写在前面
以下内容是基于Redis 6.2.6 版本整理总结
一、组织方式
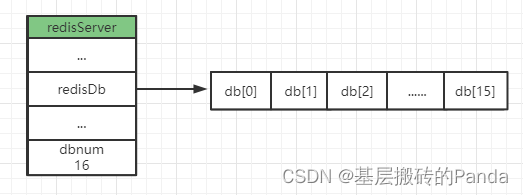
Redis服务器将所有的数据库 都保存在src/server.h/redisServer结构中的db数组中。db数组的每个entry都是src/server.h/redisDb结构,每个redisDb结构代表一个数据库。Redis默认有16个数据库。
1.1 redisServer结构定义
struct redisServer {
/* General */
pid_t pid; /* Main process pid. */
pthread_t main_thread_id; /* Main thread id */
...
redisDb *db; // db数组
...
int dbnum; // redis db的数量
...
};
1.2 redisDb 结构定义
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */ //键空间,保存数据库中所有的键值对
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
各字段含义解释:
- dict保存了数据库中的所有键值对,这个字典也被称为:键空间(key space)。键空间的键就是数据库的键,每个键都是字符串对象;键空间的值就是数据库的值,每个值可以是五种对象中的任意一种对象。
- expires用来处理键的过期行为;
- blocking_keys使用比较少,redis只有blpop、brpop等命令造成主动阻塞。
- ready_keys和blocking_keys配合使用,比如:一个客户端blpop阻塞等待数据,另一个客户端在push时,会检查blocking_keys中是否存在相应的key,如果有就将该key移动到ready_keys中,阻塞的客户端收到数据。
- watched_keys用来实现WATCH功能,实际线上环境不会使用,影响redis性能。
1.3 redisdb初始化
// src/server.c
void initServer(void) {
int j;
// ...
server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum);
// ...
/* Create the Redis databases, and initialize other internal state. */
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
server.db[j].dict = dictCreate(&dbDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires = dictCreate(&dbExpiresDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires_cursor = 0;
server.db[j].blocking_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].ready_keys = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].watched_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].id = j;
server.db[j].avg_ttl = 0;
server.db[j].defrag_later = listCreate();
listSetFreeMethod(server.db[j].defrag_later,(void (*)(void*))sdsfree);
}
//...
}
二、增删改查源码分析
2.1 新增key
/* Add the key to the DB. It's up to the caller to increment the reference
* counter of the value if needed.
*
* The program is aborted if the key already exists. */
void dbAdd(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) {
sds copy = sdsdup(key->ptr);
int retval = dictAdd(db->dict, copy, val);
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,retval == DICT_OK);
signalKeyAsReady(db, key, val->type);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyAdd(key->ptr);
}
2.2 删除key
/* This is a wrapper whose behavior depends on the Redis lazy free
* configuration. Deletes the key synchronously or asynchronously. */
int dbDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
return server.lazyfree_lazy_server_del ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
int dbSyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of
* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);
dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Tells the module that the key has been unlinked from the database. */
moduleNotifyKeyUnlink(key,val);
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key->ptr);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
#define LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD 64
int dbAsyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of
* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);
/* If the value is composed of a few allocations, to free in a lazy way
* is actually just slower... So under a certain limit we just free
* the object synchronously. */
dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Tells the module that the key has been unlinked from the database. */
moduleNotifyKeyUnlink(key,val);
size_t free_effort = lazyfreeGetFreeEffort(key,val);
/* If releasing the object is too much work, do it in the background
* by adding the object to the lazy free list.
