文章目录
- 题目描述
- 题目链接
- 题目难度——中等
- 方法一:迭代
- 代码/C++
- 代码/python
- 方法二:递归
- 代码/C++
- 总结
题目描述
或许这也是个经典的面试题,记录一手
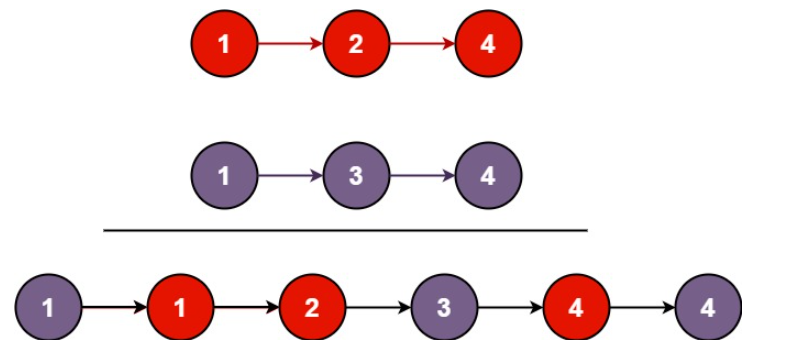
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
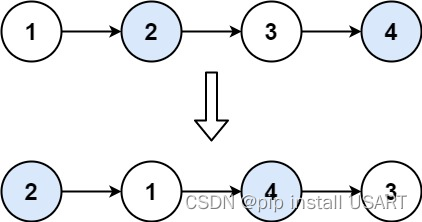
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
题目链接
题目难度——中等
方法一:迭代
我们可以借助三个指针来一次迭代的做它,每次调转两个相邻节点,都需要更新上一个结点的尾指针,所以我们需要一个dummyHead结点作为新头部,最后返回dummyHead->next即可。
代码/C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *cur, *nextOne, *pre, *dummyH;
dummyH = new ListNode(-1, head);
pre = dummyH;
cur = head;
while(cur){
nextOne = cur->next;
if(!nextOne){
break;
}
pre->next = nextOne;
cur->next = nextOne->next;
nextOne->next = cur;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummyH->next;
}
};
代码/python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummyH = ListNode(-1, head)
pre, cur = dummyH, head
while cur:
nextOne = cur.next
if not nextOne:
break
cur.next = nextOne.next
pre.next = nextOne
nextOne.next = cur
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return dummyH.next
方法二:递归
还可以用递归的方法来做,当输入结点为空指针或者只有一个结点时,说明到了尾部,递推结束,可以回归了。
代码/C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next){
return head;
}
ListNode *right = head->next;
head->next = swapPairs(right->next);
right->next = head;
return right;
}
};
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
right = head.next
head.next = self.swapPairs(right.next)
right.next = head
return right
总结
方法一迭代的时间复杂度是O(N) ,空间复杂度O(1) ,方法二递归时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(N) 。
![[设计模式] 建造者模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5524851ea0704964b5a2c8137d0fccf5.png)