39. 组合总和
看完题后的思路
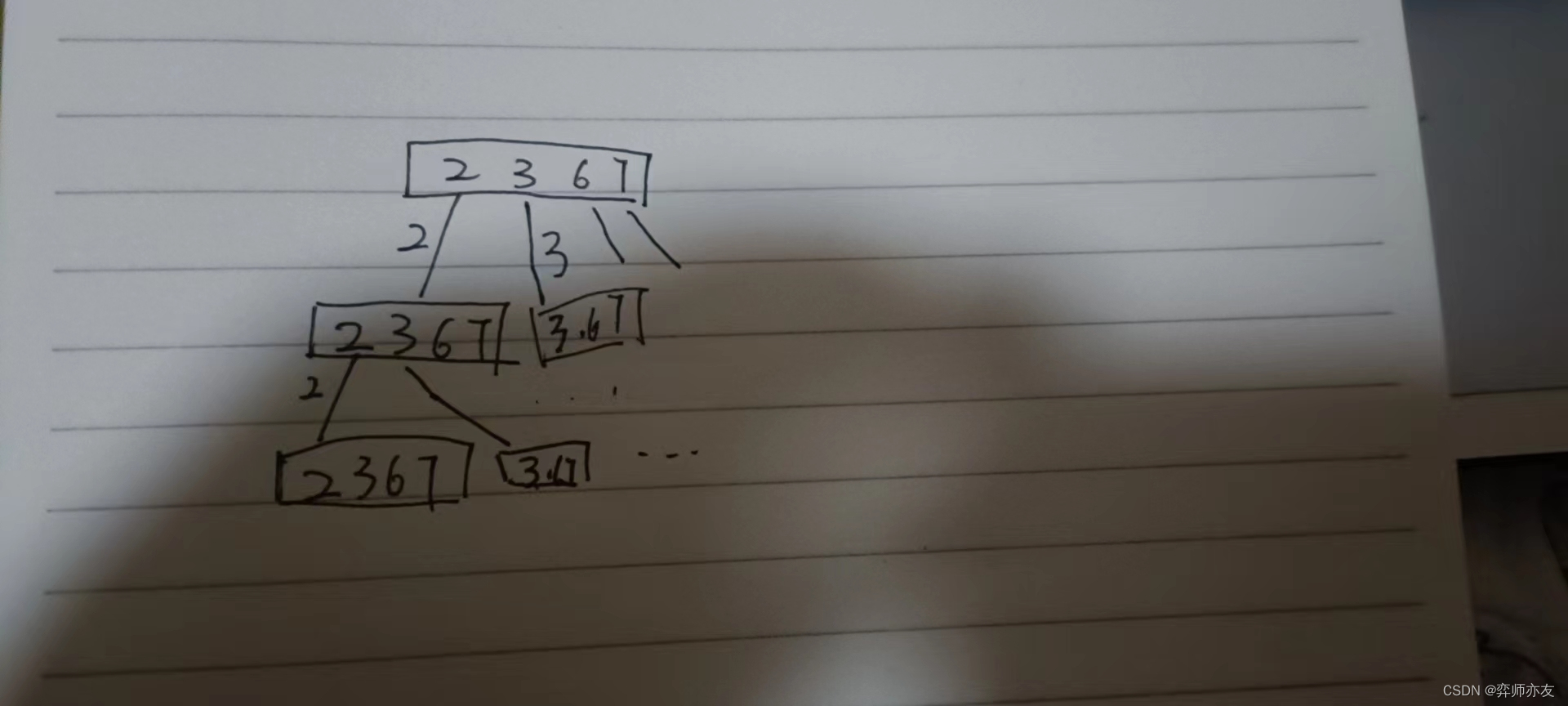
- 本题本质上还是一个传统排列题,不同之处在于每个元素可以重复选取。
- void f(【】,startIndex,sum)
- 递归终止
if(和==target){
加入;
返回;
} - 递归
for(){
剪枝;
加入;
f(xxx,startIndex);// 不变
回溯;
// 本层下一个
}
4. 剪枝
使用continue;
代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ires = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> ipath = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
combinationSumBT(candidates,target,0,0);
return ires;
}
public void combinationSumBT(int[] candidates, int target,int sum,int startIndex) {
// 出口
if (sum==target){
ires.add(new ArrayList<>(ipath));
return;
}
// 引擎
for (; startIndex < candidates.length; startIndex++) {
// 剪枝
if (candidates[startIndex]+sum>target){
continue;
}
ipath.add(candidates[startIndex]);
combinationSumBT(candidates,target,sum+candidates[startIndex],startIndex);
ipath.remove(ipath.size()-1);
// 下一次
}
}
}
复杂度
最坏 0(元素个数^target),最深target层
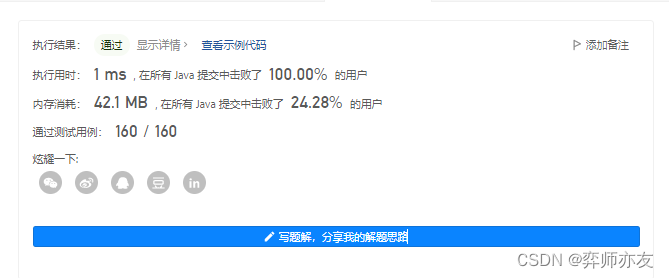
收获
1. 三刷大脑过一遍
2. 本题是组合取重复元素
40.组合总和II
看完题后的思路

- 本题是组合问题,元素有重复,结果中元素可以重复,但是要对重复的结果去重
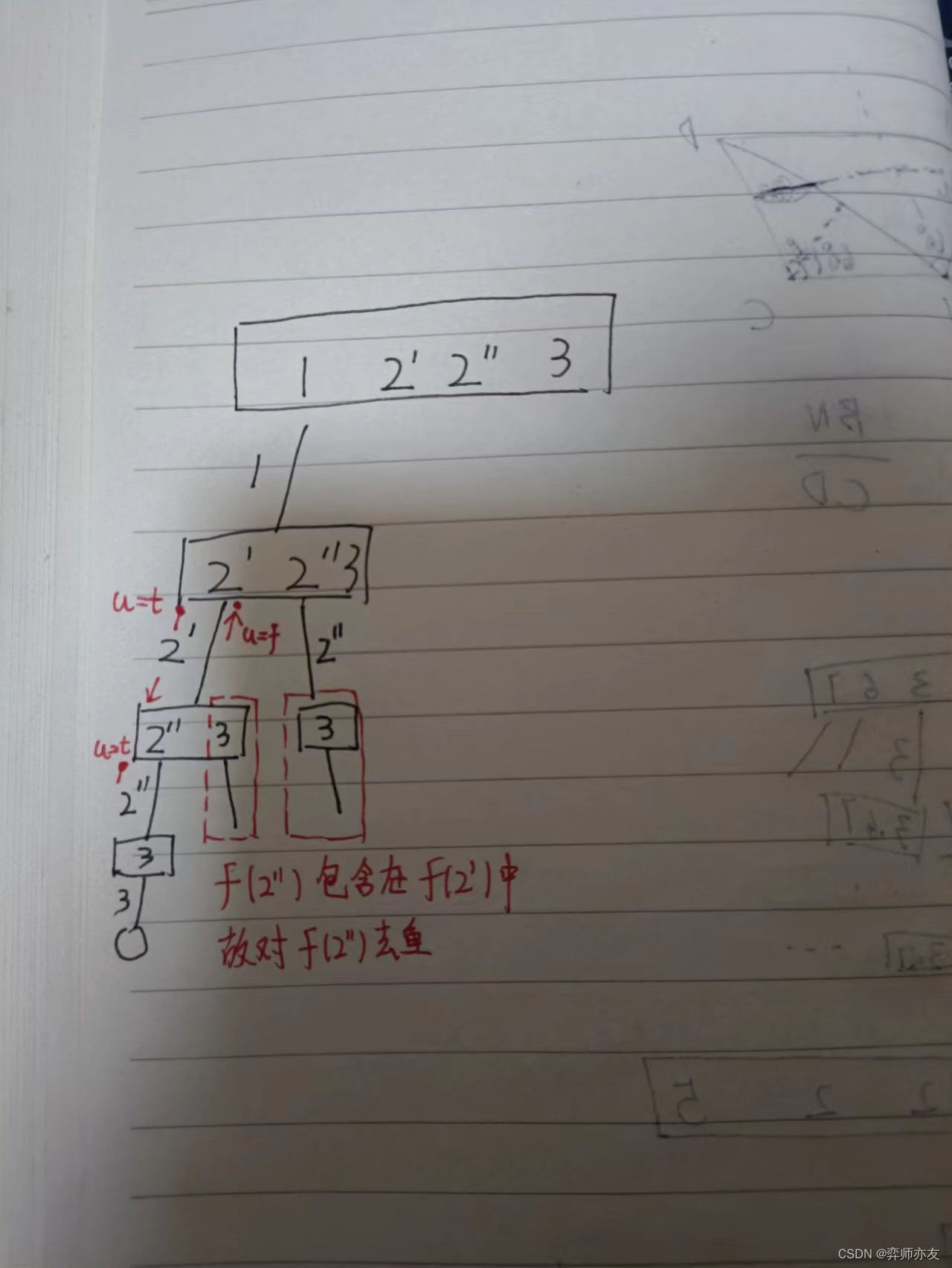
