算法拾遗二十五之暴力递归到动态规划五
- 题目一(返回K次打击后英雄把怪兽砍死的几率)【样本对应模型,N和K是样本】
- 题目二(返回组成aim的最少货币数)从左往右尝试模型
- 题目三(返回裂开的数的种类)
题目一(返回K次打击后英雄把怪兽砍死的几率)【样本对应模型,N和K是样本】

题目分析:
英雄第一次砍怪是一个0-M范围的(M+1)次的展开,第二次,第三次砍击都是M+1次的展开【可能性总数为M+1的k次方】
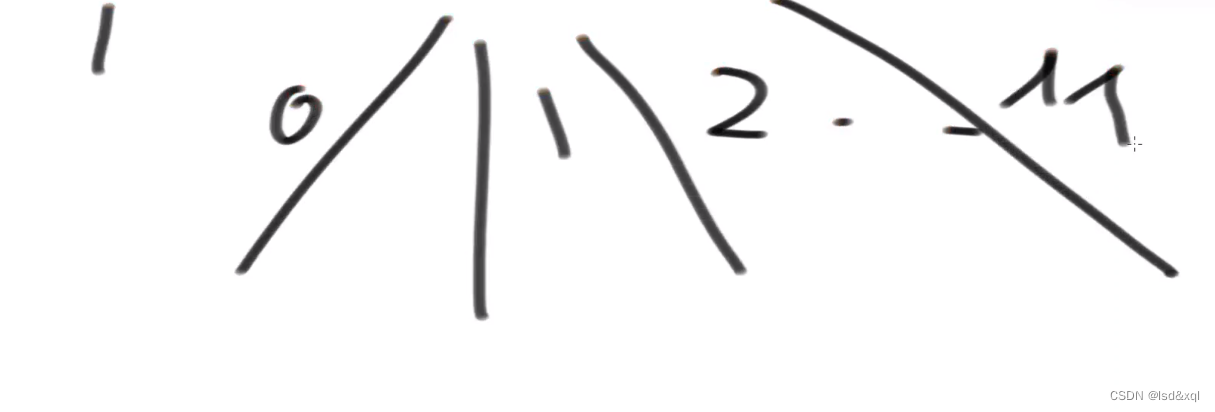
public static double right(int N, int M, int K) {
if (N < 1 || M < 1 || K < 1) {
return 0;
}
long all = (long) Math.pow(M + 1, K);
long kill = process(K, M, N);
return (double) ((double) kill / (double) all);
}
// 怪兽还剩hp点血
// 每次的伤害在[0~M]范围上
// 还有times次可以砍
// 返回砍死的情况数!
public static long process(int times, int M, int hp) {
if (times == 0) {
return hp <= 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
//如果当前怪兽的血量已经小于等于0了,还剩三刀没有砍出去,那么还剩下M+1的三次
//方的生存点【为了生成的表不到达负数,此优化可以不浪费那么多空间】
if (hp <= 0) {
return (long) Math.pow(M + 1, times);
}
long ways = 0;
