文章目录
- 一、Nginx概述
- 1.1、Nginx的特点
- 1.2、Nginx编译安装
- 1.3、Nginx运行控制
- 1.4、Nginx和Apache的区别
- 二、编译安装Nginx服务的操作步骤
- 2.1、关闭防火墙,将安装nginx所需软件包传到/opt目录下
- 2.2、安装依赖包
- 2.3、创建运行用户、组(Nginx 服务程序默认以 nobody 身份运行,建议为其创建专门的用户账号,以便更准确地控制其访问权限)
- 2.4、编译安装nginx
- 2.5、检查、启动、重启、停止 nginx服务
- 2.6、添加nginx系统服务
- 三、实例操作:编译安装Nginx服务
- 3.1、关闭防火墙,将安装nginx所需软件包传到/opt目录下
- 3.2、安装依赖包
- 3.3、创建运行用户、组
- 3.4 、编译安装Nginx
- 3.5、检查、启动、重启、停止Nginx服务
- 3.6、添加nginx 系统服务
- 四、认识Nginx服务的主配置文件
- 4.1、全局配置
- 4.2、I/O事件配置
- 五、访问状态统计配置
- 5.1、访问状态统计配置的操作步骤
- 5.2、实例操作:访问状态统计配置
- 六、基于授权的访问控制
- 6.1、基于授权的访问控制的操作步骤
- 6.2、实例操作:基于授权的访问控制
- 6.3、基于客户端访问控制
一、Nginx概述
1.1、Nginx的特点
一款高性能、轻量级web服务
• 稳定性高
• 系统资源消耗低高
• 对HTTP并发连接的处理能力
单台物理服务器可支持30000~50000个并发请求
1.2、Nginx编译安装
• 安装支持软件
• 创建运行用户、组
• 编译安装Nginx
1.3、Nginx运行控制
• 检查配置文件
• 启动、重载配置、停止Nginx
1.4、Nginx和Apache的区别
4.1 nginx相对于apache的优点∶
轻量级,同样起web服务,比apache占用更少的内存及资源
抗并发,nginx处理请求是异步非阻塞的,而apache是阻塞型的在高并发下,nginx能保持低资源低消耗高性能
高度模块化的设计,编写模块相对简单
4.2 apache相对于nginx的优点∶
Rewrite比nginx的rewrite强大 (rewrite的主要功能就是实现统一资源定位符URL的跳转)
模块多,基本想到的都可以找到
少bug, nginx的bug相对较多
超稳定
总结:一般来说,需要性能的web服务,用nginx。 若不需要性能只求稳定,就选用apache
二、编译安装Nginx服务的操作步骤
2.1、关闭防火墙,将安装nginx所需软件包传到/opt目录下
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
setenforce 0
# 将压缩包传入到/opt目录下
nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz
2.2、安装依赖包
nginx的配置及运行需要pcre、zlib等软件包的支持,因此需要安装这些安装的开发包,以便提供相应的库和头文件
yum install -y pcre-devel zlib-devel gcc gcc-c++ make
2.3、创建运行用户、组(Nginx 服务程序默认以 nobody 身份运行,建议为其创建专门的用户账号,以便更准确地控制其访问权限)
useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
2.4、编译安装nginx
cd /opt
tar zxvf nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz
./configure \
> --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ #指定nginx的安装路径
> --user=nginx \ #指定用户名
> --group=nginx \ #指定组名
> --with-http_stub_status_module #启用 http_stub_status_module模块以变持状态线计
make && make install
ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ ##让系统识别nginx的操作命令
2.5、检查、启动、重启、停止 nginx服务
nginx -t #检查配置文件是否配置 正确
#启动
nginx
#停止
cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid #先查看nginx的PID号
kill -3 <PID号> #直接杀死
kill -s QUIT <PID号> #优雅的杀死()
killall -3 nginx
killall -s QUIT nginx
#重载
kill -1 <PID号>
kill -s HUP <PID号>
killall -1 nginx
killall -s HUP nginx
#日志分割,重新打开日志文件
kill -USR1 <PID号>
#平滑升级
kill -USR2 <PID号>
新版本升级∶
tar -zxvf nginx-1.xx.xX. tar.gz
cd nginx-1.xx. xx
./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_ssl_module
make
mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx_old
cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
make upgrade
#或者先 killall nginx ,再/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
2.6、添加nginx系统服务
方法一:使用脚本
vim /etc/init.d/nginx #创建脚本文件内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
#chkconfig: - 99 20
#description:Nginx Server Control Script
COM="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
PID="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
case "$1" in
start)
$COM
;;
stop)
kill -s QUIT $(cat $PID)
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
