1. vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器。
2. 就像数组一样,vector也采用的连续存储空间来存储元素。也就是意味着可以采用下标对vector的元素进行访问,和数组一样高效。但是又不像数组,它的大小是可以动态改变的,而且它的大小会被容器自动处理。
3. 本质讲,vector使用动态分配数组来存储它的元素。当新元素插入时候,这个数组需要被重新分配大小为了增加存储空间。其做法是,分配一个新的数组,然后将全部元素移到这个数组。就时间而言,这是一个相对代价高的任务,因为每当一个新的元素加入到容器的时候,vector并不会每次都重新分配大小。
4. vector分配空间策略:vector会分配一些额外的空间以适应可能的增长,因为存储空间比实际需要的存储空间更大。不同的库采用不同的策略权衡空间的使用和重新分配。但是无论如何,重新分配都应该是对数增长的间隔大小,以至于在末尾插入一个元素的时候是在常数时间的复杂度完成的。
5. 因此,vector占用了更多的存储空间,为了获得管理存储空间的能力,并且以一种有效的方式动态增长。
6. 与其它动态序列容器相比(deques, lists and forward_lists), vector在访问元素的时候更加高效,在末尾添加和删除元素相对高效。对于其它不在末尾的删除和插入操作,效率更低。比起lists和forward_lists统一的迭代器和引用更好。
vector各个接口测试:


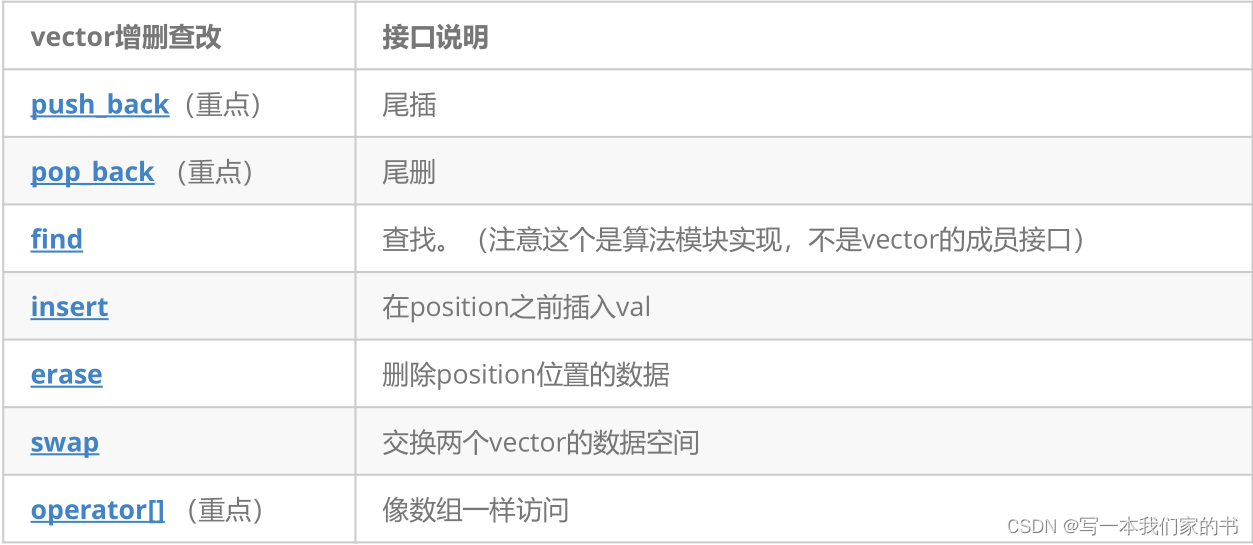
1.resize 和 reserve是重点。pj版本1.5,sgi版本 2倍扩容。resize可以扩大或者缩小size(),当capacity不够时自动进行扩容,reserve()扩大capacity起作用,但是缩小capacity不起作用。容量只能越扩越大,不会缩小。
2.提现指定容量可以减少多次自动扩容开辟空间的时间开销。
3.vector没有提供头插和头删,因为移动元素效率低下。
4..at()会做访问越界检查,[]不会。
5.insert()返回指向插入的元素的迭代器,erase()返回指向删除元素的下一个元素的迭代器(空间上是指向删除的原位置,数值上是指向下一个元素)。
capacity的代码在vs和g++下分别运行会发现,vs下capacity是按1.5倍增长的,g++是按2倍增长的。这个问题经常会考察,不要固化的认为,顺序表增容都是2倍,具体增长多少是根据具体的需求定义的。vs是PJ版本STL,g++是SGI版本STL。
reserve只负责开辟空间,如果确定知道需要用多少空间,reserve可以缓解vector增容的代价缺陷问题。
resize在开空间的同时还会进行初始化,影响size。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int>iv;
vector<int>iv1(10,2);
for (auto e : iv1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = iv1.begin(); it != iv1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < iv1.size(); ++i)
{
cout << iv1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test02()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int>v(arr, arr + 5);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test03()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int>v1(arr, arr + 5);
vector<int>v2(v1);
vector<int>::reverse_iterator rit = v2.rbegin();
while (rit != v2.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test04()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int>v1(arr, arr + 5);
cout << v1.size() << endl;
cout << v1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test05()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
cout << "size = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
}
扩容是重点
pg1.5,sgi 2倍扩容
void test06()//容量只会扩不会缩,大小随便换,容量不够就扩
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
cout << "size = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(10);
cout << "size = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(3);
cout << "size = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(20);
cout << "size = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(3);
cout << "size = " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
}
void test07()//提前指定容量
{
vector<int>v;
v.reserve(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
cout << "capacity = " << v.capacity() << endl;
}
}
void test08()
{
vector<int> iv(5, 1);
iv.resize(10, 2);
for (auto e : iv)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "size = " << iv.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << iv.capacity() << endl;
}
void test09()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.pop_back();
v.push_front
v.pop_front 没有头插头删 移动元素效率低下
v.insert(v.begin(), 10);
auto pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 1);
v.insert(pos, 20);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}
.at会对越界做检查,[]不会对越界做检查
void test10()
{
int ar[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(ar[0]);
vector<int>v(ar, ar+n);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << " ";
cout << v.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test10();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 迭代器的主要作用就是让算法能够不用关心底层数据结构,其底层实际就是一个指针,或者是对指针进行了封装,比如:vector的迭代器就是原生态指针T*。因此迭代器失效,实际就是迭代器底层对应指针所指向的空间被销毁了,而使用一块已经被释放的空间,造成的后果是程序崩溃(即如果继续使用已经失效的迭代器,程序可能会崩溃)。
对于vector可能会导致其迭代器失效的操作有:
1. 会引起其底层空间改变的操作,都有可能是迭代器失效,比如:resize、reserve、insert、assign、push_back等。
2. 指定位置元素的删除操作--erase。
erase删除pos位置元素后,pos位置之后的元素会往前搬移,没有导致底层空间的改变,理论上讲迭代器不应该会失效,但是:如果pos刚好是最后一个元素,删完之后pos刚好是end的位置,而end位置是没有元素的,那么pos就失效了。因此删除vector中任意位置上元素时,vs就认为该位置迭代器失效了。
