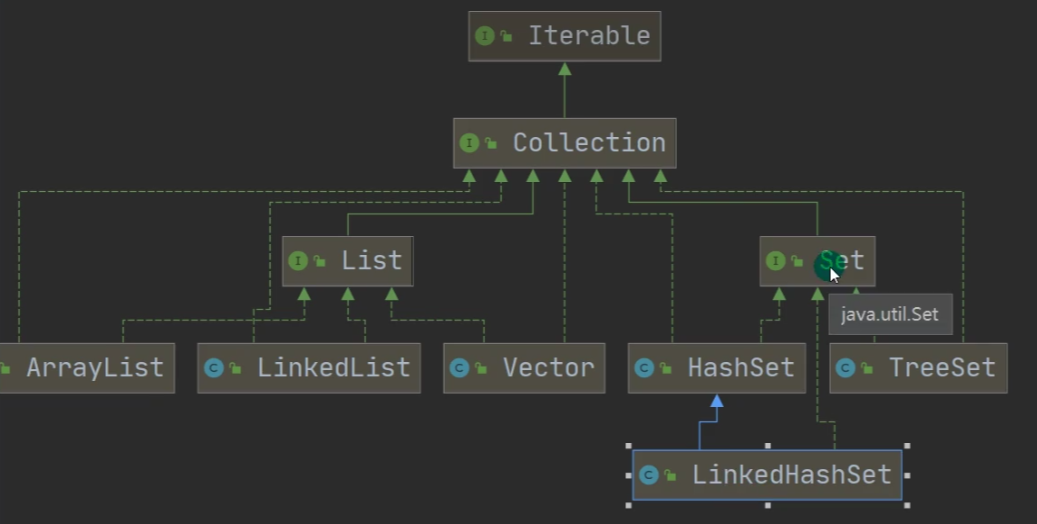
一、基本介绍:
1、Set接口的特点:
1)无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致) ,没有索引
2)不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个null
3) JDK API中Set接口的实现类有:

2、Set接口的常用方法:
和List接口一样,Set接口也是Collection的子接口,因此,常用方法和Collection接口一样.
3、Set接口的遍历方式:
同Collection的遍历方式一样,因为Set接口是Collection接口的子接口。
(1)可以使用迭代器
(2)增强for
(3)不能使用索引的方式来获取.
package Collection_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class SetMethod {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set=new HashSet();
set.add("john");
set.add("lucky");
set.add("john");
set.add("jack");
set.add(null);
set.add(null);
System.out.println("set="+set);
//set=[lucky, null, john, jack]
//取出的顺序是固定的,不会说同样的代码每次输出都不一样
set.add("smith");
System.out.println("set="+set);
//set=[lucky, null, smith, john, jack]
//遍历
//1、使用迭代器
System.out.println("=========使用迭代器=========");
Iterator iterator=set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj="+obj);
}
//2、增强for
System.out.println("=========增强for=========");
for (Object o :set) {
System.out.println("o="+o);
}
}
}
//=========使用迭代器=========
//obj=lucky
//obj=null
//obj=smith
//obj=john
//obj=jack
//=========增强for=========
//o=lucky
//o=null
//o=smith
//o=john
//o=jack
4、Set接口常用的实现类:有HashSet、TreeSet.
二、HashSet:
1、基本介绍:
(1) HashSet实现了Set接口
(2)HashSet底层实际上是HashMap, 看下源码.
public HashSet(){
map = new HashMap<>();
}(3) 可以存放null值,但是只能有一个null.
(4)HashSet不保证元素是有序的,取决于hash后,再确定索引的结果.即,不保证存放元素的顺序和取出顺序一致
(5) 不能有重复元素/对象.
