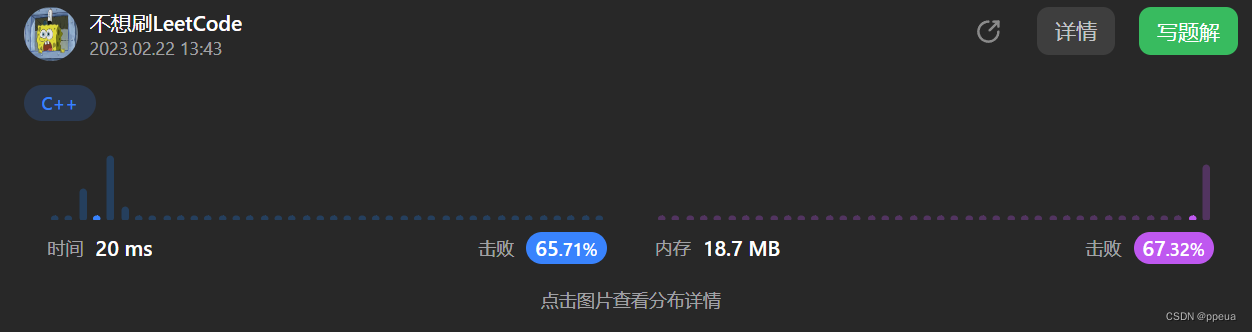
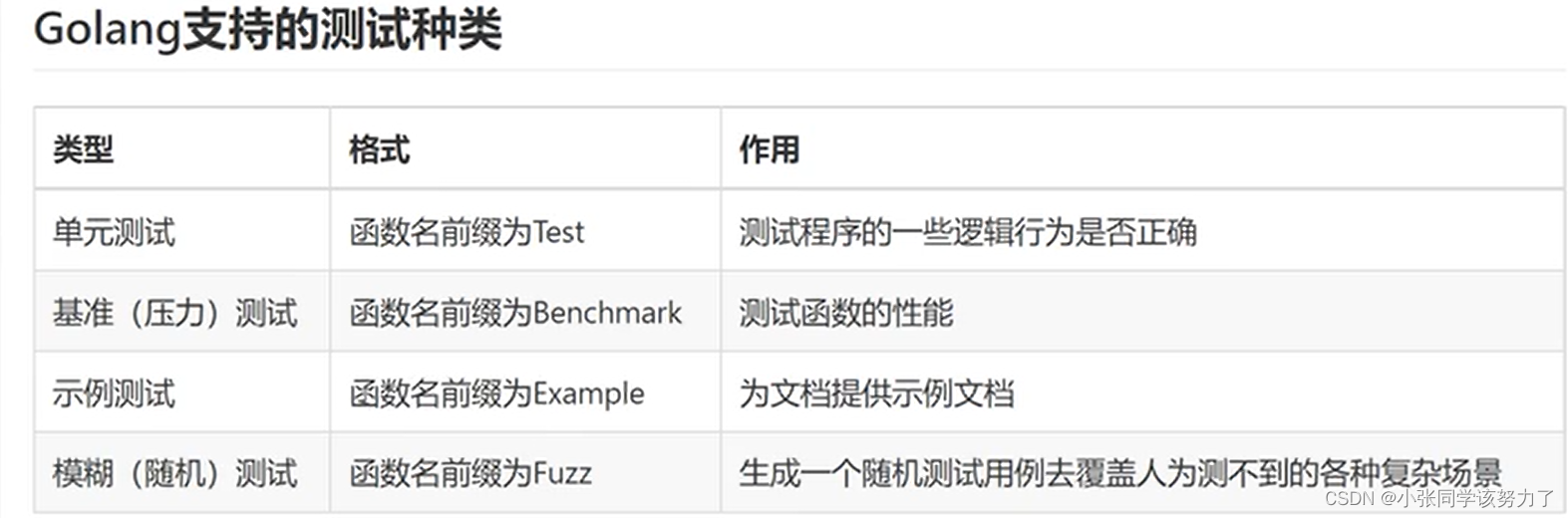
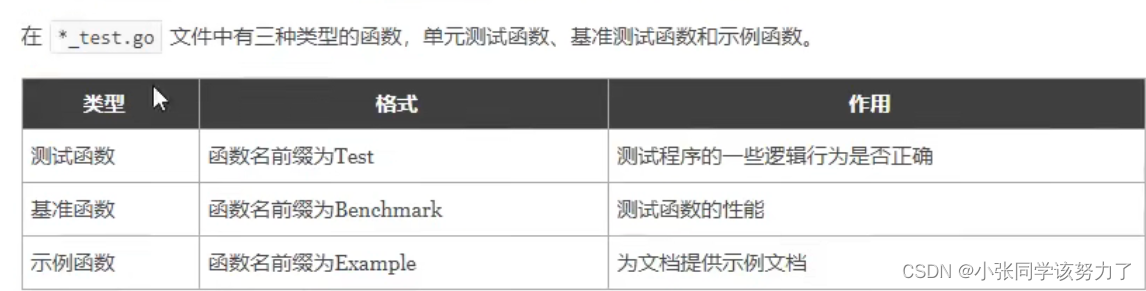
测试类型:
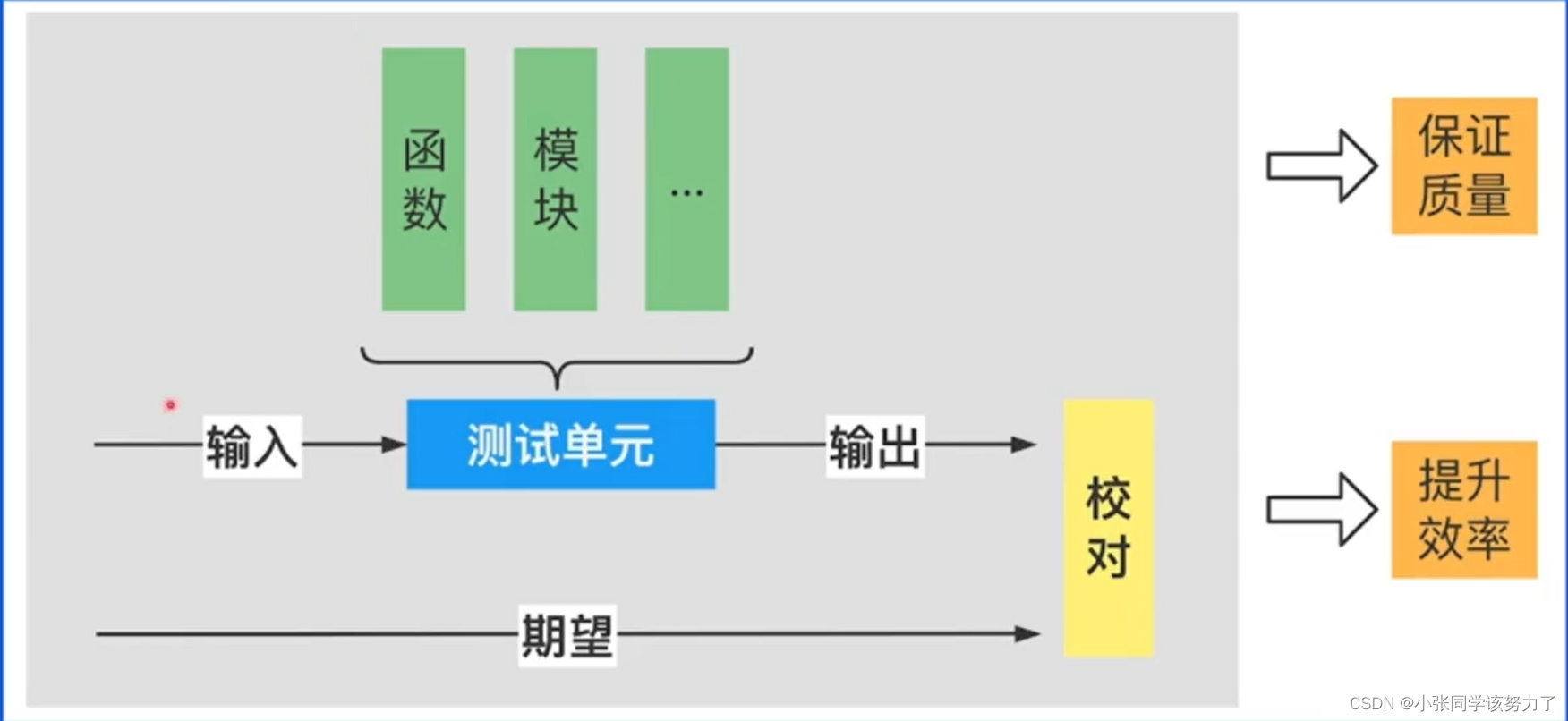
单元测试:
规则:
1.所有测试文件以_test.go结尾
2.func Testxxx(*testing.T)
3.初始化逻辑放到TestMain中
运行:
go test [flags][packages]
Go语言中的测试依赖go test命令。
go test命令是一个按照一定约定和组织的测试代码的驱动程序。在包目录内,所有以_test.go为后缀名的源代码文件都是go test测试的一部分,不会被go build编译到最终的可执行文件中
测试函数:
每个测试函数必须导入testing包,测试函数名必须以Test开头,测试函数的基本格式(签名)如下:
覆盖率:
显示代码覆盖率的命令
go test [flags][packages] --cover
1.一般覆盖率:50%~60%,较高覆盖率80%+
2.测试分支相互独立、全面覆盖
3.测试单元粒度足够小,函数单一职责
依赖:
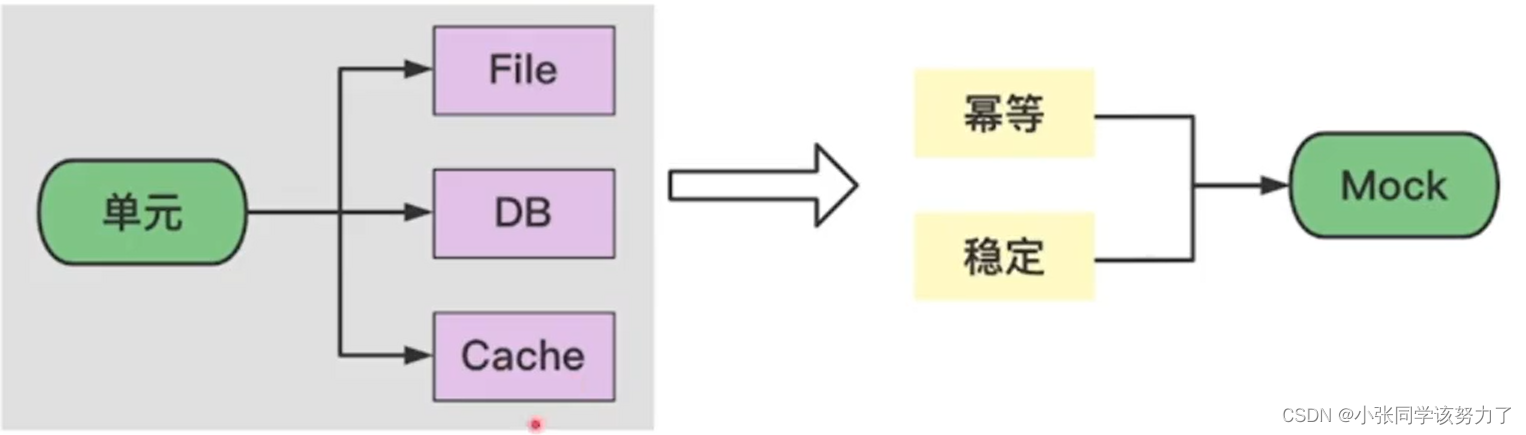
Mock
1.快速mock函数:
为一个函数打桩
为一个方法打桩
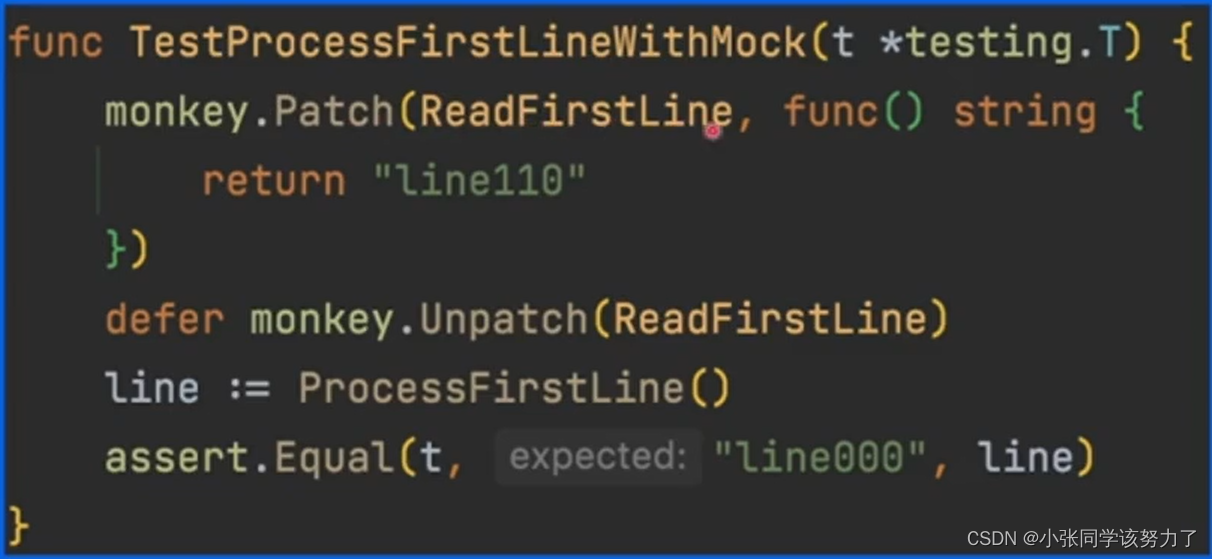
monkey打桩实例:
代码实例:
package split_string
import (
"strings"
)
//切割字符串
//example:
//abc,b=>[a c]
func Split(str string, sep string) []string {