kill -s HUP $(cat $PID)
;;
*)
echo "Usage:$0 {start|stop|restart|reload}"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
chkconfig --add nginx
systemctl daemon-reload #磁盘上的ngin服务更改,运行'systemctl daemon-reload'重新加载单元。
systemctl start nginx
systemctl stop nginx
方法二∶
vim /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=nginx
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
ExecrReload=/bin/kill -s HUP SMAINPID
ExecrStop=/bin/kill-s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
chmod 754 /lib/systemd/ system/nginx.service
systemctl start nginx.service
systemctl enable nginx.service
【Unit】∶服务的说明 Description∶ 描述服务 After∶依赖, 当依赖的服务启动之后再启动自定义的服务
【Service】服务运行参数的设置
Type=forking是后台运行的形式,使用此启动类型应同时指定PIDFile=,以便systemd能够跟踪服务的主进程。
ExecStart为服务的具体运行命令 ExecReload为重启命令 ExecStop为停止命令
PrivateTmp=True表示给服务分配独立的临时空间 注意∶ 启动、重启、停止命令全部要求使用绝对路径
【Install】服务安装的相关设置,可设置为多用户
三、实例操作:编译安装Nginx服务
3.1、关闭防火墙,将安装nginx所需软件包传到/opt目录下
[root@cm ~]# cd /opt
[root@cm opt]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@cm opt]# ls
nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz rh
[root@cm opt]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@cm opt]# systemctl disable firewalld
[root@cm opt]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
[root@cm opt]# systemctl status firewalld.service
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:firewalld(1)

3.2、安装依赖包
[root@cm opt]# yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel gcc gcc-c++ make

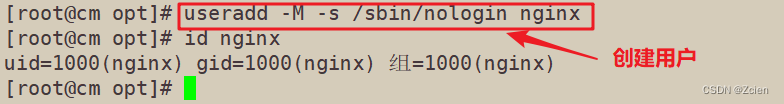
3.3、创建运行用户、组
[root@cm opt]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
[root@cm opt]# id nginx
uid=1000(nginx) gid=1000(nginx) 组=1000(nginx)
3.4 、编译安装Nginx
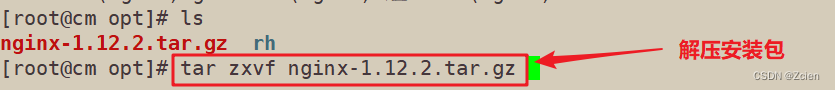
3.4.1 解压Nginx软件包
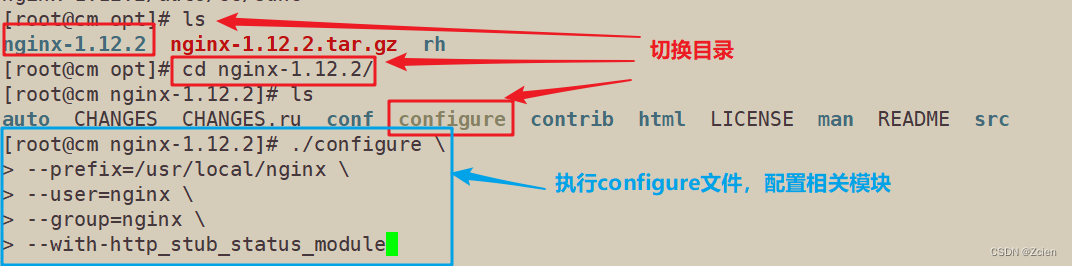
[root@cm opt]# ls
nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz rh
[root@cm opt]# tar zxvf nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
3.4.2 安装相关模块
[root@cm opt]# ls
nginx-1.12.2 nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz rh
[root@cm opt]# cd nginx-1.12.2/
[root@cm nginx-1.12.2]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE man README src
[root@cm nginx-1.12.2]# ./configure \
> --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
> --user=nginx \
> --group=nginx \
> --with-http_stub_status_module
3.4.3 编译安装
[root@cm nginx-1.12.2]# make -j2 && make install

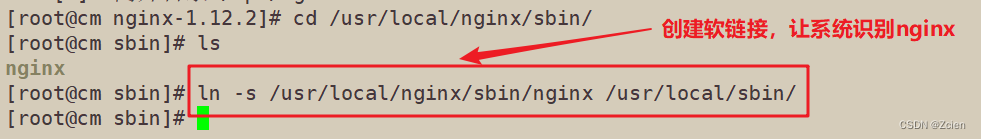
3.4.4 将Nginx链接到/user/local/sbin下
[root@cm nginx-1.12.2]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
[root@cm sbin]# ls
nginx
[root@cm sbin]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/
3.5、检查、启动、重启、停止Nginx服务
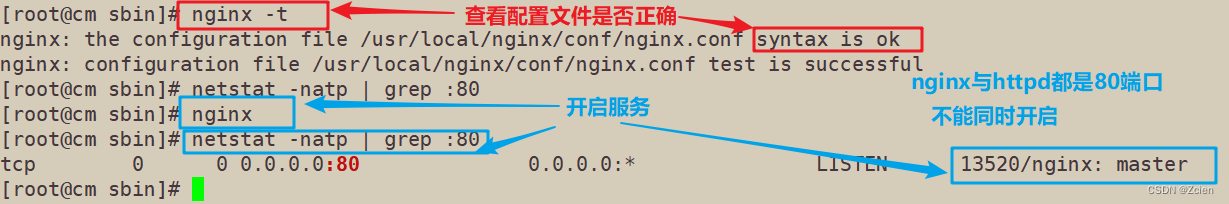
3.5.1 检查和启动
[root@cm sbin]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@cm sbin]# netstat -natp | grep :80
[root@cm sbin]# nginx
[root@cm sbin]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13520/nginx: master
3.5.2 停止、重启nginx服务
5.2.1 停止nginx服务
