1.友元 的三种形式
/*********** 友元 ************
* ①全局函数做友元
* ②类做友元
* ③类成员函数做友元
* **************************/
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/* ③类函数友元 : 程序规则{ 自上而下,从左往右 }*/
class House; /*提前空声明*/
class Auntie
{
public:
/*** 注意:是类内声明,类外实现(在被友元类后类外实现) ***/
void cleaning(House value); /* 保洁|清洁 函数 ---> 想让该函数做友元*/
void burning(House value); /* 烧房子函数 ---> 不想让该函数做友元*/
};
/*********** 友元 ************
* ①全局函数做友元
* ②类做友元
* ③类成员函数做友元
* **************************/
class House
{
/***** 全局友元函数:友元声明 ******/
friend void detection(House value);
/***** 类:友元声明 *****/
friend class Girls;
/***** 类函数:友元声明 ****/
friend void Auntie::cleaning(House value);
//friend void Auntie::burning(House value); 不想让该函数为友元
public:
int m_corridor = 1; /*走廊*/
protected:
int m_parlor = 2; /*客厅*/
private:
int m_bedroom = 3; /*卧室*/
};
/* ①全局友元函数 */
void detection(House value)
{
cout << "\n————————————————————————————————————————" << endl;
cout << "检测走廊:" << value.m_corridor << endl;
cout << "检测客厅:" << value.m_parlor << endl;
cout << "检测卧室:" << value.m_bedroom << endl;
}
/* ②类友元 */
class Girls /*闺蜜类*/
{
public:
static void visit(House value)
{
cout << "\n————————————————————————————————————————" << endl;
cout << "参观走廊:" << value.m_corridor << endl;
cout << "参观客厅:" << value.m_parlor << endl;
cout << "参观卧室:" << value.m_bedroom << endl;
}
int GetBedroom()const
{
return this->house.m_bedroom; /* 参观卧室 */
}
House house; /* 当成成员 */
};
/* ③类函数友元 : 程序规则{ 自上而下,从左往右 } ,需要在被友元类之后类外实现*/
void Auntie::cleaning(House value) /* 类友元函数 */
{
cout << "\n————————————————————————————————————————" << endl;
cout << "清洁走廊:" << value.m_corridor << endl;
cout << "清洁客厅:" << value.m_parlor << endl;
cout << "清洁卧室:" << value.m_bedroom << endl;
}
void Auntie::burning(House value) /* 非类友元函数 */
{
cout << "\n————————————————————————————————————————" << endl;
// cout << "烧走廊:" << value.m_corridor << endl;
// cout << "烧客厅:" << value.m_parlor << endl;
// cout << "烧卧室:" << value.m_bedroom << endl;
}
int main()
{
/* 1.实例化对象 */
House house;
/* 2.调用友元 */
/* 2.1 调用全局友元函数 */
detection(house);
/* 2.2 调用友元类 */
Girls girls;
girls.visit(house);
cout << "参观卧室:" << girls.GetBedroom() << endl;
/* 2.3 调用类友元函数 */
Auntie auntie;
auntie.cleaning(house); /* 调用类友元函数 : 清洁 */
auntie.burning(house); /* 调用非类友元函数:烧房子*/
return 0;
}
2.运算符号重载 (简单)
/******** 运算符重载 **********************************************
* 支持: 类外 和 类内
* 注意: 调用直接使用运算符时不能同时存在类内和类外定义,只能存其一
* 如果按照本质调用则可以同时存在
*
* —————————————————————— 本质调用
* 类外:实现的时候,必须(满参数),直接调用函数名
* 类内:类内实现,第一个参数不用填,使用this代替,直接调用函数名
* —————————————————————— 套路规则
* 一般情况提供类内运算符重载,且{类内声明,类内实现},不提倡{类内声明类外实现}
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/******** 运算符重载 **********************************************
* 支持: 类外 和 类内
* 注意: 调用直接使用运算符时不能同时存在类内和类外定义,只能存其一
* 如果按照本质调用则可以同时存在
*
* —————————————————————— 本质调用 ——————————————————————
* 类外:实现的时候,必须(满参数),直接调用函数名
* 类内:类内实现,第一个参数不用填,使用this代替,直接调用函数名
* —————————————————————— 套路规则 ——————————————————————
* 一般情况提供类内运算符重载,且{类内声明,类内实现},不提倡{类内声明类外实现}
* **************************************************************/
class People
{
public:
People(string name = "",int age = 0):m_name(name),m_age(age){} /* 构造函数 */
public:
string m_name; /*姓名*/
int m_age; /*年龄*/
private:
string m_sex; /*性别*/
public:
People operator +(People value2) /*类内声明,类内实现*/
{
People temp;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_age = this->m_age + value2.m_age;
return temp;
}
};
#if 0/**** 类外运算符重载 *** 假如这里要使用需要在类里面 加友元函数 */
People operator +(People value1,People value2) /*调用类外本质:如果按照本质调用则可以同时存在*/
{
People temp;
temp.m_name = value1.m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_age = value1.m_age + value2.m_age;
temp.m_sex = value1.m_sex + value2.m_sex;
return temp;
}
#endif
int main()
{
People people1("张三",18);
People people2("李四",18);
People people3;
/***** 1.直接调用运算符(由C++编译器给你选择) *****/
//people3 = people1 + people2; /* 调用直接使用运算符时不能同时存在类内和类外定义,只能存其一 */
/***** 2.调用类外函数名 *****/
people3 = operator +(people1,people2); /*调用类外本质:如果按照本质调用则可以同时存在*/
/***** 3.调用类内函数名 ******/
//people3 = people1.operator +(people2); /* 张三 + 李四 */
//people3 = people2.operator +(people1); /* 李四 + 张三 */
cout << "姓名:" << people3.m_name << "\t年龄:" << people3.m_age << endl;
return 0;
}
3.运算符重载 (复杂)
重载的函数有 :
/* 四则运算重载 */ (参数的 const 是防止在函数里面改变 数据的值 后面的const 是把函数定义为常量函数,(常量对象只能调用常量函数,别的成员函数都不能调用。 ) ,参数的 & 是一个小的技巧,因为 指针是 4 个字节, 而 类的字节可能 很大!!)