需改处: 同一层中,本元素如果与上一个元素相等,直接剪枝。
难点: 如何判断是本层 还是下一层
层去重的逻辑:
using: 表示尚在使用
初始using=false,当使用到我(加入数组),using=ture,执行完成,回溯时,using=false;
如果我前面的节点与我相同:
(1)using[前面的节点]=false;表示我前面的节点已经使用完回溯了,或者压根没用上
对于已经回溯完:我的结果肯定包含在前面结果中,所以我跳过
对于没用上,它被剪枝了,我俩一样,也肯定被剪枝
(2)using[前面的节点]=ture; 它一定在我前面,且正在使用,我一定是它的子节点。
代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ires = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> ipath = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
boolean[] using = new boolean[candidates.length];
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSum2BT(candidates,target,0,0,using);
return ires;
}
public void combinationSum2BT(int[] candidates, int target,int sum,int startIndex,boolean[] using) {// using[] 是否正在使用
// 出口
if (sum==target){
ires.add(new ArrayList<>(ipath));
return;
}
// 引擎
for (; startIndex < candidates.length; startIndex++) {
// 剪枝
if (candidates[startIndex]+sum>target){
return; // 因为是拍好序的
}
if (startIndex!=0&&candidates[startIndex-1]==candidates[startIndex]&&!using[startIndex-1]){
continue;
}
using[startIndex]=true;