* Note that if the object is shared, to reclaim it now it is not
* possible. This rarely happens, however sometimes the implementation
* of parts of the Redis core may call incrRefCount() to protect
* objects, and then call dbDelete(). In this case we'll fall
* through and reach the dictFreeUnlinkedEntry() call, that will be
* equivalent to just calling decrRefCount(). */
if (free_effort > LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD && val->refcount == 1) {
atomicIncr(lazyfree_objects,1);
bioCreateLazyFreeJob(lazyfreeFreeObject,1, val);
dictSetVal(db->dict,de,NULL);
}
}
/* Release the key-val pair, or just the key if we set the val
* field to NULL in order to lazy free it later. */
if (de) {
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key->ptr);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
2.3 查找key
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
* Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
* a copy on write madness. */
if (!hasActiveChildProcess() && !(flags & LOOKUP_NOTOUCH)){
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
updateLFU(val);
} else {
val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
}
return val;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
/* Lookup a key for read operations, or return NULL if the key is not found
* in the specified DB.
*
* As a side effect of calling this function:
* 1. A key gets expired if it reached it's TTL.
* 2. The key last access time is updated.
* 3. The global keys hits/misses stats are updated (reported in INFO).
* 4. If keyspace notifications are enabled, a "keymiss" notification is fired.
*
* This API should not be used when we write to the key after obtaining
* the object linked to the key, but only for read only operations.
*
* Flags change the behavior of this command:
*
* LOOKUP_NONE (or zero): no special flags are passed.
* LOOKUP_NOTOUCH: don't alter the last access time of the key.
*
* Note: this function also returns NULL if the key is logically expired
* but still existing, in case this is a slave, since this API is called only
* for read operations. Even if the key expiry is master-driven, we can
* correctly report a key is expired on slaves even if the master is lagging
* expiring our key via DELs in the replication link. */
robj *lookupKeyReadWithFlags(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
robj *val;
if (expireIfNeeded(db,key) == 1) {
/* If we are in the context of a master, expireIfNeeded() returns 1
* when the key is no longer valid, so we can return NULL ASAP. */
if (server.masterhost == NULL)
goto keymiss;
/* However if we are in the context of a slave, expireIfNeeded() will