[root@cm sbin]# cd /usr/local/nginx/logs/
[root@cm logs]# ls
access.log error.log nginx.pid
[root@cm logs]# cat nginx.pid
13520
[root@cm logs]# pgrep nginx -l
13520 nginx
13521 nginx
[root@cm logs]# lsof -i :80
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
nginx 13520 root 6u IPv4 76974 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
nginx 13521 nginx 6u IPv4 76974 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
[root@cm logs]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 13520 1 0 20:55 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx
nginx 13521 13520 0 20:55 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 13618 8613 0 21:01 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@cm logs]# ss -natp | grep nginx
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* users:(("nginx",pid=13521,fd=6),("nginx",pid=13520,fd=6))
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13520/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# kill -3 13520
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
[root@cm logs]# nginx
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13650/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# kill -s QUIT 13650
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
[root@cm logs]# nginx
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13665/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# killall -3 nginx
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
[root@cm logs]# nginx
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13683/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# killall -s QUIT nginx
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80

5.2.2 重载服务
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13772/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# kill -1 13772
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13772/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# kill -s HUP 13772
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13772/nginx: master
[root@cm logs]# killall -1 nginx
[root@cm logs]# killall -s HUP nginx
[root@cm logs]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13772/nginx: master

3.6、添加nginx 系统服务
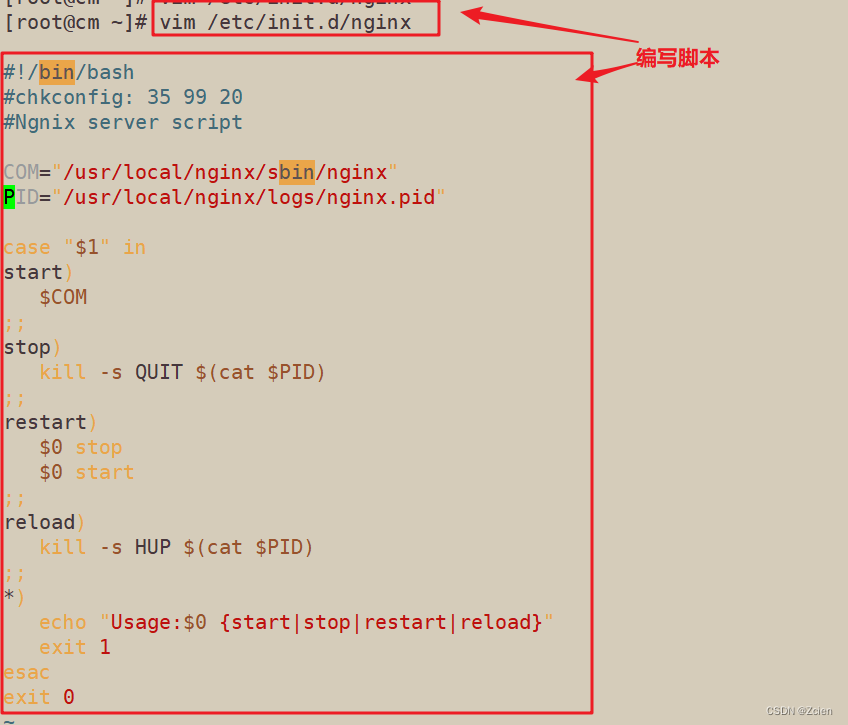
6.1 创建脚本文件
[root@cm ~]# vim /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/bash
#chkconfig 35 99 20
#Ngnix server script
COM="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
PID="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
case "$1" in
start)
$COM
;;
stop)
kill -s QUIT $(cat $PID)
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
kill -s HUP $(cat $PID)
;;
*)
echo "Usage:$0 {start|stop|restart|reload}"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
6.2 赋予权限 并添加到系统服务内
[root@cm ~]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
[root@cm ~]# chkconfig --add nginx

6.3 nginx启动服务服务测试
[root@cm ~]# systemctl stop nginx
Warning: nginx.service changed on disk. Run 'systemctl daemon-reload' to reload units.