package Collection_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(null);
hashSet.add(null);
System.out.println("hashset="+hashSet);
//hashset=[null]
}
}
package Collection_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set=new HashSet();
set.add("john");
set.add("tom");
set =new HashSet();
System.out.println("set="+set);//set=[]
set.add("lucy");//ok
set.add("lucy");//no
set.add(new Dog("tom"));//ok
set.add(new Dog("tom"));//ok 不同对象
System.out.println("set="+set);
//set=[Dog{name='tom'}, Dog{name='tom'}, lucy]
//经典面试题
set.add(new String("hsp"));//ok
set.add(new String("hsp"));//加入不了 看源码
System.out.println("set="+set);
//set=[Dog{name='tom'}, hsp, Dog{name='tom'}, lucy]
}
}
class Dog{
private String name;
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2、HashSet底层机制说明:(主要研究源码)
HashSet底层是HashMap,HashMap底层是(数组+链表+红黑树)
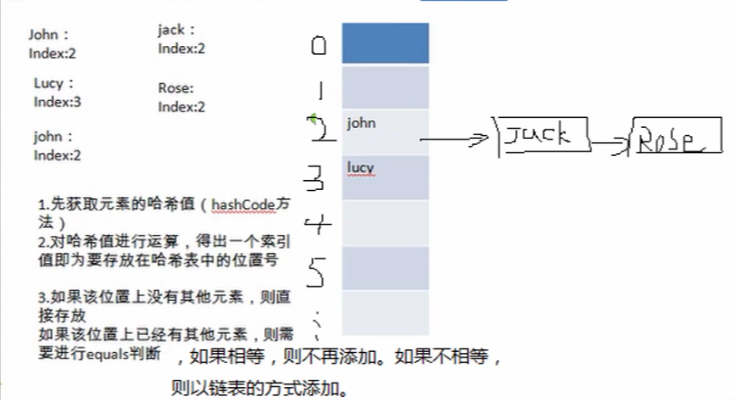
package Collection_;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetStructure {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、创建一个Node类型的数组
Node[] table=new Node[16];
System.out.println("table="+table);
//2、创建结点
Node john=new Node("jonh",null);
table[2]=john;
Node jack=new Node("jack",null);
john.next=jack;//将jack结点挂载到john
Node rose=new Node("Rose",null);
jack.next=rose;//将rose结点挂载到jack
System.out.println("table="+table);
}
}
class Node{//结点,存储数据,可以指向下一个结点,从而形成链表
Object item;//存放数据
Node next;//指向下一个结点
public Node(Object item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"item=" + item +
", next=" + next +
'}';
}
}
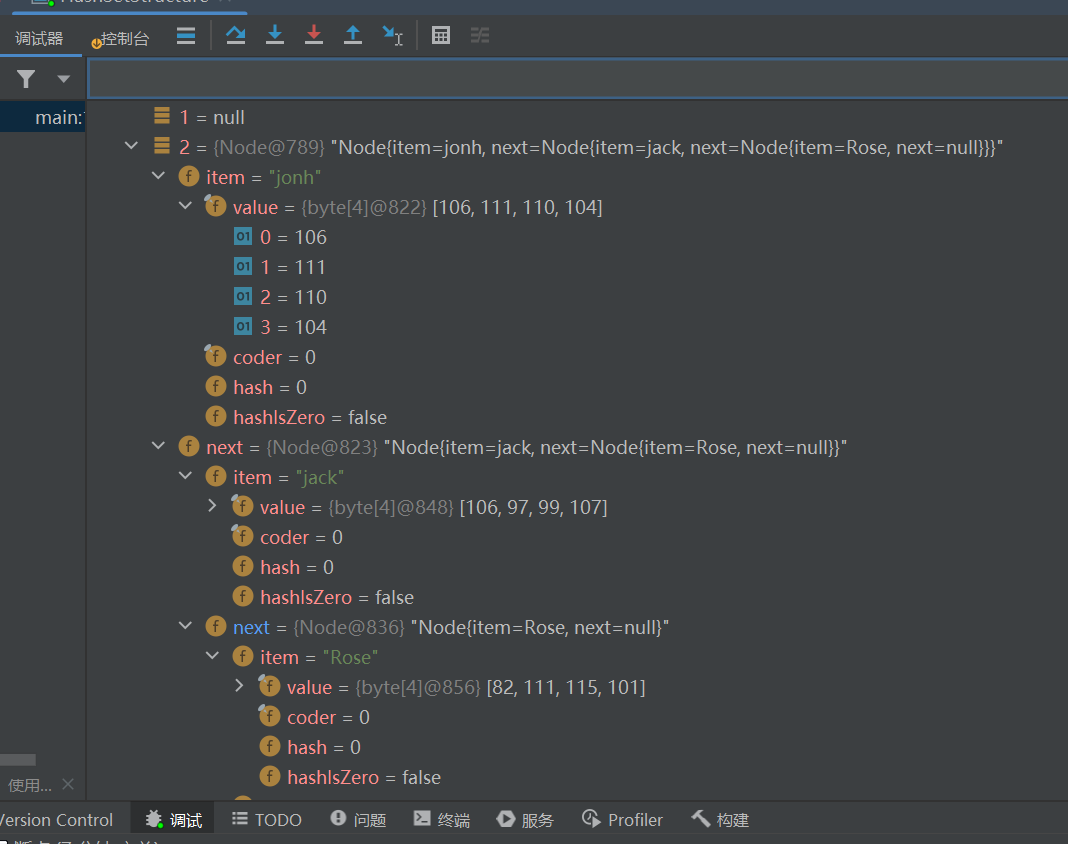


注意:equals的判断标准并不能简单地认为是两个字符串比较,因为String已经重写了equals方法,所以equals的判断标准和String没有关系,要视具体情况而定
//源码部分,非战斗人员,请做好撤退准备
package Collection_;
import javax.swing.tree.TreeNode;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetSource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet=new HashSet();
hashSet.add("java");
hashSet.add("php");
hashSet.add("java");
System.out.println("set="+hashSet);
/*
追源码:
//1、执行HashSet()
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
//2、执行add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
//PRESENT的源码: private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();主要起到占位的作用
}
//3、执行put方法,该方法会执行hash(key),得到key对应的hash值,
//(hash(key)与hashcode不一样,hash(key)里面还包含了算法)相关算法: (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)
public V put(K key, V value) {//是PRESENT的值
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
//4、执行 putVal(核心代码)
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;//定义了辅助变量
//table是HashMap的一个数组,类型是Node[]
//if语句表示如果当前table是null,或者大小=0
//就是第一次扩容到16个空间
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//(1)根据key,得到hash去计算该key应该存放到table表的哪个索引位置
//并把这个位置的对象,赋给p
//(2)判断p是否为null
//(2.1)如果p为null,表示还没有存放元素,就创建一个Node(key="java",value=PRESENT)
//(2.2)否则,就放在该位置tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//一个开发技巧提示:在需要局部变量(辅助变量)时,再创建
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果当前索引位置对应的链表的第一个元素和准备添加的key的hash值一样
//并且满足下面两个条件之一:
//(1)准备加入的key和p指向的Node的结点的key是同一个对象
//(2)p指向的Node结点的key的equals()和准备加入的key比较后相同
//就不能加入
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//再判断p是不是一棵红黑树
//如果是一棵红黑树,就调用putTreeVal来进行添加
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//如果table对应索引位置,已经是一个链表,就使用for循环比较
//(1)依次和该链表的每一元素比较后,都不相同,就加入到该链表的最后
// 注意在把元素添加到链表后,立即判断该链表是否已经达到8个结点
// 就调用treeifyBin()对当前这个链表进行树化(转成红黑树)
// 注意,在转成红黑树时,要进行判断,判断条件
// if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
// resize();
// 如果上面条件成立,先table扩容
// 只有上面条件不成立时,才进行转成红黑树
//(2)依次和该链表的每一个元素比较过程中,如果有相同情况,就直接break
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
//size就是我们每加入一个结点Node(k,v,h,next),size++
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
*/
}
}
3、练习题:
(1)
//我的代码:
package Collection_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
Employee[] employees = new Employee[4];
employees[0]=new Employee("jack", 18);
employees[1]=new Employee("tom", 19);
employees[2]=new Employee("rose", 20);
