一、Collection体系结构
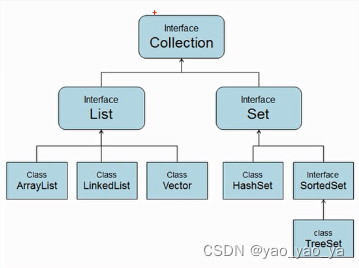
Collection体系结构的根接口,代表一组对象,称为“集合”。
List接口的特点:有序、有下标、元素可重复。
Set 接口的特点:无序、无下标、元素不能重复。
二、Collection父接口
特点:代表一组任意类型的对象,无序、无下标、不能重复。
方法:
1. 添加一个对象
boolean add(Object obj)2. 将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中。
boolean addAll(Collection c)3. 清空此集合中的所有元素
void clear()4. 检查此集合中是否包含 o 对象
boolean contains(Object o)5. 比较此集合是否与指定对象相等
boolean equals(Object o)6. 此集合是否为空
boolean isEmpty()7. 在此集合中移除 o 对象
boolean remove (Object o)8. 返回此集合中的元素个数
int size()9. 将此集合转换成数组
Object[] toArray()三、Collection接口的使用
详看代码注释:
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
1. 接口的使用(1):添加元素 删除元素 遍历元素 判断
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* Collection接口的使用:
* (1)添加元素
* (2)删除元素
* (3)遍历元素
* (4)判断
*/
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合 不能实例化,但可以创建对象
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//1.添加元素
collection.add("西瓜");
collection.add("苹果");
collection.add("香蕉");
collection.add("榴莲");
collection.add("葡萄");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());//size()指元素长度
System.out.println(collection);
System.out.println("------------------");
//2.删除
collection.remove("苹果");
System.out.println("删除之后:"+collection.size());
System.out.println("------------------");
//3.遍历元素
//(1)使用增强for
for (Object object:collection) {
System.out.println(object);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
//(2)使用迭代器 Interator
//先用hasNext()判断有没有下一个元素
//next()取出下一个元素,在继续往后移一位
//remove()删除元素
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String str = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(str);
//在使用叠加器遍历过程中不允许使用其他并发修改集合的方法
//collection.remove(str); 不能collection删除方法
it.remove(); // 可以,属于叠加器的清除
}
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println("------------------");
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜"));//判断该元素是否存在
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty()); //判断是否为空 空(true) 不为空(false)
System.out.println("------------------");
//5.清空
collection.clear();
System.out.println("清空之后:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection);
}
}
简单粗暴!
感谢ლ(°◕‵ƹ′◕ლ)!!!
![[短的文章] Spring Boot 日志创建使用、日志级别、@Slf4j、日志持久化——Spring Boot 系列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/13588e5daa7a7d802f61e1a700aaad3d.png)






![[附源码]java毕业设计疫情防控期间网上教学管理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d902728649074f0db00dee6d44fdda84.png)