//0-M范围内减血【等概率每种概率】
for (int i = 0; i <= M; i++) {
ways += process(times - 1, M, hp - i);
}
return ways;
}
改dp,可变参数有N和K
ublic static double dp11(int N, int M, int K) {
if (N < 1 || M < 1 || K < 1) {
return 0;
}
long all = (long) Math.pow(M + 1, K);
long[][] dp = new long[K + 1][N + 1];
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int times = 1; times <= K; times++) {
dp[times][0] = (long) Math.pow(M + 1, times);
for (int hp = 1; hp <= N; hp++) {
long ways = 0;
//0-M范围内减血【等概率每种概率】
for (int j = 0; j <= M; j++) {
//hp-j = 0时上步骤已经算了
if (hp - j >= 0) {
ways += dp[times - 1][hp - j];
} else {
ways += (long) Math.pow(M + 1, times - 1);
}
}
dp[times][hp] = ways;
}
}
long kill = dp[K][N];
return ((double) kill / (double) all);
}
二维表枚举行为优化:
找依赖关系,假设有dp(5,10),还剩五滴血,可以砍十刀,假设攻击范围为(0,3)
for (int j = 0; j <= M; j++) {
//hp-j = 0时上步骤已经算了
if (hp - j >= 0) {
ways += dp[times - 1][hp - j];
} else {
ways += (long) Math.pow(M + 1, times - 1);
}
}
它依赖dp(4,10)dp(4,9) dp(4,8)dp(4,7);需要将这些状态累加起来,得到dp(5,10)
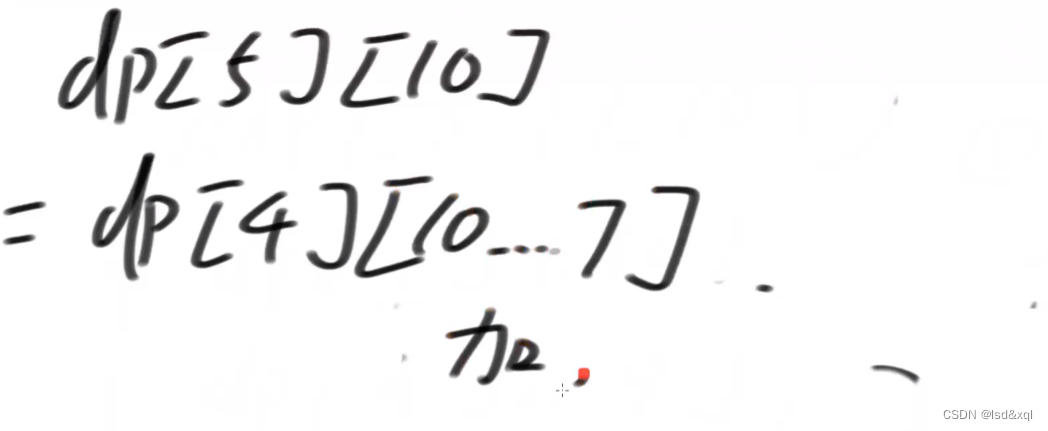
dp(5,10)依赖于(4,10…7)
dp(5,11)依赖于dp(4,11…8)
dp(5,11) = dp(5,10)+dp(4,11)-dp(4,7)可由此推导而出。
同理假设M=7,可得如下式子:
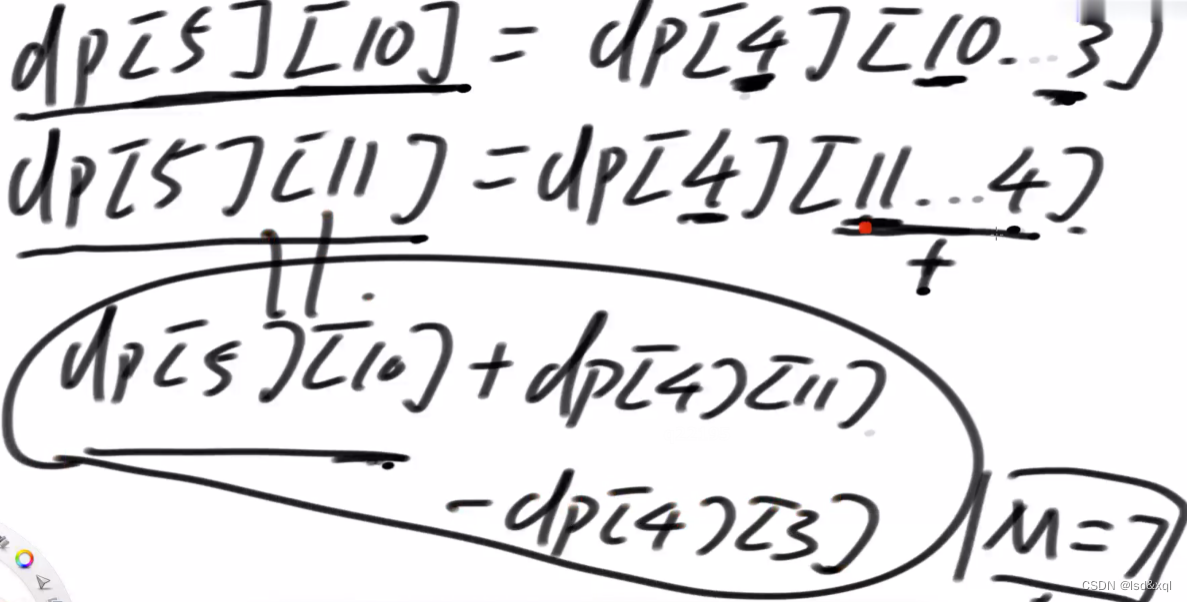
再推导通式:
dp【i】【j-1】= dp【i-1】【j-1…j-1-M】
dp【i】【j】= dp【i】【j-1】+dp【i-1】【j】-dp【i-1】【j-1-M】
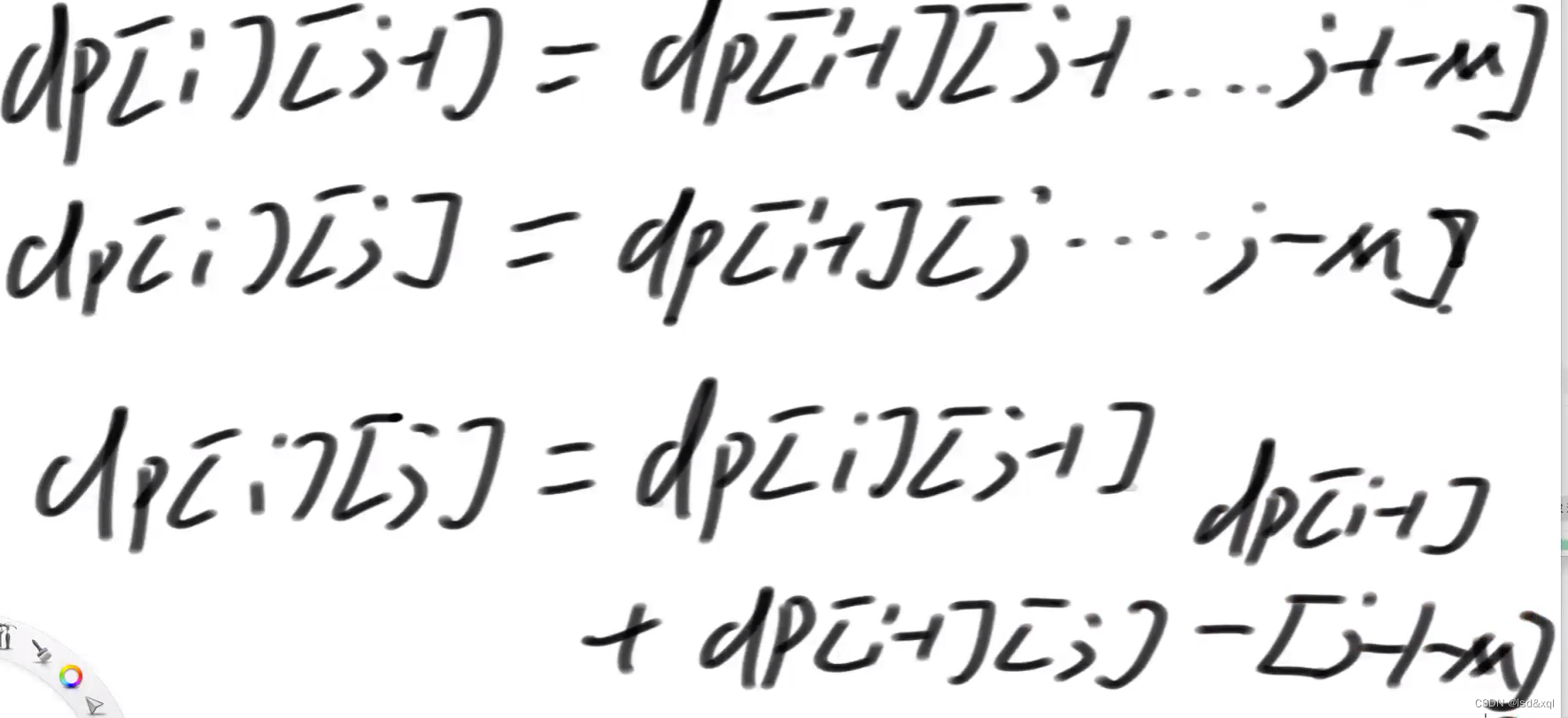
public static double dp22(int N, int M, int K) {
if (N < 1 || M < 1 || K < 1) {
return 0;
}
long all = (long) Math.pow(M + 1, K);
long[][] dp = new long[K + 1][N + 1];
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int times = 1; times <= K; times++) {
dp[times][0] = (long) Math.pow(M + 1, times);