[root@cm ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@cm ~]# systemctl stop nginx
[root@cm ~]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13772/nginx: master
[root@cm ~]# kill -3 13772
[root@cm ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@cm ~]# netstat -natp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 15369/nginx: master
[root@cm ~]# systemctl stop nginx
[root@cm ~]# netstat -natp | grep :80

四、认识Nginx服务的主配置文件
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
4.1、全局配置
#user nobody; #运行用户,若编译时未指定则默认为 nobody
worker_processes 1; #工作进程数量,可配置成服务器内核数 * 2,如果网站访问量不大,一般设为1就够用了
#error_log logs/error.log; #错误日志文件的位置
#pid logs/nginx.pid; #PID 文件的位置
4.2、I/O事件配置
events {
use epoll; #使用epoll模型,2.6及以上版本的系统内核,建议使用epoll模型以提高性能
worker_connections 4096; #每个进程处理 4096个连接
}
如提高每个进程的连接数还需执行"ulimit -n 65535"命令临时修改本地每个进程可以同时打开的最大文件数。
在Linux平台上, 在进行高并发TCP连接处理时, 最高的并发数量都要受到系统对用户 单—一进程同时可打开文件数量的限制(这是因为系统为每个TCP连接都要创建一个socket句柄,每个socket句柄同时也是一个文件句柄)。
可使用ulimit -a命令查看系统允许当前用户进程打开的文件数限制。
3、HTTP 配置
http {
include mime.types; ##文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream; ##默认文件类型
##日志格式设定
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main; #日志格式设定
sendfile on; ##支持文件发送(下载)
##此选项允许或禁止使用socket的TCP cORK的选项(发送数据包前先缓存数据),此选项仅在使用sendfile的时候使用
#tcp_nopush on;
##连接保持超时时间,单位是秒
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on; ##gzip模块设置,设置是否开启gzip压缩输出
server {
listen 80; ##监听地址及端口
server_name www.clj.com; ##站点域名,可以有多个,用空格隔开
#charset utf-8; #网页的默认字符集
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / { ##根目录配置
root html; ##网站根目录的位置/usr/local/nginx/html
index index.html index.htm; ##默认首页文件名
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; ##内部错误的反馈页面
location = /50x.html { ##错误页面配置
root html;
}
日志格式设定∶
$ remote_addr与$http x forwarded for用以记录客户端的ip地址;
$ remote user∶ 用来记录客户端用户名称;
$ time local∶ 用来记录访问时间与时区;$request∶用来记录请求的url与http协议;
$status∶ 用来记录请求状态;成功是200,
$body bytes sent ∶ 记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;
$http referer∶ 用来记录从哪个页面链接访问过来的;
$http user agent∶记录客户浏览器的相关信息;
通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过Sremote_add拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的iP地址。反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客户端的请求的服务器地址。
location常见配置指令, root、alias、proxy_ pass
root (根路径配置)∶ 请求ww.clj.com/test/1.jpg,会返回文件/usr/local/nginx/html/test/1.jpg
alias (别名配置)∶请求www.clj.com/test/1.jpg,会返回文件/usr/local/nginx/html/1.jpg
proxy_pass (反向代理配置)∶
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/; ------------- 会转发请求到http∶//127.0.0.1∶8080/1.jpg