var ret=make([]string,0,strings.Count(str,sep)+1)//预先分配好内存
index := strings.Index(str, sep)
for index >= 0 {
ret = append(ret, str[:index])
str = str[index+len(sep):]
index = strings.Index(str, sep)
}
if str != "" {
ret = append(ret, str)
}
return ret
}
package split_string
import (
"reflect"
"testing"
)
func TestSplit(t *testing.T) {
ret := Split("babcbef", "b")
want := []string{"", "a", "c", "ef"}
if !reflect.DeepEqual(ret, want) {
//测试用例失败了
t.Errorf("want:%v but got:%v\n", want, ret)
}
} //测试用例一
func Test2Split(t *testing.T) {
ret := Split("a:b:c", ":")
want := []string{"a", "b", "c"}
if !reflect.DeepEqual(ret, want) {
t.Fatalf("want:%v but get:%v\n", want, ret)
}
} //测试用例二
//一次测试多个
func Test3Split(t *testing.T) {
type testCase struct {
str string
sep string
want []string
}
testGroup := []testCase{
testCase{"babcbef", "b", []string{"", "a", "c", "ef"}},
testCase{"a:b:c", ":", []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
testCase{"abcdef", "bc", []string{"a", "def"}},
testCase{"沙河有沙又有河", "有", []string{"沙河", "沙又", "河"}},
}
for _, test := range testGroup {
got := Split(test.str, test.sep)
if !reflect.DeepEqual(got, test.want) {
t.Fatalf("want:%#v got:%#v\n", test.want, got)
}
}
}
//子测试
func Test4Split(t *testing.T) {
type testCase struct {
str string
sep string
want []string
}
testGroup := map[string]testCase{
"case 1": testCase{"babcbef", "b", []string{"", "a", "c", "ef"}},
"case 2": testCase{"a:b:c", ":", []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
"case 3": testCase{"abcdef", "bc", []string{"a", "def"}},
"case 4": testCase{"沙河有沙又有河", "有", []string{"沙河", "沙又", "河"}},
}
for name, test := range testGroup {