for (int hp = 1; hp <= N; hp++) {
dp[times][hp] = dp[times][hp - 1] + dp[times - 1][hp];
//减去的那个要保证不越界
if (hp - 1 - M >= 0) {
dp[times][hp] -= dp[times - 1][hp - 1 - M];
} else {
//拿不到格子的情况数
dp[times][hp] -= Math.pow(M + 1, times - 1);
}
}
}
long kill = dp[K][N];
return ((double) kill / (double) all);
}
题目二(返回组成aim的最少货币数)从左往右尝试模型

public static int minCoins(int[] arr, int aim) {
return process(arr, 0, aim);
}
// arr[index...]面值,每种面值张数自由选择,
// 搞出rest正好这么多钱,返回最小张数
// 拿Integer.MAX_VALUE标记怎么都搞定不了
public static int process(int[] arr, int index, int rest) {
if (index == arr.length) {
//如果已经没用钱了但是剩余的钱数等于0那么返回0张,否则返回maxvalue表明凑不齐
return rest == 0 ? 0 : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//当前面值的钱乘以张数
for (int zhang = 0; zhang * arr[index] <= rest; zhang++) {
//index+1表示0位置的做了决定了,然后需要下一个位置做后续的决定
int next = process(arr, index + 1, rest - zhang * arr[index]);
if (next != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
ans = Math.min(ans, zhang + next);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
改dp:
public static int dp1(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (aim == 0) {
return 0;
}
int N = arr.length;
//0-N 0-aim
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1];
//BaseCase
dp[N][0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= aim; j++) {
dp[N][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
//位置依赖,N行已经填过了,从N-1往上填
for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int zhang = 0; zhang * arr[index] <= rest; zhang++) {
int next = dp[index + 1][rest - zhang * arr[index]];
if (next != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
ans = Math.min(ans, zhang + next);