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; --------------会转发请求到http∶//127.0.0.1∶8080/test/1.jpg
五、访问状态统计配置
5.1、访问状态统计配置的操作步骤
1.1.先使用命令/usr/local/nginx/ sbin/nginx -V查看E安装的Nginx 是否包含HTTP_STUB_STATUS模块
1.2.修改 nginx.conf 配置文件,指定访问位置并添加 stub_status 配置(修改之前进行备份)
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
cp nginx.conf nginx.conf.bak
vim nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.clj.com;
charset utf-8;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
##添加 stub_status 配置
location /status { ##访问位置为/status
stub_status on; ##打开状态统计功能
access_log off; ##关闭此位置的日志记录
}
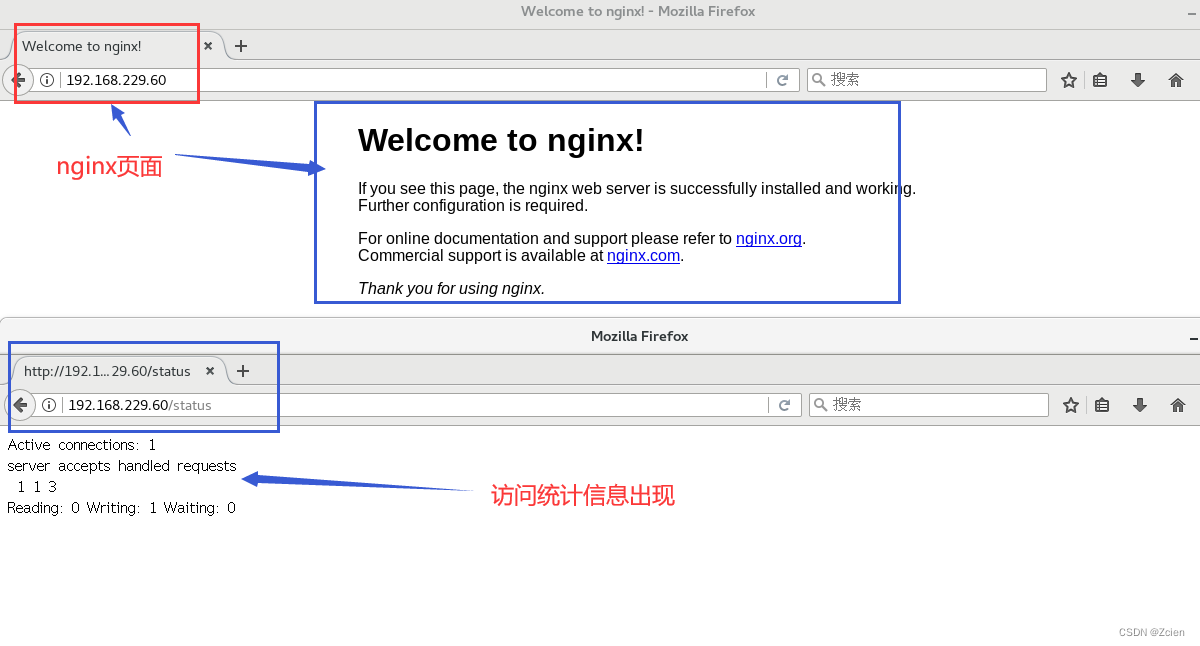
1.3、重启服务,访问测试
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问 http;//192.168.229.60/status
Active connections ∶ 表示当前的活动连接数;
server accepts handled requests∶表示已经处理的连接信息,三个数字依次表示已处理的连接数、成功的TCP握手次数已处理的请求数。
可curl http∶//192.168.80.10/status 结合 awk与if 语句进行性能监控
5.2、实例操作:访问状态统计配置
2.1 使用命令/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V查看已安装的 Nginx 是否包含HTTP_STUB STATUS模块
[root@cm ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
[root@cm sbin]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.12.2
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module
[root@cm sbin]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.12.2

2.2 修改nginx.conf 配置文件,指定访问位置并添加stub_status 配置
[root@cm sbin]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
[root@cm conf]# ls
fastcgi.conf fastcgi_params.default mime.types nginx.conf.default uwsgi_params
fastcgi.conf.default koi-utf mime.types.default scgi_params uwsgi_params.default
fastcgi_params koi-win nginx.conf scgi_params.default win-utf
[root@cm conf]# cp nginx.conf{,.bak}
[root@cm conf]# ls
fastcgi.conf fastcgi_params.default mime.types nginx.conf.bak scgi_params.default win-utf
fastcgi.conf.default koi-utf mime.types.default nginx.conf.default uwsgi_params
fastcgi_params koi-win nginx.conf scgi_params uwsgi_params.default
[root@cm conf]# vim nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.ly.com;
charset utf-8;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}

2.3 重启服务后进行访问测试

六、基于授权的访问控制
6.1、基于授权的访问控制的操作步骤
1.1 生成用户密码认证文件
yum install -y httpd-tools
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db zhangsan
chown nginx /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db
chmod 400 /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db
1.2 修改主配置文件相对应目录,添加认证配置项
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
.....
server {
location / {
.....