迭代器失效解决办法:在使用前,对迭代器重新赋值即可。
迭代器失效的例子:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//扩容会导致迭代器失效
void test1()
{
int ar[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(ar[0]);
vector<int>v(ar, ar +n);
//v.reserve(20);//提前指定指定较大空间可以解决这个问题
auto it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);
cout << *it << endl;
v.push_back(20);
it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);//不提前指定大空间就需要重新给迭代器赋值来解决问题
cout <<*it << endl;
}
//会导致空间重新分配的操作都有可能让迭代器失效
void test02()
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
vector<int> v(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
// 使用find查找3所在位置的iterator
vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
// 删除pos位置的数据,导致pos迭代器失效。
v.erase(pos);
//cout << *pos << endl; // 此处会导致非法访问 1.空间角度有效 2.数据角度无效 vs报错 vc6不报错
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}删除所有偶数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
int ar[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(ar[0]);
vector<int>v(ar, ar +n);
auto pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);
auto it = v.erase(pos);
cout << *it << endl;//返回值空间上指向同一个空间,树数值上指向下一个元素
}
int main()
{
test01();
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };//还能这样定义
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
it = v.erase(it);//返回下一个位置
//++it;//迭代器失效
else
++it;
}
return 0;
}vector模拟实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vld.h>
using namespace std;
namespace hym
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
vector() :_First(nullptr), _Last(nullptr), _End(nullptr) {}
size_t size()const
{
return _Last - _First;
}
size_t capacity()const
{
return _End - _First;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _First;
}
iterator end()
{
return _Last;
}
public:
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
//扩容
size_t old_size = size();
T* new_first = new T[n];
memcpy(new_first, _First, sizeof(T) * old_size);
delete[] _First;
_First = new_first;
_Last = _First + old_size;
_End = _First + n;
}
}
void resize(size_t n, const T& x = T())
{
if (n <= size())
{
_Last = _First + n;
return;
}
if (n > capacity())
{
reserve(n);
}
iterator cur = _Last;
_Last = _First + n;
while (cur != _Last)
{
*cur = x;
++cur;
}
}
iterator insert(iterator _P, const T& x)
{
if (_Last == _End)
{
size_t p_size = _P - _First;
size_t new_size = size() == 0 ? 1 : size() * 2;
reserve(new_size);
//修改_P迭代器
_P = _First + p_size;
}
iterator end = _Last;
while (end > _P)
{
*end = *(end - 1);
--end;
}
*_P = x;
++_Last;
return _P;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(_Last, x);
}
~vector()
{
delete _First;
_First = _Last = _End = nullptr;
}
private:
iterator _First;
iterator _Last;
iterator _End;
};
}
void test01()
{
hym::vector<int>v;
auto pos = v.begin();
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
pos = v.insert(pos, 1);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
pos = v.insert(pos, 2);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
pos = v.insert(pos, 3);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
pos = v.insert(pos, 4);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
//cout << *it << endl;//插入后返回值指向插入点
for (auto e : v)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void test02()
{
hym::vector<int>v;
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(50);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(15);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
}
void test03()
{
hym::vector<int>v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
for (auto e : v)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void test04()
{
hym::vector<int>v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(3);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(70,9);
cout << "size= " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << v.capacity() << endl;
for (auto e : v)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
using namespace hym;
void main()
{
test04();
system("pause");
}