* not really try to expire the key, it only returns information
* about the "logical" status of the key: key expiring is up to the
* master in order to have a consistent view of master's data set.
*
* However, if the command caller is not the master, and as additional
* safety measure, the command invoked is a read-only command, we can
* safely return NULL here, and provide a more consistent behavior
* to clients accessing expired values in a read-only fashion, that
* will say the key as non existing.
*
* Notably this covers GETs when slaves are used to scale reads. */
if (server.current_client &&
server.current_client != server.master &&
server.current_client->cmd &&
server.current_client->cmd->flags & CMD_READONLY)
{
goto keymiss;
}
}
val = lookupKey(db,key,flags);
if (val == NULL)
goto keymiss;
server.stat_keyspace_hits++;
return val;
keymiss:
if (!(flags & LOOKUP_NONOTIFY)) {
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_KEY_MISS, "keymiss", key, db->id);
}
server.stat_keyspace_misses++;
return NULL;
}
三、增删改查图示
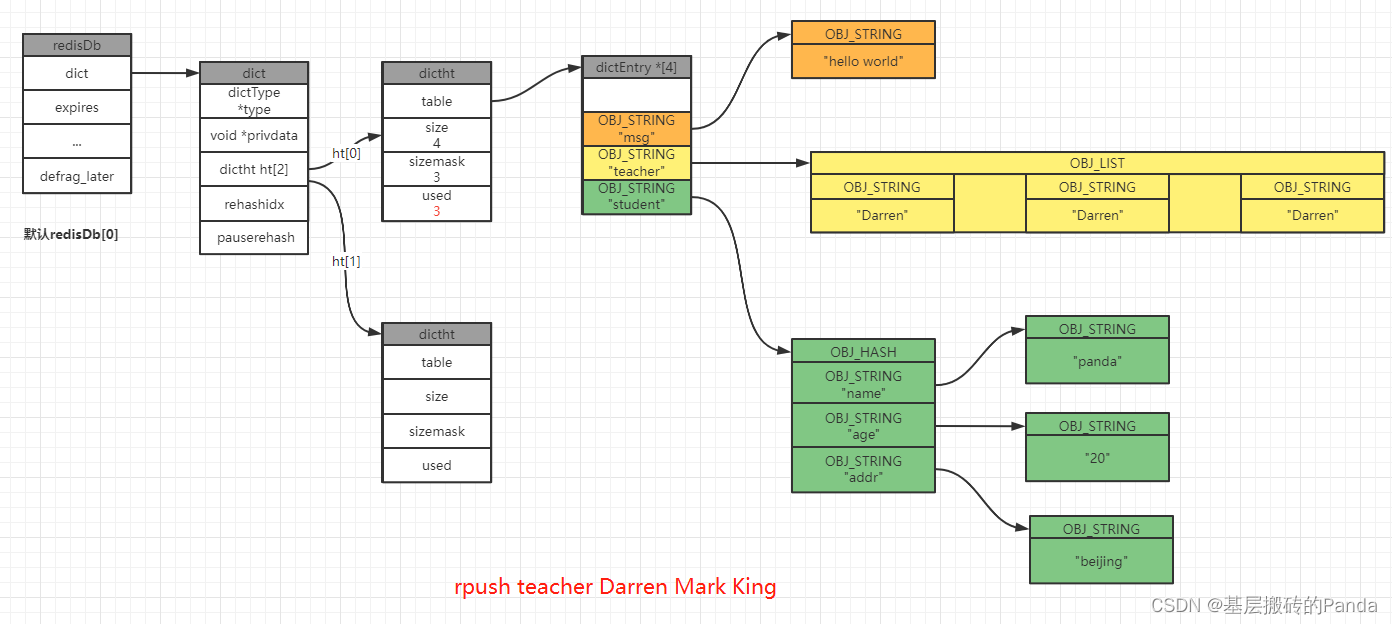
3.1 新增键值对
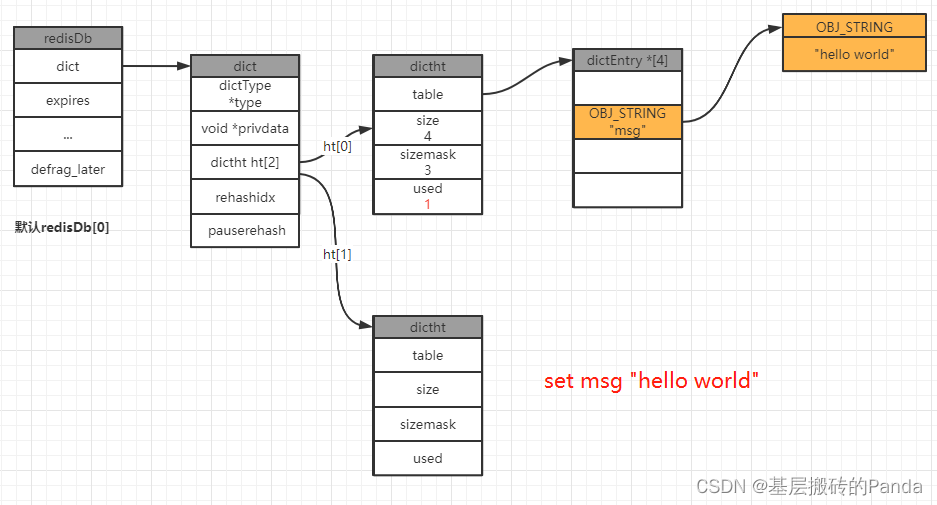
举例:我们在一个空的redis数据库中执行分别执行以下命令:
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
(empty array) // 表示此时数据库中没有任何数据
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> set msg "hello world"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
