}
else if (y->pid_ != x->id_ && (y->g_ > x->g_ + this->getCost(x, y)))
{
this->insert(x, x->g_);
}
else if (y->pid_ != x->id_ && (x->g_ > y->g_ + this->getCost(y, x)) && y->t == CLOSED && (y->g_ > k_old))
{
this->insert(y, y->g_);
}
}
}
return open_list_.begin()->first;
}

5.2 Python实现
def processState(self) -> float:
# get node in OPEN set with min k value
node = self.min_state
self.EXPAND.append(node)
if node is None:
return -1
# record the min k value of this iteration
k_old = self.min_k
# move node from OPEN set to CLOSED set
self.delete(node)
# k_min < h[x] --> x: RAISE state (try to reduce k value by neighbor)
if k_old < node.h:
for node_n in self.getNeighbor(node):
if node_n.h <= k_old and node.h > node_n.h + self.cost(node, node_n):
# update h_value and choose parent
node.parent = node_n.current
node.h = node_n.h + self.cost(node, node_n)
# k_min >= h[x] -- > x: LOWER state (cost reductions)
if k_old == node.h:
for node_n in self.getNeighbor(node):
if node_n.t == 'NEW' or \
(node_n.parent == node.current and node_n.h != node.h + self.cost(node, node_n)) or \
(node_n.parent != node.current and node_n.h > node.h + self.cost(node, node_n)):
# Condition:
# 1) t[node_n] == 'NEW': not visited
# 2) node_n's parent: cost reduction
# 3) node_n find a better parent
node_n.parent = node.current
self.insert(node_n, node.h + self.cost(node, node_n))
else:
for node_n in self.getNeighbor(node):
if node_n.t == 'NEW' or \
(node_n.parent == node.current and node_n.h != node.h + self.cost(node, node_n)):
node_n.parent = node.current
self.insert(node_n, node.h + self.cost(node, node_n))
else:
if node_n.parent != node.current and \
node_n.h > node.h + self.cost(node, node_n):
self.insert(node, node.h)
else:
if node_n.parent != node.current and \
node.h > node_n.h + self.cost(node, node_n) and \
node_n.t == 'CLOSED' and \
node_n.h > k_old:
self.insert(node_n, node_n.h)
return self.min_k

完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
🔥 更多精彩专栏:
- 《ROS从入门到精通》
- 《Pytorch深度学习实战》
- 《机器学习强基计划》
- 《运动规划实战精讲》
- …