同步工具类:CyclicBarrier
- 介绍
- 源码分析
- CyclicBarrier 基于ReetrantLock + Condition实现。
- 构造函数
- await() 函数
- 业务场景
- 方案一:
- 代码实现
- 测试截图
- 方案二
- 代码实现
- 测试打印
- 总结
介绍
官方介绍:
一种同步辅助工具,允许一组线程都等待对方到达共同的障碍点。CyclicBarrier在涉及固定大小的线程组的程序中非常有用,这些线程组偶尔必须彼此等待。该屏障被称为循环屏障,因为它可以在释放等待线程后重新使用。
CyclicBarrier支持可选的Runnable命令,该命令在参与方中的最后一个线程到达后,但在释放任何线程之前,在每个障碍点运行一次。此屏障动作对于在任何一方继续之前更新共享状态都很有用。
通俗理解:
它可以协同多个线程,让多个线程在这个栅栏前等待,直到所有线程都达到了这个栅栏时,再一起继续执行后面的动作.
举个例子,你和朋友约定在公交站汇合,去公园玩。这个公交站相当于栅栏。只有你们都到了公交站,才一起去公园。
源码分析
CyclicBarrier 基于ReetrantLock + Condition实现。
/** The lock for guarding barrier entry */
//用于线程之间互相唤醒
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Condition to wait on until tripped */
private final Condition trip = lock.newCondition();
//总线程数
private final int parties;
构造函数
可以看到,不仅可以传入 参与方的总数量(即 parties)。还可以传入一个回调函数,当所有的线程被唤醒时,barrierAction 被执行,该参数可以为空。
/**
* Creates a new {@code CyclicBarrier} that will trip when the
* given number of parties (threads) are waiting upon it, and which
* will execute the given barrier action when the barrier is tripped,
* performed by the last thread entering the barrier.
*
* @param parties the number of threads that must invoke {@link #await}
* before the barrier is tripped
* @param barrierAction the command to execute when the barrier is
* tripped, or {@code null} if there is no action
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parties} is less than 1
*/
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {
if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.parties = parties;
this.count = parties;
this.barrierCommand = barrierAction;
}
await() 函数
1.CyclicBarrier 是可以被重用的。
2.CyclicBarrier 会响应中断,N 个线程还没有到齐,如果有线程收到了中断信号,所有阻塞的线程也会被唤醒。也就是 breakBarrier函数。然后count 被重置为初始值(parties),重新开始
3.构造函数传入的回调函数,barrierAction 只会被最后一个线程执行一次。
public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException {
try {
return dowait(false, 0L);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new Error(toe); // cannot happen
}
}
/**
* Main barrier code, covering the various policies.
*/
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final Generation g = generation;
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
if (Thread.interrupted()) { //响应中断
breakBarrier(); //唤醒所有阻塞的线程
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int index = --count; //每个线程调用一次await(). count 减一,当count==0时,则唤醒其他的所有线程
if (index == 0) { // tripped
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
if (command != null)// 一起唤醒之和,如果回调函数不为空,还需要执行回调函数
command.run();
ranAction = true;
nextGeneration();//唤醒其他所有线程,并将count值复原。
//用于下一次的CyclicBarrier.这是可以复用的原因
return 0;
} finally {
if (!ranAction)
breakBarrier();
}
}
// loop until tripped, broken, interrupted, or timed out
//当count>0,说明 人没有到齐,需要阻塞自己
for (;;) {
try {
if (!timed)
trip.await();//当阻塞自己的时候,await方法会释放锁,这样其他线程调用await方法时会执行--count
else if (nanos > 0L)
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
//响应中断,如果有线程收到了中断信号,所有的阻塞线程也会被唤醒。
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
// We're about to finish waiting even if we had not
// been interrupted, so this interrupt is deemed to
// "belong" to subsequent execution.
//如果不是响应的中断,说明是被 sigalAll唤醒。则自己唤醒
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
if (g != generation)//从阻塞中被唤醒,然后返回
return index;
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void nextGeneration() {
// signal completion of last generation
// 唤醒所有阻塞的线程
trip.signalAll();
// set up next generation
// 设置初始值,开始下一个轮回
count = parties;
generation = new Generation();
}
业务场景
10 个求职者一起来公司应聘,招聘方式为笔试和面试。首先,需要等10个人到期后,开始笔试,笔试结束之后,再一起参加面试。把10个人看作10个线程。如图所示:

方案一:
采用一个CyclicBarrier.重复实现两次等待
代码实现
class Solver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier barrier=new CyclicBarrier(10);