}
}
dp[index][rest] = ans;
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
缩减枚举行为【观察临近位置法】:
假设面值为3元,然后从14位置开始减,然后选一个最小
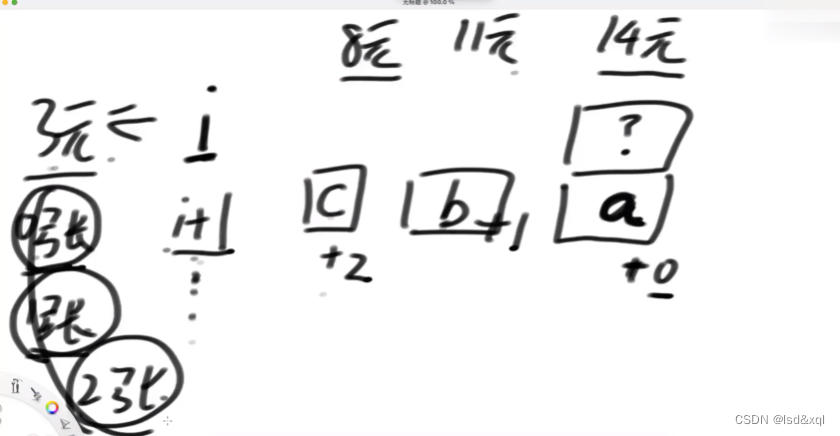
找与对号相邻的叉号:
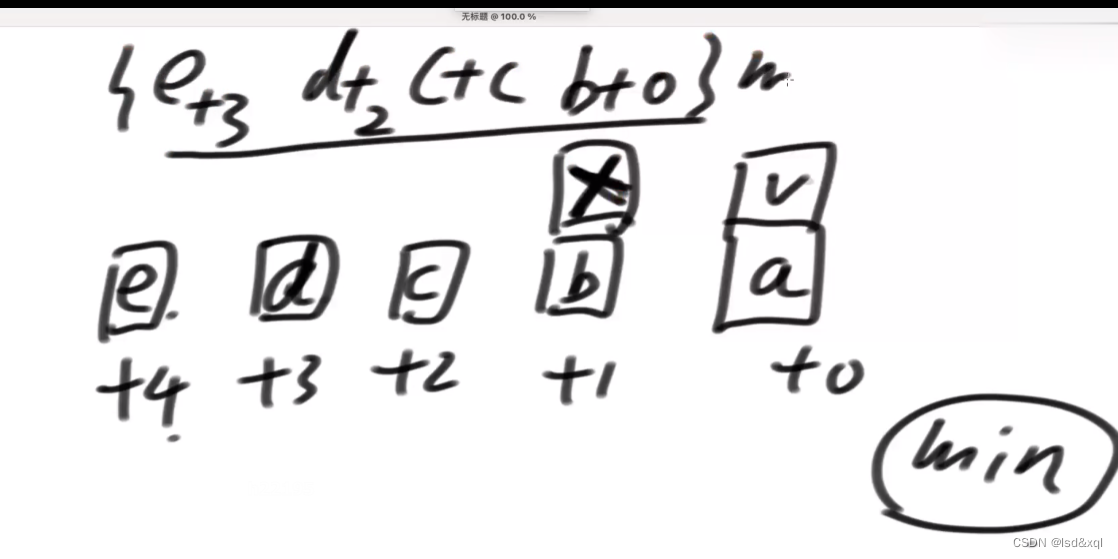
则推导为对号=(X+1,a+0)取一个最小值
public static int dp2(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (aim == 0) {
return 0;
}
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1];
dp[N][0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= aim; j++) {
dp[N][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
//取对号
dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1][rest];
if (rest - arr[index] >= 0
//X决策全都无效则不进下一步比较
&& dp[index][rest - arr[index]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
dp[index][rest] = Math.min(dp[index][rest], dp[index][rest - arr[index]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
