create React App 脚手架工具创建项目
1.下载插件
2.打开终端
npx create-react-app my-app //my-app是自己创建的项目名
创建完成后cd my-app,到该项目的盘符执行npm start,就可以运行起来了
组件通讯
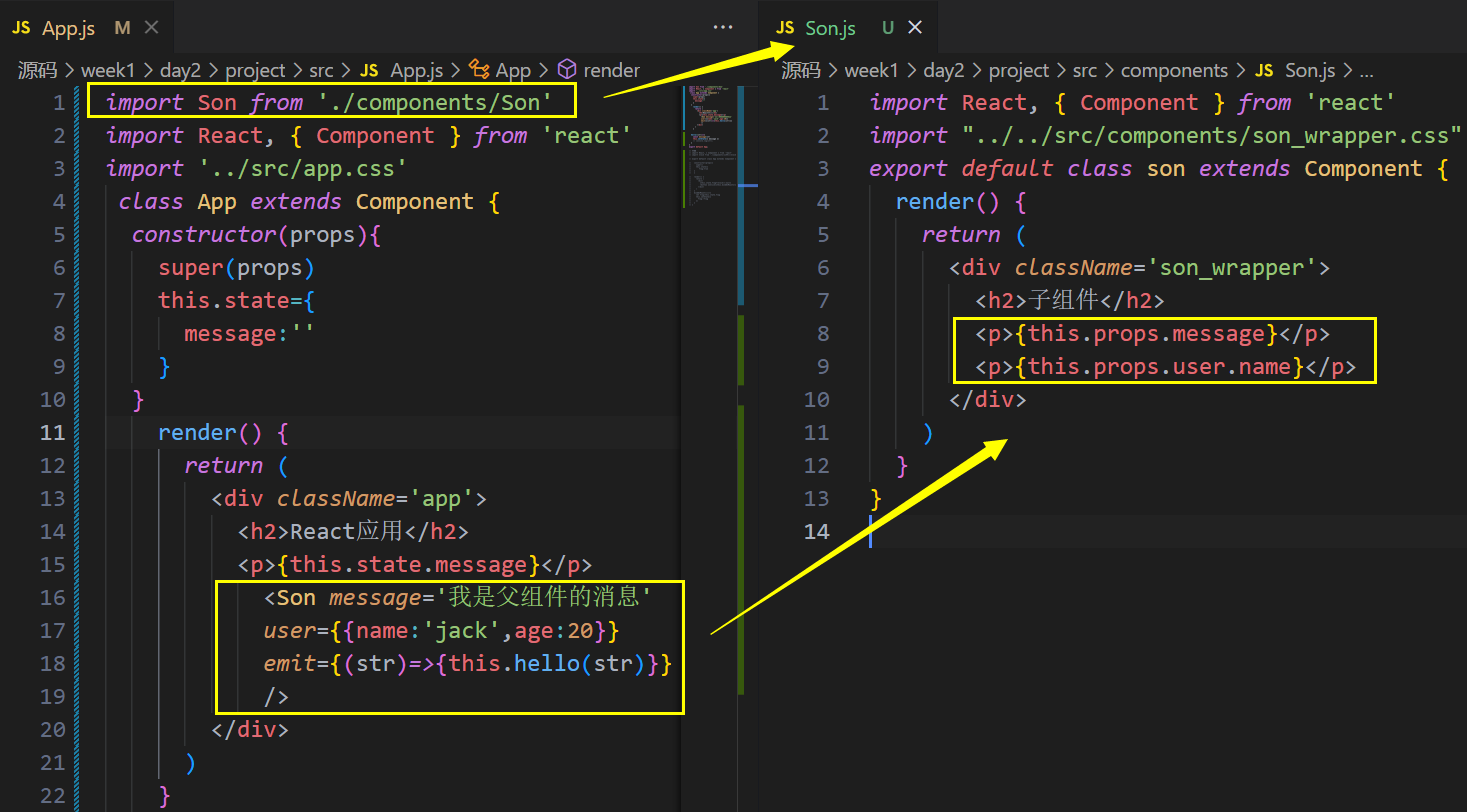
父传子
在父亲组件中引用子组件
在render()中使用子组件
在子组件中直接使用This.props.xxx
props
1. 值是只读的,不能修改
2. 任意类型数据 数值、字符串、数组、对象、函数、JSX(vue插槽slot) ...