People operator +(const People &value2) const
People operator -(const People &value2) const
People operator *(const People &value2) const
People operator /(const People &value2) const
People operator %(const People &value2) const
/* 四则运算重载,非同类型高阶重载 */ (这里参数不使用指针的原因是 int 类型的字节也是 4个字节)
People operator +(int age) const
People operator +(string name) const
/* 赋值运算符 */
void operator =(const People &value2)
void operator +=(const People &value2)
void operator -=(const People &value2)
void operator /=(const People &value2)
void operator *=(const People &value2)
void operator %=(const People &value2)
/* 赋值运算符,非同类型高阶重载*/
void operator =(string name)
void operator =(int age) //使用 等于符号改变 age 的值
/* 关系运算符 */
bool operator ==(const People &value2)
bool operator !=(const People &value2)
/* 关系运算符,非同类型高阶重载*/
bool operator ==(string name)
/*单目运算符: ++,--(前置和后置的区分,后置需要一个int占位) */
(为什么前置 加了 引用 因为前置需要返回已经改变的 类参数, 后置是返回 没有改变的类参数
i=1;
++i = 2;
i++ =1;
)
People &operator ++() //前置 (前++ )
People &operator --() //前置
const People operator ++(int) //后置
const People operator --(int) //后置
/* 单目运算符: << , >> , & , | ^ */
People operator <<(int num)
People operator >>(int num)
People operator &(int num)
/* 单目运算符 高阶: << , >> , & , | ^ */ (这里有点难 )
/****** 由于遇到了 extern ostream cout 整个程序只有一个流,所以需要权限和引用 */
friend ostream &operator <<(ostream &out,const People &value) (这里的第二个参数可以不要 & , 但是加了 & 可以减少字节的运用!!)
friend istream &operator >>(istream &in,People &value) (这里第二个参数必须使用 & 因为这里是局部变量需要使用引用, 来改变值, 没有引用的话,我们的参数就不会改变 )
/* 其他运算符操作: () 仿函数,通常做算法策略 */
void operator ()(/*参数列表*/)
bool operator ()(int value) /* 一元谓词 */
bool operator ()(int value1,int value2) /* 二元谓词 */
/* 其他运算符操作: [ ] */
int &operator [](int index) //重载中括号
const int operator [](string com) //const 返回的零时变量不可以被改变,就像 ((i++)++)不可以一样。(不能无限套娃!!) 但是 (++(++i))可以无限套娃!!
