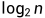背景
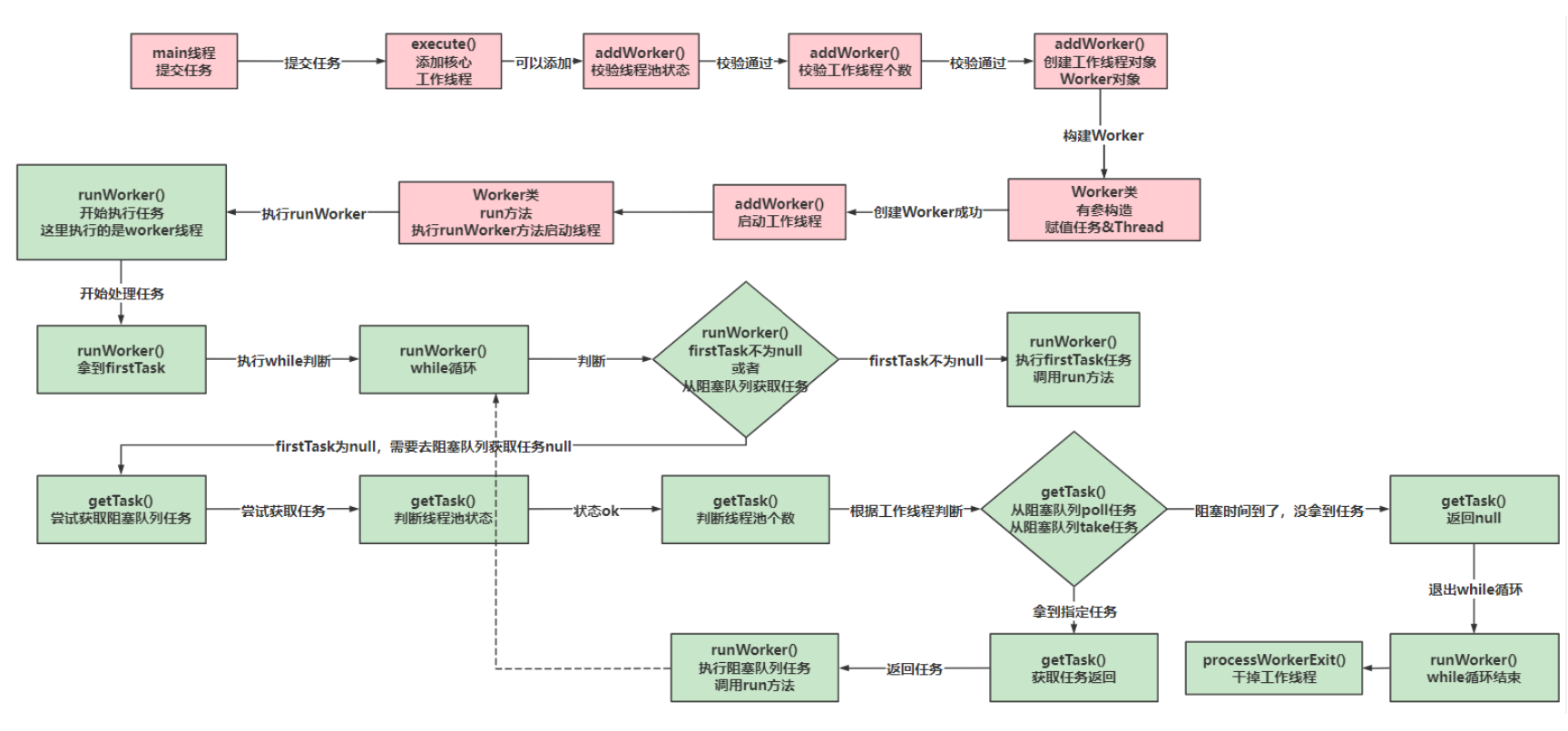
我们都知道hbase的数据是分布在多台RegionServer角色的机器上的,每个RegionServer都有一到多个Region管理不同rowkey范围的数据,所以建表前通过合理的Region的分区及数量,可以避免热点读写问题和充分利用各RegionServer的资源,vmaster-hbase提供了预分区的功能
手动分区
用户根据数据特点和资源组机器数量提供分割点
1.1分割点是字符串


1.2分割点是整数
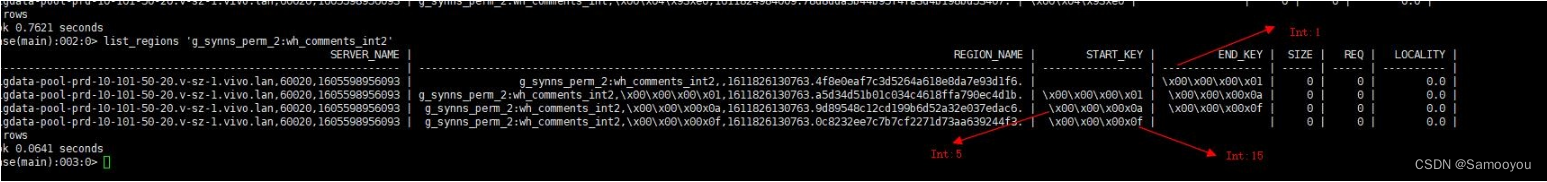
hbase存储的都是二进制的byte,所有Int类型的分割点都要转换为十六进制传入,比如我们有如下分割点:1,10,15,每个分割点都是一个Int类型,可以利用Bytes.toHex(Bytes.toBytes(splitPoint))得出分割点的十六进制表示: 分割点十六进制表示
1.2.1分割点十六进制表示
| Int | 十六进制表示 |
|---|---|
| 1 | \x00\x00\x00\x01 |
| 10 | \x00\x00\x00\x0a |
| 15 | \x00\x00\x00\x0f |
1.2.2分割点测试

自动分区
2.1 HexStringSplit
分区数根据机器数选择,推荐每台机器20~30个region
rowkey是整数时,建议采用此分区算法,HexStringSplit将整个无符号整数范围00000000~FFFFFFFF根据region数据平均划分,转化为十六进制字符,长度不够8自动左填充'0',调用Bytes.toBytes(bigIntegerString)转到字节数组,核心代码如下:
2.1.1Rowkey范围切分
public byte[][] split(int n) {
Preconditions.checkArgument(lastRowInt.compareTo(firstRowInt) > 0,
"last row (%s) is configured less than first row (%s)", lastRow,
firstRow);
// +1 to range because the last row is inclusive
BigInteger range = lastRowInt.subtract(firstRowInt).add(BigInteger.ONE);
Preconditions.checkState(range.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(n)) >= 0,
"split granularity (%s) is greater than the range (%s)", n, range);
BigInteger[] splits = new BigInteger[n - 1];
BigInteger sizeOfEachSplit = range.divide(BigInteger.valueOf(n));
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// NOTE: this means the last region gets all the slop.
// This is not a big deal if we're assuming n << MAXHEX
splits[i - 1] = firstRowInt.add(sizeOfEachSplit.multiply(BigInteger
.valueOf(i)));
}
return convertToBytes(splits);
}
|
2.1.2分割点转为字节数组
/**
* Returns the bytes corresponding to the BigInteger
*
* @param bigInteger number to convert
* @param pad padding length
* @return byte corresponding to input BigInteger
*/
public static byte[] convertToByte(BigInteger bigInteger, int pad) {
String bigIntegerString = bigInteger.toString(16);
bigIntegerString = StringUtils.leftPad(bigIntegerString, pad, '0');
return Bytes.toBytes(bigIntegerString);
} |
2.2 UniformSplit
分区数根据机器数选择,推荐每台机器20~30个region
当rowkey是原始字节数组byte[],raw byte的范围是\x00~\xff,rowKey接近统一随机的byte值比如hashes,采用此分区算法,UniformSplit采用BigInteger的toByteArray()转化分割点
2.2.1分割点算法