子传父
在父亲组件中引用子组件
在render()中使用子组件
在子组件中直接使用This.props.自定义属性,并将内容传到父组件中,用Str来接收,执行hello方法。

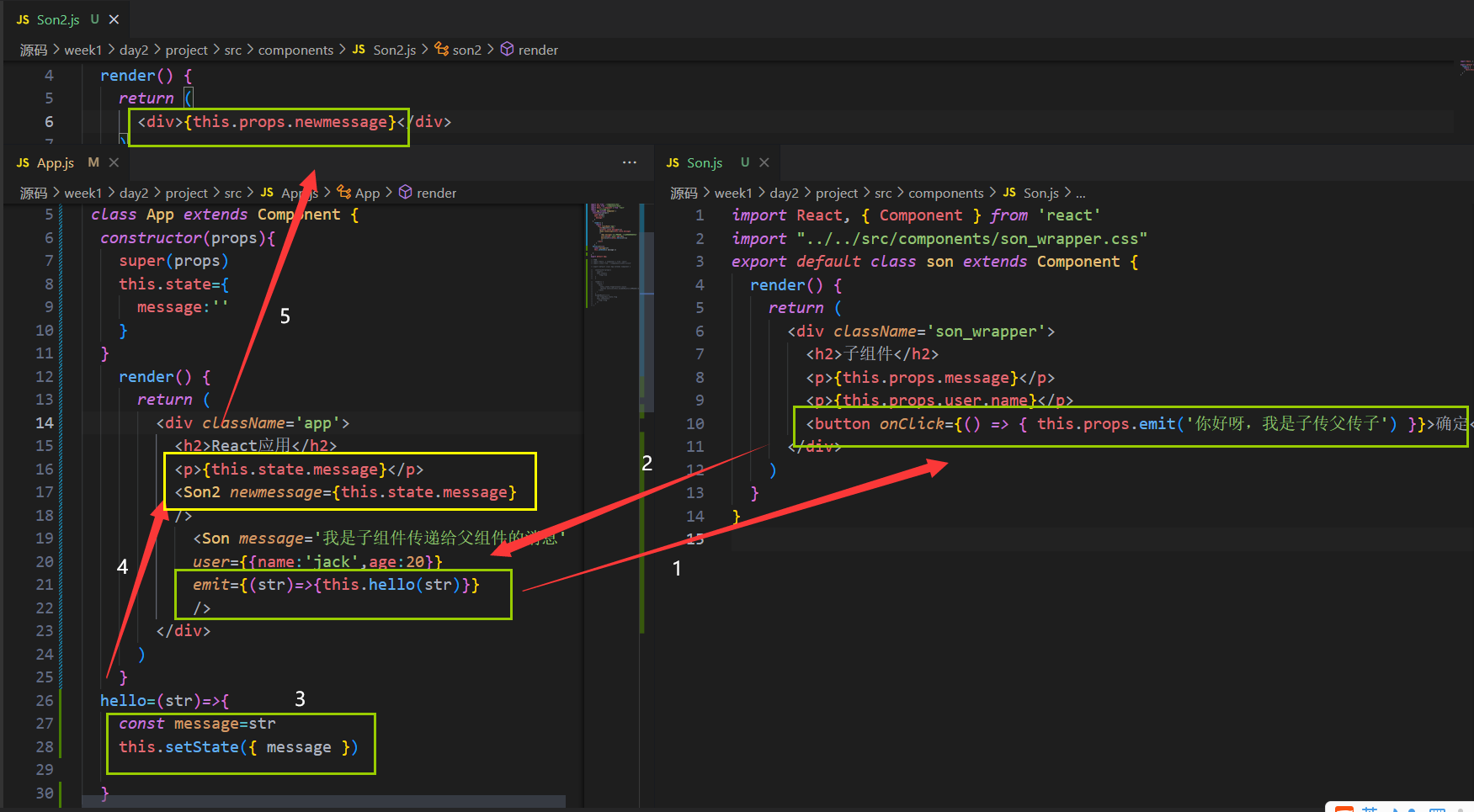
兄弟组件:
兄弟通信的精髓在于,子组件1传递给父亲组件,父亲组件再把值传递给子组件2
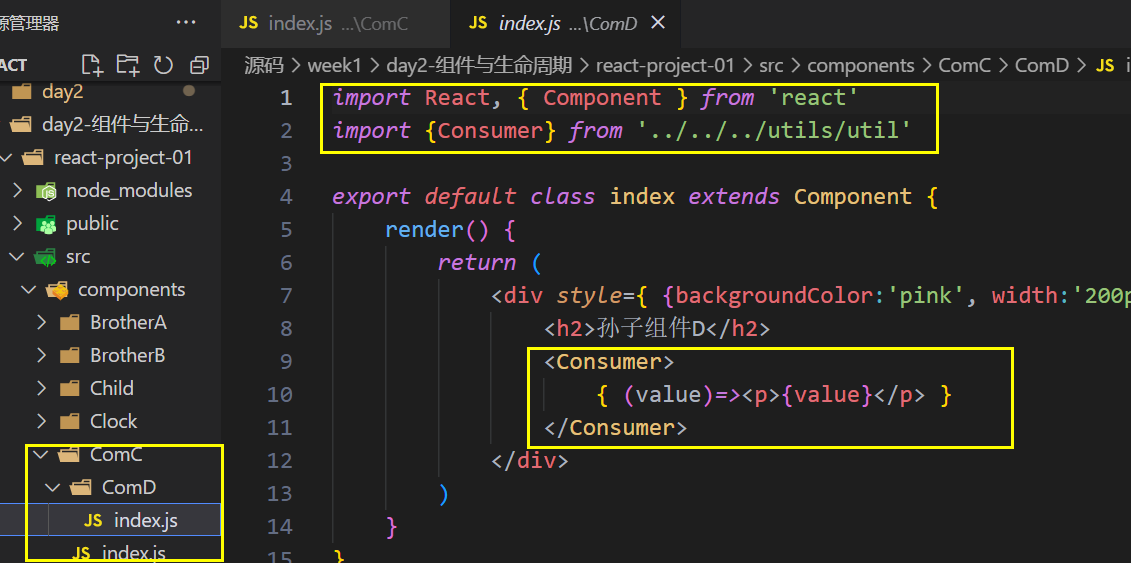
跨组件通信
实现方式:
1. 创建Context对象,导出Provider和Consumer对象(我写在utils里面,进行的引入)
2. 使用Provider包裹根组件提供数据,在APP中
3. 需要用到数据的组件使用Consumer包裹获取数据

React生命周期:
https://projects.wojtekmaj.pl/react-lifecycle-methods-diagram/
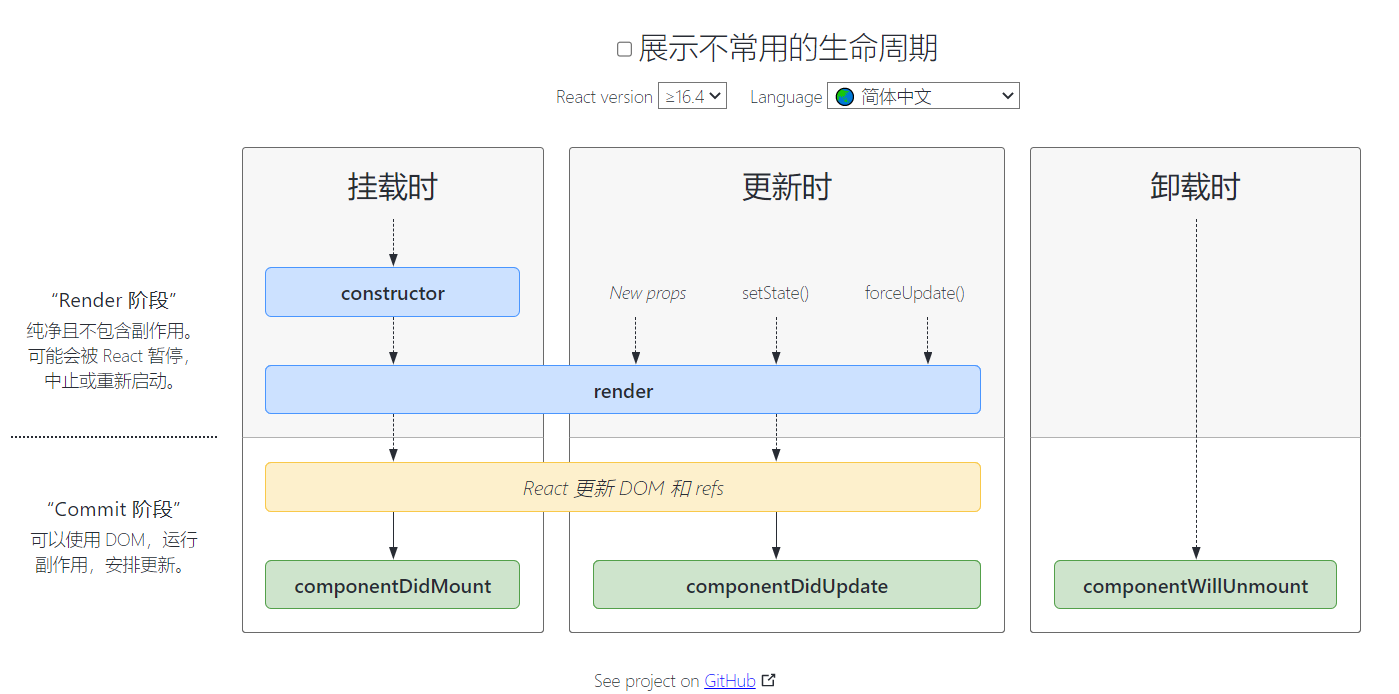
案例:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Clock extends Component {
constructor(props){
super()
this.state={
date: new Date(),
message:'生命周期'
}
}
render() {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<h1>{this.state.message}</h1>
<h2>时钟组件,动态更新时间</h2>
<h3>当前时间 {this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}</h3>
</React.Fragment>
)
}
componentDidMount(){
this.timer()
console.log('componentDidMount 组件挂载时>>>');
}
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log('componentDidUpdate 组件更新时>>>');
}
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('componentWillUnmount 组件卸载时');
clearInterval(this.timerID)
}
timer(){
this.timerID=setInterval(()=>{
this.setState({
date:new Date()
})
},1000)
}
}
APP.js
// import React, { Component } from 'react'
// import Clock from './components/定时器/Clock'
// export default class App extends Component {
// constructor(props){
// super()
// this.state={
// flag:true
// }
// }
// render() {
// return (
// <div>
// {this.state.flag?<Clock/>:null}
// <button onClick={this.bindUnMount}>关闭组件</button>
// </div>
// )
// }
// bindUnMount=()=>{
// let flag=this.state.flag
// this.setState({
// flag:!flag
// })
// }
// }