employees[3]=new Employee("rose", 20);
hashSet.add(employees[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < employees.length; i++) {
int tmp=0;
Iterator iterator=hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
if (employees[i].getAge() == hashSet.hashCode()|| employees[i].getName().equals(hashSet.hashCode())) {
break;
}
}
hashSet.add(employees[i]);
}
for (Object o :hashSet) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
//老师的代码:
package Collection_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("milan",18));
hashSet.add(new Employee("jack",28));
hashSet.add(new Employee("milan",18));
System.out.println("hashSet="+hashSet);
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
//重写equals()方法和hashCode()方法:
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
//hashSet=[Employee{name='milan', age=18}, Employee{name='jack', age=28}]
·重写equals()方法和hashCode()方法:
alt+insert----> ---->下一步---->
---->下一步---->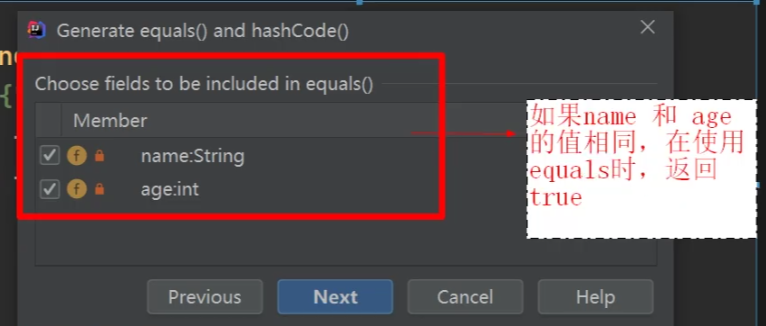 ---->下一步---->
---->下一步---->
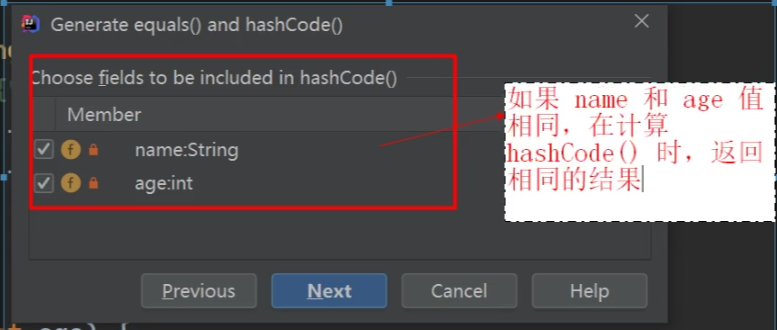
(2)
//我的代码
package Collection_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet=new HashSet();
MyDate jack=new MyDate(2000,1,1);
MyDate tom=new MyDate(2001,2,2);
hashSet.add(new Employee("jack",20000,jack));
hashSet.add(new Employee("tom",30000,tom));
hashSet.add(new Employee("jack",20000,jack));
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private double sal;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee(String name, double sal, MyDate birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return Objects.equals(name, employee.name) && Objects.equals(birthday, employee.birthday);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, birthday);
}
}
class MyDate{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDate{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
'}';
}
}
//[Employee{name='jack', sal=20000.0, birthday=MyDate{year=2000, month=1, day=1}}, Employee{name='tom', sal=30000.0, birthday=MyDate{year=2001, month=2, day=2}}]