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
//开启10个线程模拟10个求职者
new Thread(new JobHunt(barrier)).start();
}
}
}
class JobHunt implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;
public JobHunt(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) {
this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//赶来公司路上
doOnTheWay();
//到公司后,看人是否到齐,如果没有到齐,就阻塞,
// 到齐了就开始笔试
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 已经来公司了...");
cyclicBarrier.await();
doWriteExam();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 笔试做完了....");
cyclicBarrier.await();
doInterview();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 面试完啦.....");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 模拟在路上方法
*/
public void doOnTheWay(){
doCostTime(2000);
}
/**
* 模拟笔试过程
*/
public void doWriteExam(){
doCostTime(3000);
}
/**
* 模拟面试过程
*/
public void doInterview(){
doCostTime(5000);
}
private void doCostTime(int time){
Random random=new Random();
try {
//随机休眠时间
int count=random.nextInt(time);
// System.out.println(count);
Thread.sleep(count);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
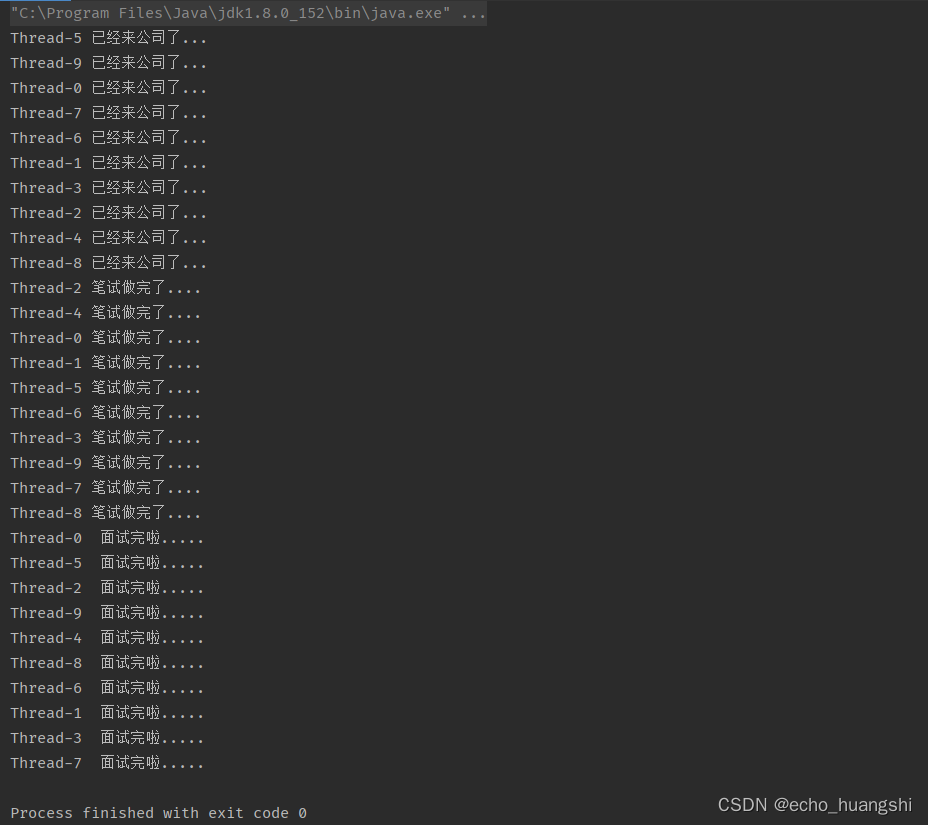
测试截图
从截图中我们可以看出,CyclicBarrier 实现了大家一起等待,直至人到齐了再去一起做笔试或者面试。
方案二
由于两次等待结束后,打印的消息不一样。所以我们采用两个 CyclicBarrier。分别传入不同的 barrierAction,来实现自定义的 等待结束后的打印事件。
代码实现
class Solver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将笔试等待的回调函数传入
CyclicBarrier barrierOnWriteExam=new CyclicBarrier(10,new BarrierActionOnWriteExam());
//将面试等待的回调函数传入
CyclicBarrier barrierOnInterview=new CyclicBarrier(10,new BarrierActionOnInterview());
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
//开启10个线程模拟10个求职者
new Thread(new JobHunt(barrierOnWriteExam,barrierOnInterview)).start();
}
}
}
class JobHunt implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrierOnWriteExam;
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrierOnInterview;
public JobHunt(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrierOnWriteExam,CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrierOnInterview) {
this.cyclicBarrierOnWriteExam = cyclicBarrierOnWriteExam;
this.cyclicBarrierOnInterview= cyclicBarrierOnInterview;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//赶来公司路上
doOnTheWay();
//到公司后,看人是否到齐,如果没有到齐,就阻塞,
// 到齐了就开始笔试
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 已经来公司了...");
cyclicBarrierOnWriteExam.await();
doWriteExam();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 笔试做完了....");
cyclicBarrierOnInterview.await();
doInterview();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 面试完啦.....");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 模拟在路上方法
*/
public void doOnTheWay(){
doCostTime(2000);
}
/**
* 模拟笔试过程
*/
public void doWriteExam(){
doCostTime(3000);
}
/**
* 模拟面试过程
*/
public void doInterview(){
doCostTime(5000);
}
private void doCostTime(int time){
Random random=new Random();
try {
//随机休眠时间
int count=random.nextInt(time);
// System.out.println(count);
Thread.sleep(count);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class BarrierActionOnWriteExam implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//自定义等待完成后的回调函数
System.out.println("大家人到齐了,开始笔试吧");
}
}
class BarrierActionOnInterview implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//自定义等待完成后的回调函数
System.out.println("大家人到齐了,开始面试吧");
}
}
测试打印
通过打印结果可以看到,首先是能正确实现效果。其次 是通过传入 回调事件参数给 CyclicBarrier,可以很方便实现 自己的业务逻辑。

总结
虽然 CountDownLatch 和CyclicBarrier 都能实现多个线程一起等待然后一起做某些事情。
CountDownLatch 更多的是 一个主线程等待 分支线程完成。然后主线程去做其他事情。
CyclicBarrier 是 大家分别做某些事情,等每个人都做完后,大家再一起去做另外一件事情。
并且两者实现的 原理完全不同。
希望通过本文大家能对 CyclicBarrier 有个更加理性的认识。多敲敲小demo。看能否有优化的地方。这样才能更好的理解。
CountDownLatch 学习的地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/echohuangshihuxue/article/details/129280219