##添加认证配置##
auth basic "secret"; #设置密码提示框文字信息
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db;
}
}
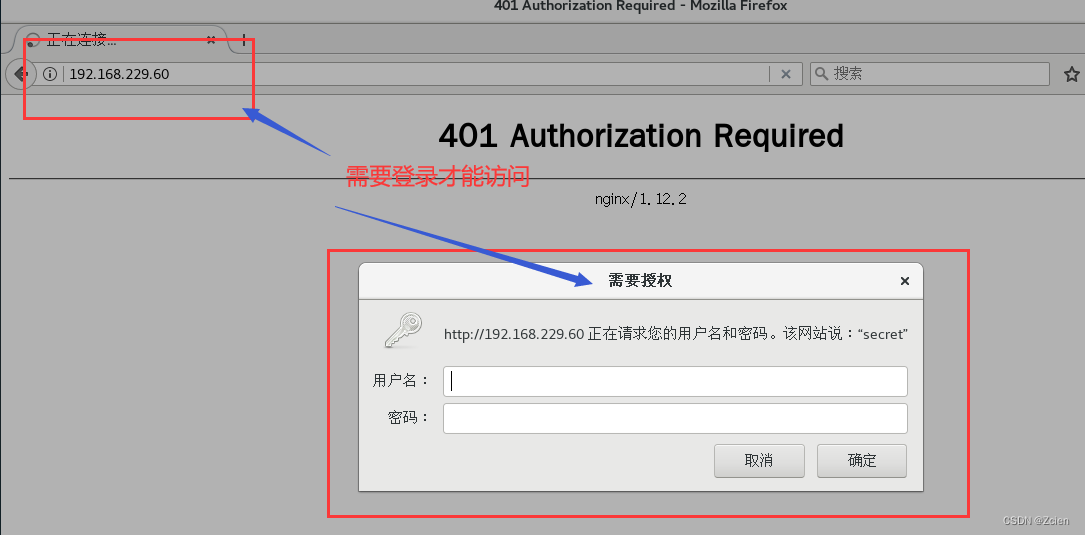
1.3 重启服务,访问测试
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx.service
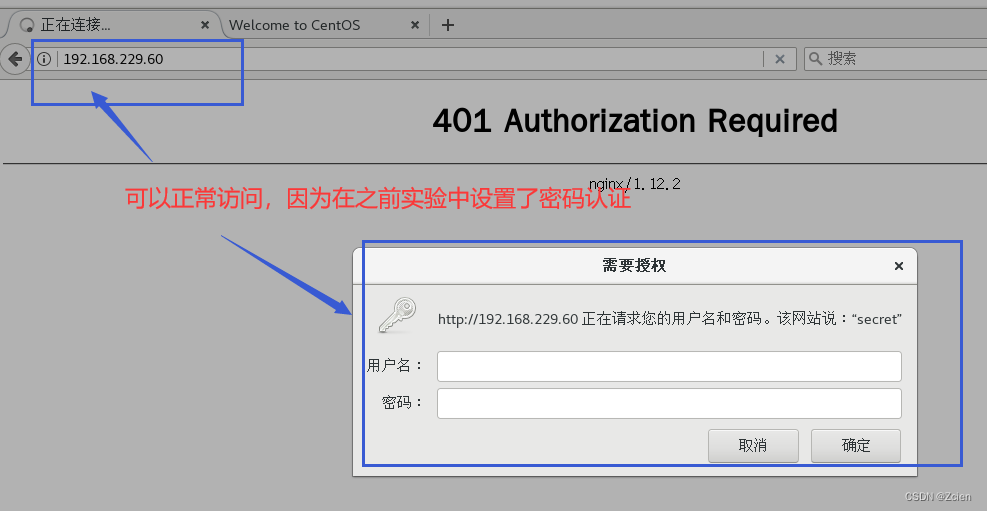
浏览器访问 http∶//192.168.229.60
6.2、实例操作:基于授权的访问控制
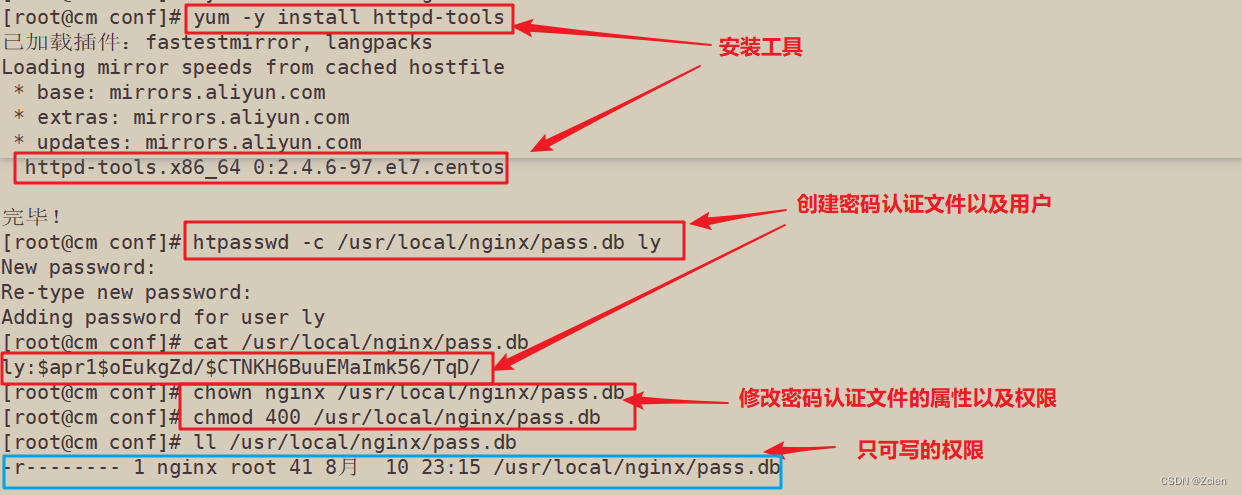
2.1 生成用户密码认证文件
```bash
[root@cm conf]# yum -y install httpd-tools
[root@cm conf]# htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/pass.db ly
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user ly
[root@cm conf]# cat /usr/local/nginx/pass.db
ly:$apr1$oEukgZd/$CTNKH6BuuEMaImk56/TqD/
[root@cm conf]# chown nginx /usr/local/nginx/pass.db
[root@cm conf]# chmod 400 /usr/local/nginx/pass.db
[root@cm conf]# ll /usr/local/nginx/pass.db