/**
* Iterate over keys within the passed range.
*/
public static Iterable<byte[]> iterateOnSplits(
final byte[] a, final byte[]b, boolean inclusive, final int num)
{
byte [] aPadded;
byte [] bPadded;
if (a.length < b.length) {
aPadded = padTail(a, b.length - a.length);
bPadded = b;
} else if (b.length < a.length) {
aPadded = a;
bPadded = padTail(b, a.length - b.length);
} else {
aPadded = a;
bPadded = b;
}
if (compareTo(aPadded,bPadded) >= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("b <= a");
}
if (num <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("num cannot be <= 0");
}
byte [] prependHeader = {1, 0};
final BigInteger startBI = new BigInteger(add(prependHeader, aPadded));
final BigInteger stopBI = new BigInteger(add(prependHeader, bPadded));
BigInteger diffBI = stopBI.subtract(startBI);
if (inclusive) {
diffBI = diffBI.add(BigInteger.ONE);
}
final BigInteger splitsBI = BigInteger.valueOf(num + 1);
//when diffBI < splitBI, use an additional byte to increase diffBI
if(diffBI.compareTo(splitsBI) < 0) {
byte[] aPaddedAdditional = new byte[aPadded.length+1];
byte[] bPaddedAdditional = new byte[bPadded.length+1];
for (int i = 0; i < aPadded.length; i++){
aPaddedAdditional[i] = aPadded[i];
}
for (int j = 0; j < bPadded.length; j++){
bPaddedAdditional[j] = bPadded[j];
}
aPaddedAdditional[aPadded.length] = 0;
bPaddedAdditional[bPadded.length] = 0;
return iterateOnSplits(aPaddedAdditional, bPaddedAdditional, inclusive, num);
}
final BigInteger intervalBI;
try {
intervalBI = diffBI.divide(splitsBI);
} catch(Exception e) {
LOG.error("Exception caught during division", e);
return null;
}
final Iterator<byte[]> iterator = new Iterator<byte[]>() {
private int i = -1;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return i < num+1;
}
@Override
public byte[] next() {
i++;
if (i == 0) return a;
if (i == num + 1) return b;
BigInteger curBI = startBI.add(intervalBI.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i)));
byte [] padded = curBI.toByteArray();
if (padded[1] == 0)
padded = tail(padded, padded.length - 2);
else
padded = tail(padded, padded.length - 1);
return padded;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
return new Iterable<byte[]>() {
@Override
public Iterator<byte[]> iterator() {
return iterator;
}
};
} |