题目三(返回裂开的数的种类)

暴力递归方式:
// n为正数
public static int ways(int n) {
if (n < 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
//要拆一个5,就假设上一步拆出来的是1,然后还剩5要拆
return process(1, n);
}
// 上一个拆出来的数是pre
// 还剩rest需要去拆
// 返回拆解的方法数
public static int process(int pre, int rest) {
//说明之前的数都严格遵循了左边的数比右边的数小
if (rest == 0) {
return 1;
}
//前置的数如果比剩下的数大那么走不通
if (pre > rest) {
return 0;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int first = pre; first <= rest; first++) {
ways += process(first, rest - first);
}
return ways;
}
改dp找依赖关系
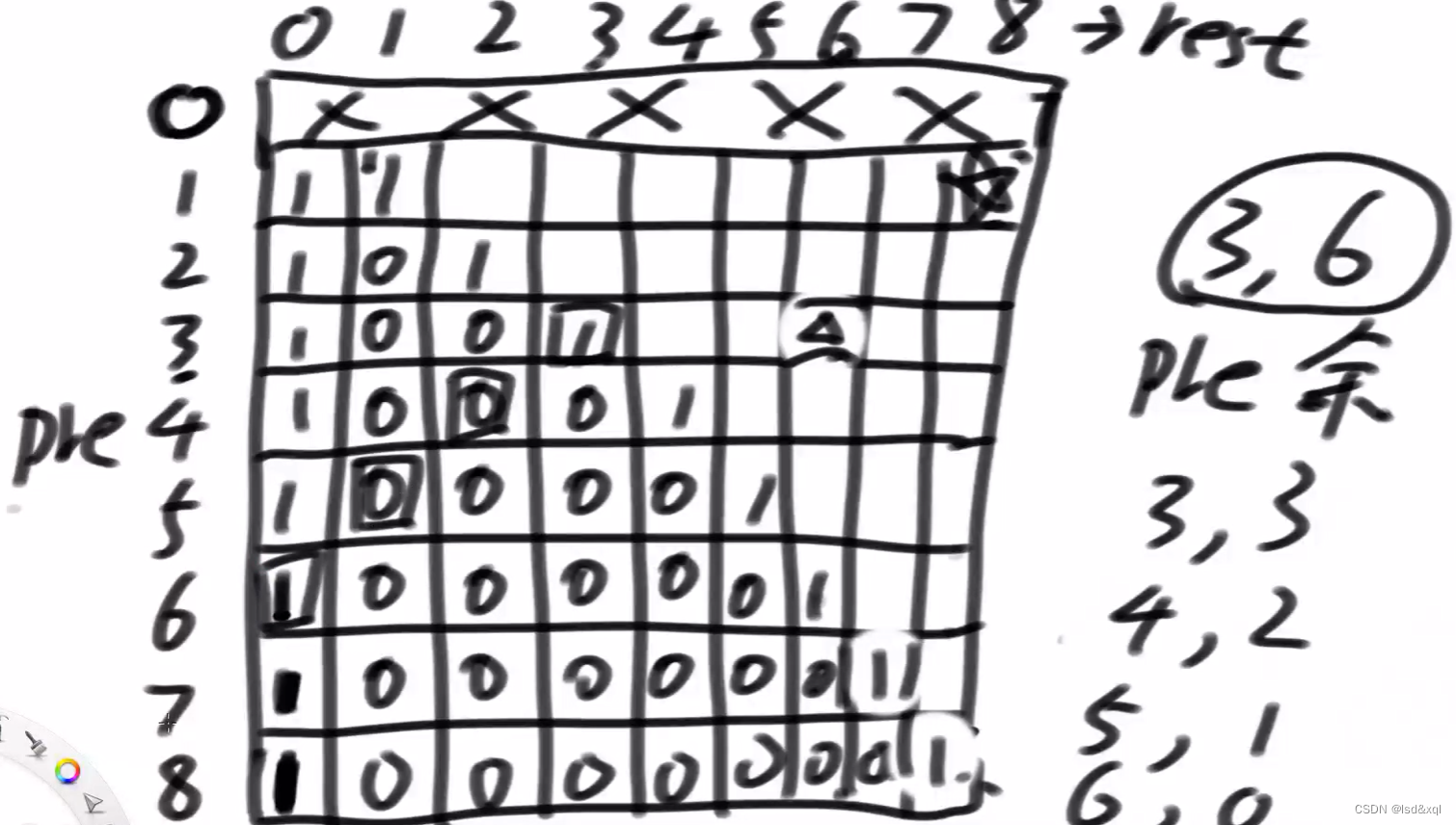
发现能按照从最右下角逐步往上填入:
public static int dp1(int n) {
if (n < 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
//pre=0是没用的
for (int pre = 1; pre <= n; pre++) {
//rest=0的时候要返回1
dp[pre][0] = 1;