-r-------- 1 nginx root 41 8月 10 23:15 /usr/local/nginx/pass.db
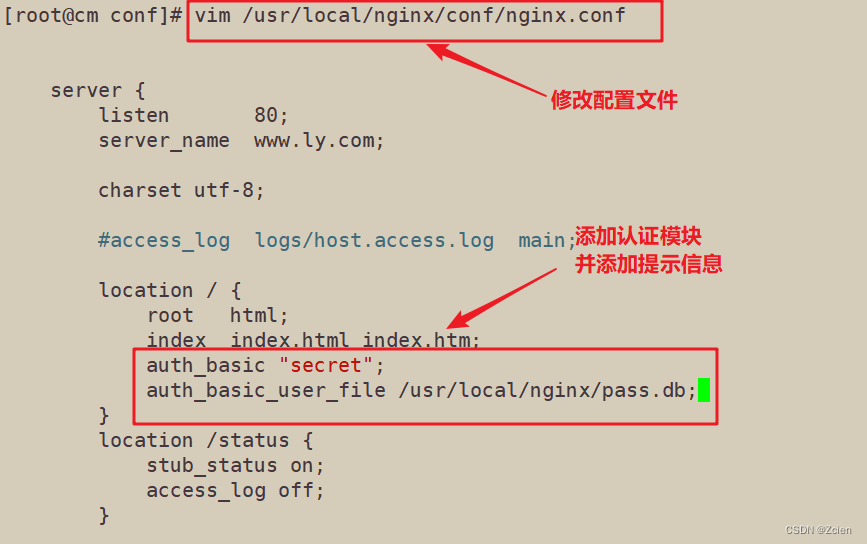
2.2 修改主配置文件相对应目录,添加认证配置项
[root@cm conf]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.ly.com;
charset utf-8;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
auth_basic "secret";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/pass.db;
}
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
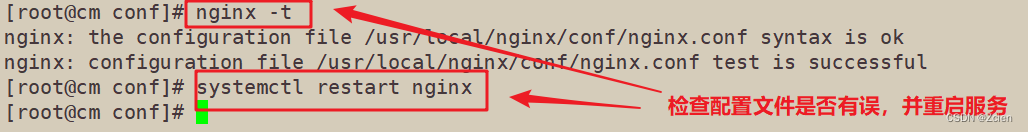
2.3 重启服务,访问测试
[root@cm conf]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@cm conf]# systemctl restart nginx
6.3、基于客户端访问控制
3.1 基于客户端访问控制的操作步骤
访问控制规则如下:
• deny IP/IP段: 拒绝某个IP或IP段的客户端访问
• allow IP/IP 段: 允许某个IP或IP段的客户端访问
• 规则从上往下执行,如匹配则停止,不再往下匹配
```bash
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