三、LinkedHashSet

1、基本介绍:
(1)LinkedHashSet 是 HashSet的子类
(2)LinkedHashSet 底层是一个 LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个数组+双向链表
(3)LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使 用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的。
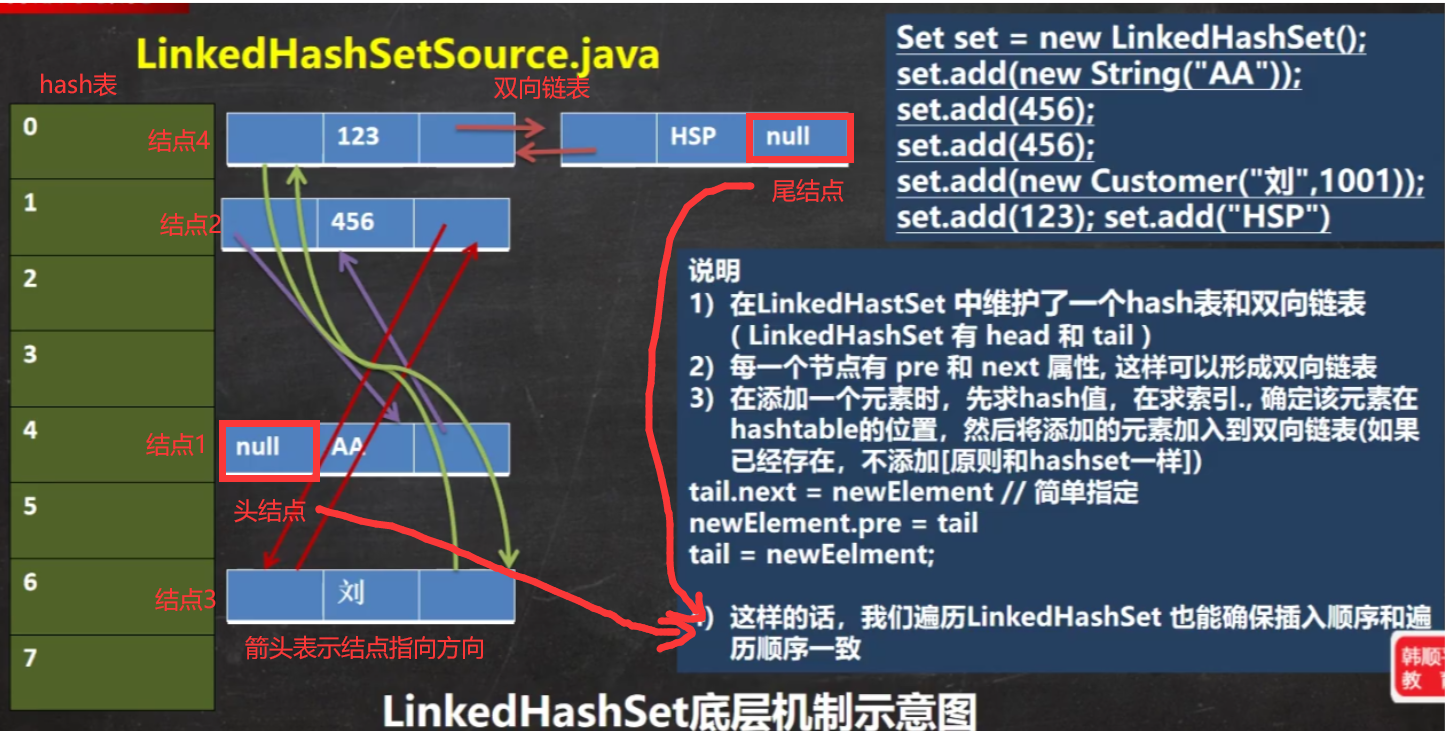
(4)LinkedHashSet 不允许添重复元素
2、LinkedHashSet底层机制:
package Collection_;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class LinkedHashSetSource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
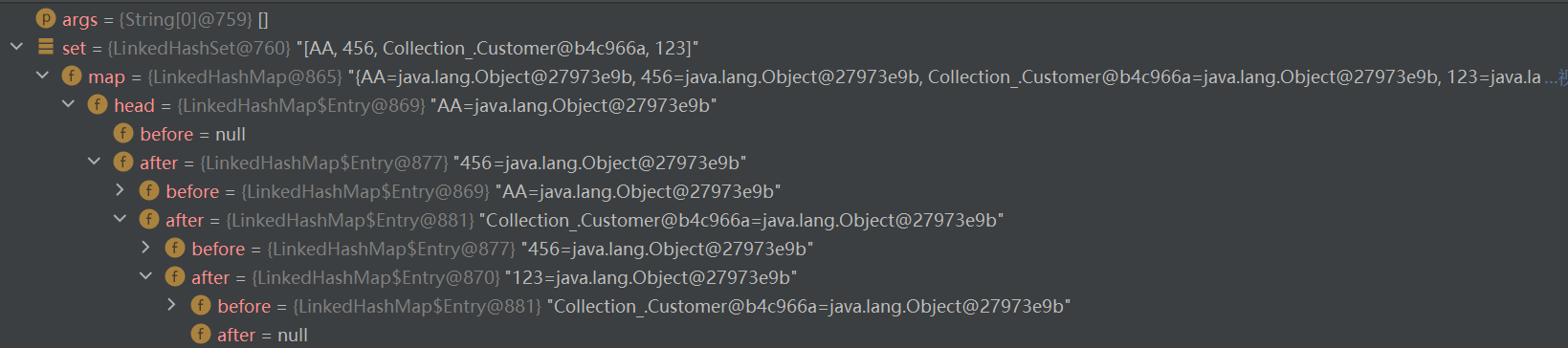
Set set=new LinkedHashSet();
set.add(new String("AA"));
set.add(456);
set.add(456);
set.add(new Customer("刘",1001));
set.add(123);
set.add("HSP");
}
}
class Customer{
private String name;
private int no;
public Customer(String name, int no) {
this.name = name;
this.no = no;
}
}
3、练习题:
//我的代码:
package Collection_;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class LinkedHashSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set linkedHashSet=new LinkedHashSet();
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥拓",1000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪",300000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("法拉利",10000000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("保时捷",70000000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪",300000));
System.out.println("linkedHashSet="+linkedHashSet);
}
public static class Car {
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Car car = (Car) o;
return Double.compare(car.price, price) == 0 && Objects.equals(name, car.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, price);
}
}
}
//linkedHashSet=[Car{name='奥拓', price=1000.0}, Car{name='奥迪', price=300000.0}, Car{name='法拉利', price=1.0E7}, Car{name='保时捷', price=7.0E7}]






![python学习——numpy库的使用[超详细的学习笔记]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f85bdaf3c1074ce1bfd672c3e42ecc44.jpeg)