//行列相等时为1(8,8)
dp[pre][pre] = 1;
}
//从n-1行开始
for (int pre = n - 1; pre >= 1; pre--) {
//rest<pre的时候为0 rest=pre的时候为1已经填了,所以rest从pre+1开始
for (int rest = pre + 1; rest <= n; rest++) {
int ways = 0;
//抄递归
for (int first = pre; first <= rest; first++) {
ways += dp[first][rest - first];
}
dp[pre][rest] = ways;
}
}
return dp[1][n];
}
分析位置依赖:观察X号位置
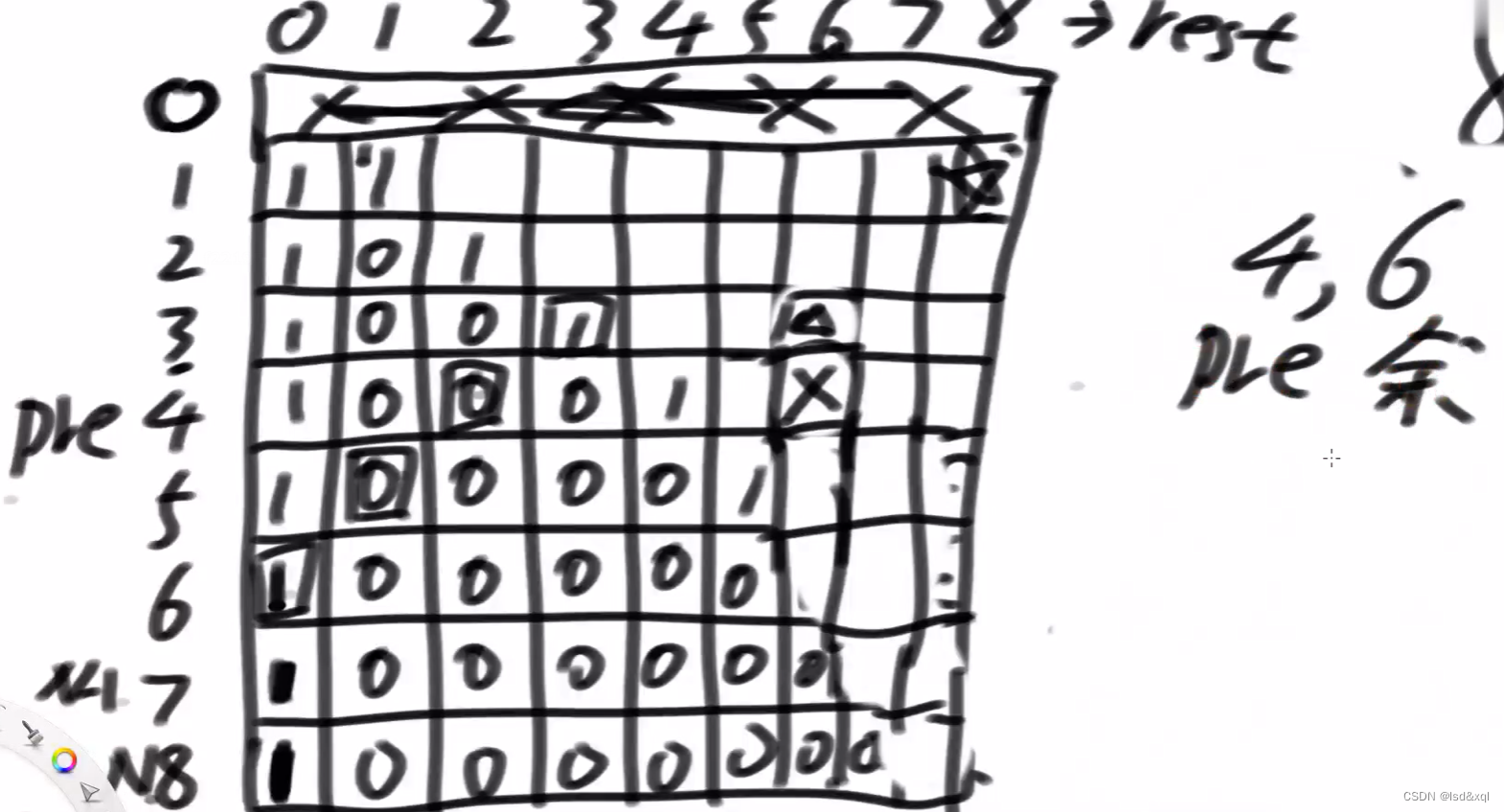
以(4,6)为例:
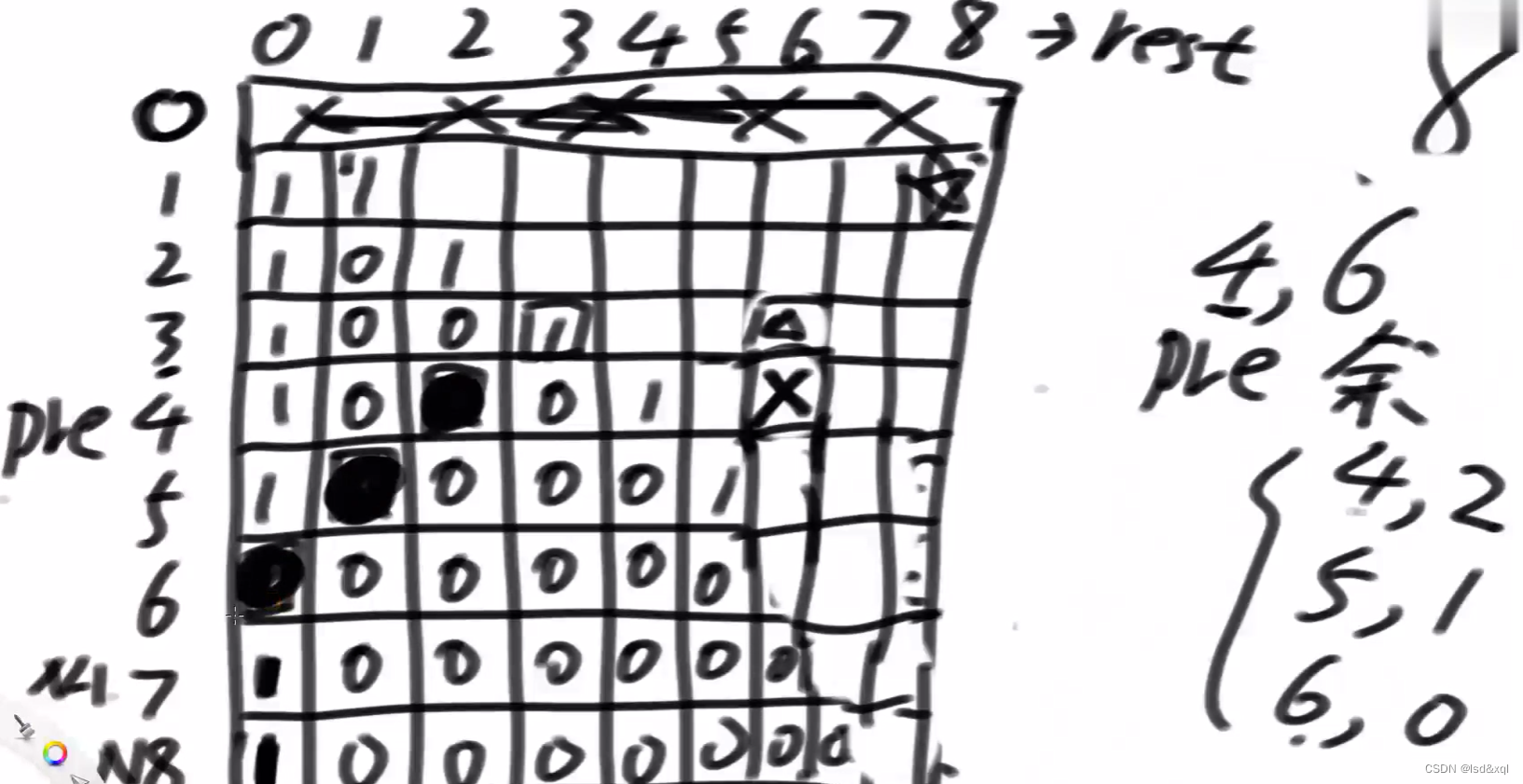
发现左边格子依赖关系为(pre,rest-pre)
public static int dp2(int n) {
if (n < 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
for (int pre = 1; pre <= n; pre++) {
dp[pre][0] = 1;
dp[pre][pre] = 1;
}
for (int pre = n - 1; pre >= 1; pre--) {
for (int rest = pre + 1; rest <= n; rest++) {
dp[pre][rest] = dp[pre + 1][rest];
dp[pre][rest] += dp[pre][rest - pre];
}
}
return dp[1][n];
}