auth_basic "secret";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db;
# 添加控制规则
deny 192.168.80.77; #拒绝访问的客户端IP
allow all; #允许其他所有客户端访问
}
systemctl restart nginx
3.2 实例操作:基于客户端访问控制
3.2.1 在主配置文件中添加控制规则
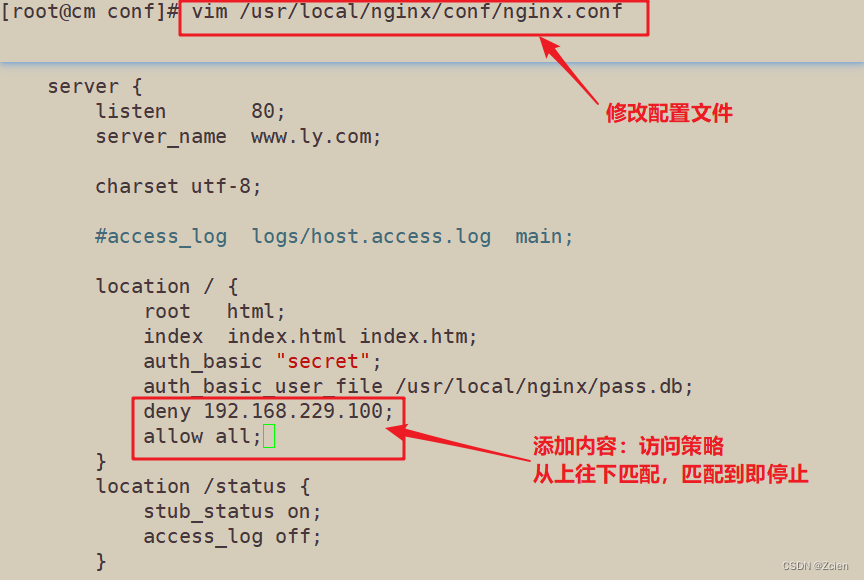
[root@cm conf]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.ly.com;
charset utf-8;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
auth_basic "secret";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/pass.db;
deny 192.168.229.100;
allow all;
}
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
3.2.2 重启服务并访问测试
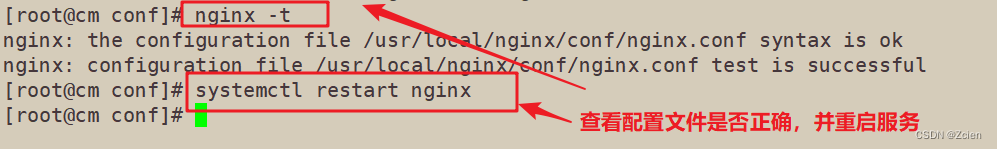
[root@cm conf]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@cm conf]# systemctl restart nginx
使用被拒绝的客户端进行访问测试
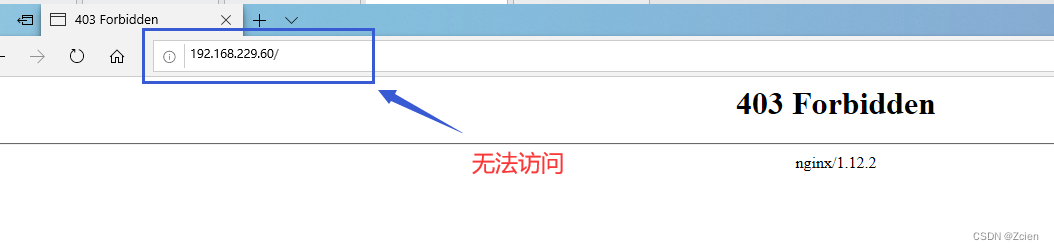
使用其他客户端进行访问测试