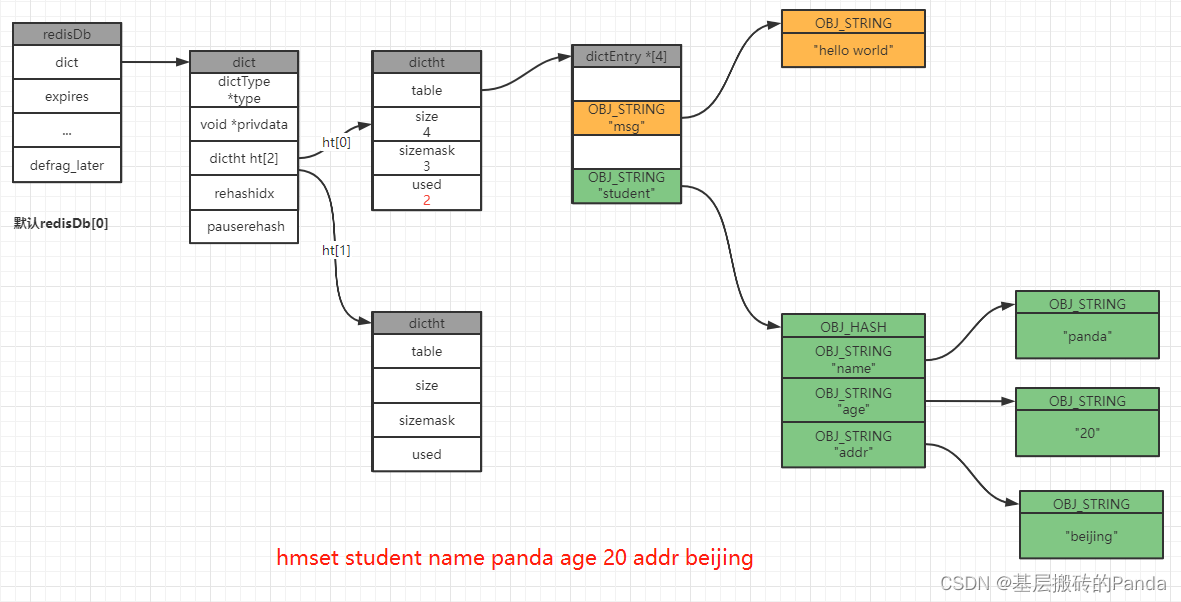
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> hmset student name panda age 20 addr beijing
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> rpush teacher Darren Mark King
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
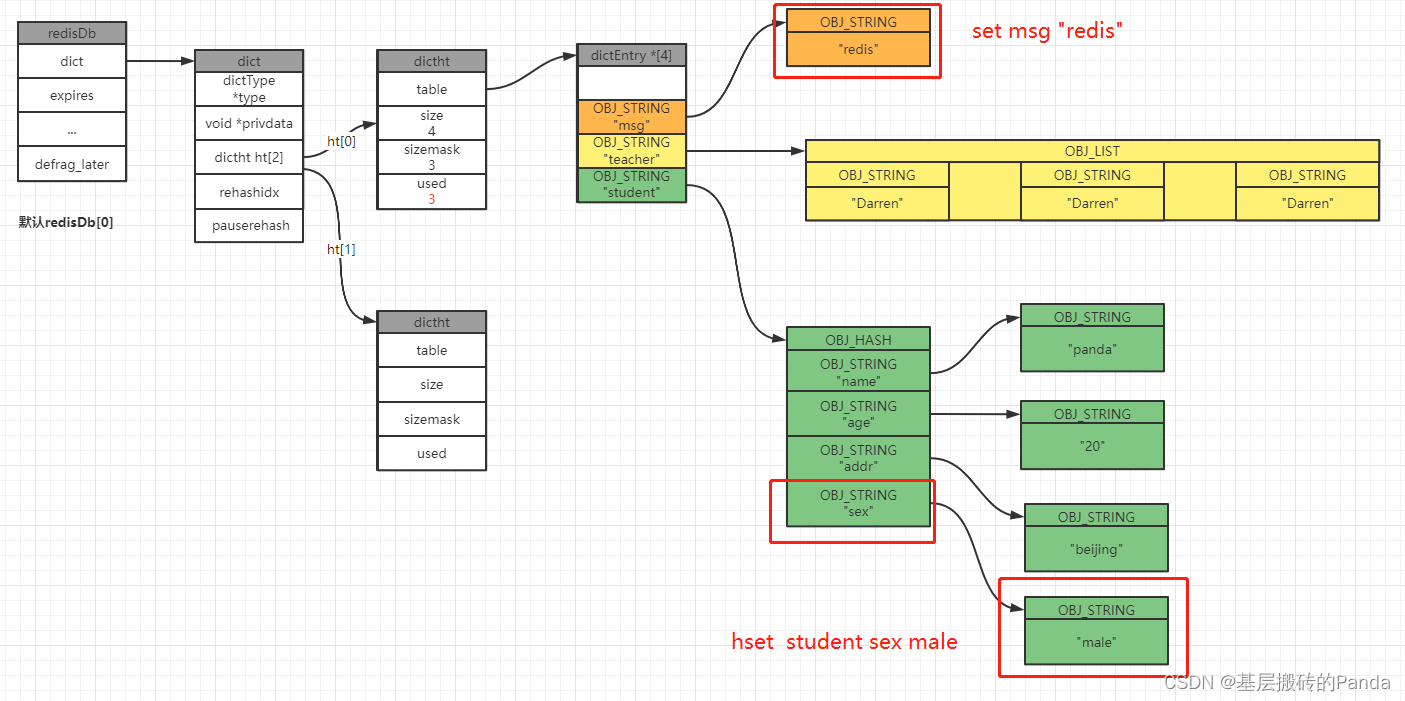
3.2 更新键值对
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> set msg "redis"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> get msg
"redis"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> hset student sex male
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
3.3 获取键的值
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> get msg
"redis"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> hmget student name age addr sex
1) "panda"
2) "20"
3) "beijing"
4) "male"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
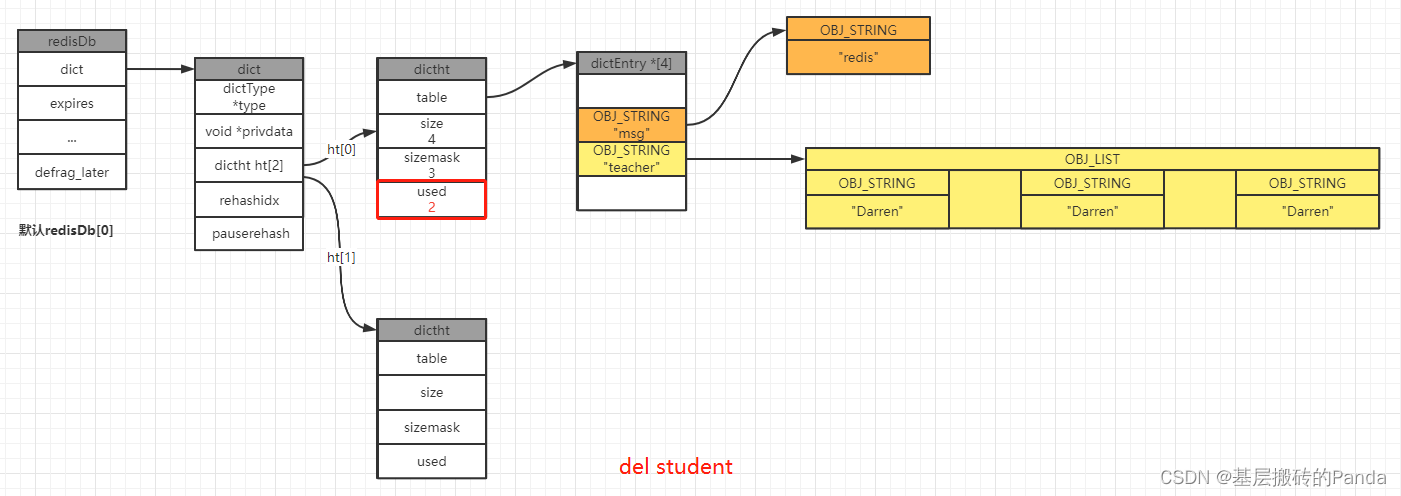
3.4 删除键值对
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "msg"
2) "student"
3) "teacher"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> del student
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "msg"
2) "teacher"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>




![[附源码]java毕业设计渔具店管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b364784041f1434fb6f5efc7f10019de.png)