t.Run(name, func(t *testing.T) {
got := Split(test.str, test.sep)
if !reflect.DeepEqual(got, test.want) {
t.Fatalf("want:%#v got:%#v\n", test.want, got)
}
})
}
} //会把每个map中的样例试结果都打印出来


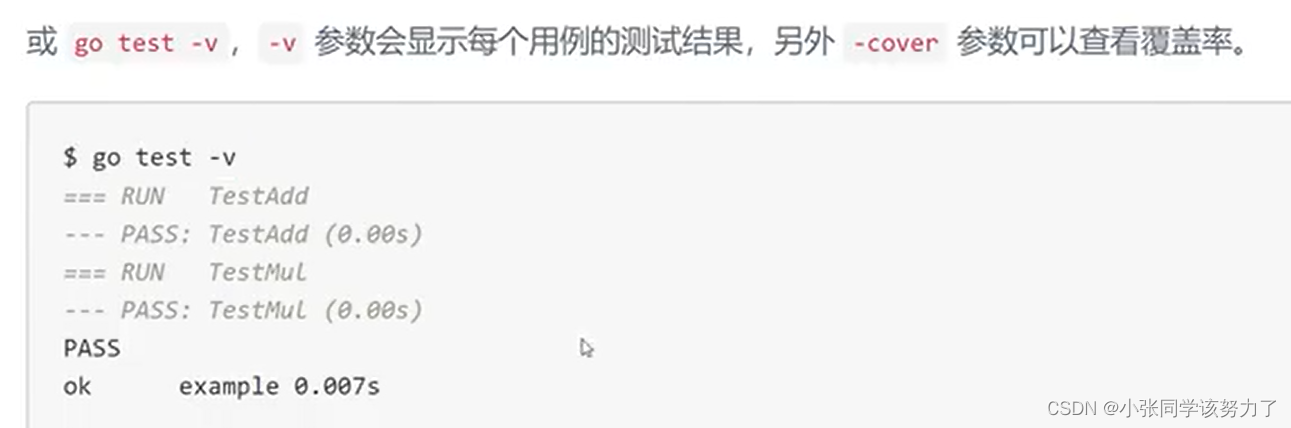
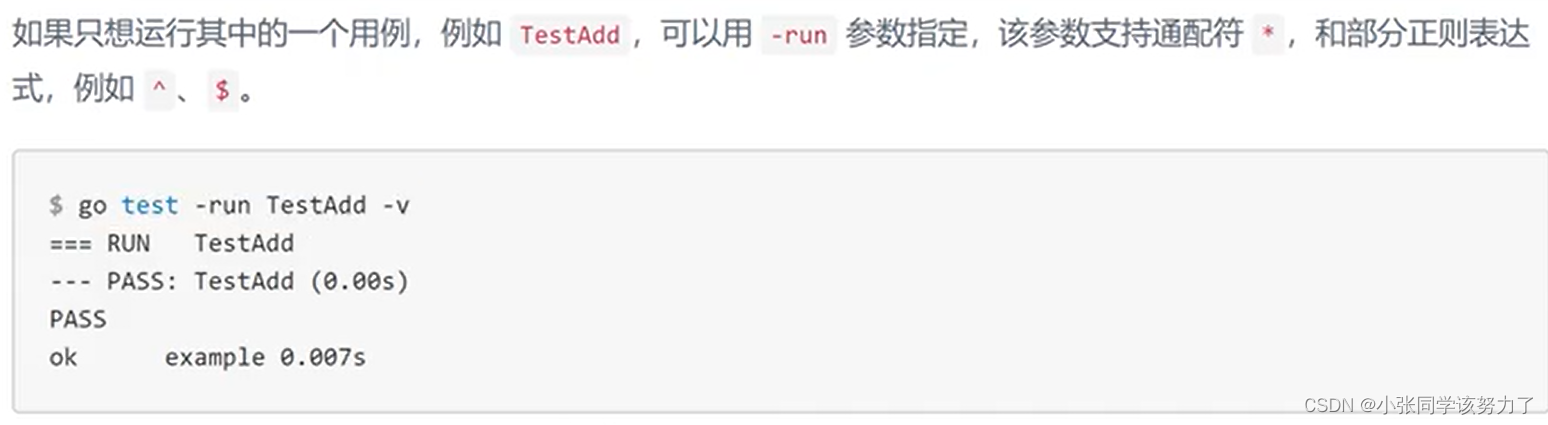
//在split_string终端下
go test //进行测试
go test -v//查看测试细节
go test -cover//语句覆盖率
go test -cover -coverprofile=cover.out//将测试结果生成文件
go tool -cover -html=cover.out //生成html文件来分析cover.out,绿色覆盖,红色未覆盖
//好的测试,测试函数覆盖率:100% 测试覆盖率:60%
基准测试:
func BenchmarkSplit(b *testing.B){
for i:=0;i<b.N;i++{
Split("a:b:c:d:e",":")
}
}
go test -bench=Split
//goos: windows windows平台
// goarch: amd64 amd64位
// pkg: test/split_string
// cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-8750H CPU @ 2.20GHz
// BenchmarkSplit-12 12核 3869991 执行次数 307.2 ns/op 307.2ns/次
// PASS
// ok test/split_string 1.539s
go test -benchmem //增加了查看对内存的申请情况
网络测试:
func TestHelloHandler(t *testing.T) {
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:0")
handleError(t, err)
defer ln.Close()
http.HandleFunc("/hello", HelloHandler)
go http.Serve(ln, nil)
resp, err := http.Get("http://" + ln.Addr().String() + "hello")
handleError(t, err)
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
handleError(t, err)
if string(body) != "hello world!" {
t.Fatal("expected hello world,but got", string(body))
}
}
基准测试
1.优化代码,需要对当前代码分析
2.内置的测试框架提供了基准测试的能力
func BenchmarkSelect(b *testing.B) {
InitServerIndex()
b.ResetTimer() //定时器重置
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
Select()
}
}
func BenchmarkSelectParallel(b *testing.B) {
InitServerIndex()
b.ResetTimer()
b.RunParallel(func(pb *testing.PB) {
for pb.Next() {
Select()
}
})
}