ipath.add(candidates[startIndex]);
combinationSum2BT(candidates,target,sum+candidates[startIndex],startIndex+1,using);
// 回溯
using[startIndex]=false;
ipath.remove(ipath.size()-1);
// 下一次
}
}
}
复杂度
收获
1. 三刷看一遍
2. 横向去重
131.分割回文串

- 这是一个标准切割问题
- v f(【】,startIndex)
- 出口 if(startIndex==数组长度){加入,return}
- 回溯
与标准模板不同 ipath.add([].子串(startIndex,i)) - 剪枝
不是回文串 continus
直接看代码
代码
class Solution {
List<List<String>> sres = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> spath = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
partitionBT(s,0);
return sres;
}
public void partitionBT(String s,int startIndex) {
if (startIndex==s.length()){
sres.add(new ArrayList<>(spath));
return;
}
// 引擎
for (int i = startIndex; i <s.length() ; i++) {
// 剪枝
if (!isPalindrome(s,startIndex,i)){
continue;
}
spath.add(s.substring(startIndex,i+1));
partitionBT(s,i+1);
spath.remove(spath.size()-1);
// 本层下一个
}
}
//判断是否是回文串
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int startIndex, int end) {
for (int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
复杂度
收获
- 标准分割问题
- 三刷敲一遍