/* 其他运算符操作 : -> 很明显是指针操作*/ //重载指针
Grade *operator ->()
People.h
#ifndef PEOPLE_H
#define PEOPLE_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class People
{
public:
People(string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0); /*构造函数*/
public:
string m_name;
string m_sex;
int m_age;
public:
void Print(); /*打印参数信息*/
public: /* 四则运算重载 */
People operator +(const People &value2) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age + value2.m_age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex + value2.m_sex;
return temp;
}
People operator -(const People &value2) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age - value2.m_age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex + value2.m_sex;
return temp;
}
People operator *(const People &value2) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age * value2.m_age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex + value2.m_sex;
return temp;
}
People operator /(const People &value2) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age / value2.m_age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex + value2.m_sex;
return temp;
}
People operator %(const People &value2) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age % value2.m_age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + value2.m_name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex + value2.m_sex;
return temp;
}
public: /* 四则运算重载,非同类型高阶重载 */
People operator +(int age) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age + age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex;
return temp;
}
People operator +(string name) const
{
People temp;
temp.m_age = this->m_age;
temp.m_name = this->m_name + name;
temp.m_sex = this->m_sex;
return temp;
}
public: /* 赋值运算符 */
void operator =(const People &value2)
{
this->m_age = value2.m_age;
this->m_sex = value2.m_sex;
this->m_name = value2.m_name + "牛逼的王";
}
void operator +=(const People &value2)
{
this->m_age += value2.m_age;
this->m_sex += value2.m_sex;
this->m_name += value2.m_name + "牛逼的王";
}
void operator -=(const People &value2)
{
this->m_age -= value2.m_age;
this->m_sex = value2.m_sex;
this->m_name = value2.m_name + "牛逼的王";
}
void operator /=(const People &value2)
{
this->m_age /= value2.m_age;
this->m_sex = value2.m_sex;
this->m_name = value2.m_name + "牛逼的王";
}
void operator *=(const People &value2)
{
this->m_age *= value2.m_age;
this->m_sex = value2.m_sex;
this->m_name = value2.m_name + "牛逼的王";
}
void operator %=(const People &value2)
{
this->m_age %= value2.m_age;
this->m_sex = value2.m_sex;
this->m_name = value2.m_name + "牛逼的王";
}
public: /* 赋值运算符,非同类型高阶重载*/
void operator =(string name)
{
this->m_name = name;
}
void operator =(int age)
{
this->m_age = age;
}
public: /* 关系运算符 */
bool operator ==(const People &value2)
{
if(this->m_name == value2.m_name&&this->m_age == value2.m_age&&this->m_sex == value2.m_sex)
{
return true; /*真*/
}
return false; /*假*/
}
bool operator !=(const People &value2)
{
if(this->m_age != value2.m_age)
{
return true; /*真*/
}
return false; /*假*/
}
public: /* 关系运算符,非同类型高阶重载*/
bool operator ==(string name)
{
if(this->m_name == name)
{
return true; /*真*/
}
return false; /*假*/
}
public: /* 单目运算符: ++,--(前置和后置的区分,后置需要一个int占位) */
People &operator ++()
{
this->m_age += 1;
return *this;
}
People &operator --()
{
this->m_age -= 1;
return *this;
}
const People operator ++(int)
{
/***********People temp(*this) 解释********
*People value1; //变量
*People *ptr = new People;//指针
*People value2(value1); //拷贝构造 - 变量
*People value2(*ptr); //拷贝构造 - 指针
* ________________________________________
*this 是指针 , *指针 === 变量
******************************************/
People temp(*this); /* 拷贝构造 */
this->m_age += 1;
return temp;
}
const People operator --(int)
{
People temp(*this);
this->m_age -= 1;
return temp;
}
public: /* 单目运算符: << , >> , & , | ^ */
People operator <<(int num)
{
People temp(*this);
temp.m_age = temp.m_age << num;
return temp;
}
People operator >>(int num)
{
People temp(*this);
temp.m_age = temp.m_age >> num;
return temp;
}
People operator &(int num)
{
People temp(*this);
temp.m_age = temp.m_age & num;
return temp;
}
public: /* 单目运算符 高阶: << , >> , & , | ^ */
/****** 由于遇到了 extern ostream cout 整个程序只有一个流,所以需要权限和引用 */
friend ostream &operator <<(ostream &out,const People &value)
{
out << value.m_name << "\t"
<< value.m_age << "\t"
<< value.m_sex;
return out;
}
/****** 由于遇到了 extern istream cin 整个程序只有一个流,所以需要权限和引用 */
friend istream &operator >>(istream &in,People &value)
{
cout << "请输入姓名 性别 年龄:";
in >> value.m_name >> value.m_sex >> value.m_age;
return in;
}
public: /* 其他运算符操作: () 仿函数,通常做算法策略 */
void operator ()(/*参数列表*/)
{
cout << "仿函数策略" << endl;
}
bool operator ()(int value) /* 一元谓词 */
{
if(value == 1) return true;
return false;
}
bool operator ()(int value1,int value2) /* 二元谓词 */
{
if(value1 == value2) return true;
return false;
}
public: /* 其他运算符操作: [] */
int addr[10] = {0};
int addr_len = -1; /*当前使用的长度*/
int addr_max = 10; /*最大长度*/
int &operator [](int index)
{
return this->addr[index];
}
const int operator [](string com)
{
if(com == "max") return addr_max;
if(com == "len") return addr_len;
return 0;
}
public: /* 其他运算符操作 : -> 很明显是指针操作*/
/**** 类内部类 ****/
class Grade
{
public:
int language; /*语文成绩*/
int math; /*数学成绩*/
};
/**** 定义变量 ***/
Grade grade = {
.language = 10,
.math = 20
};
/**** 运算符重载 ***/
Grade *operator ->()
{
return &(this->grade);
}
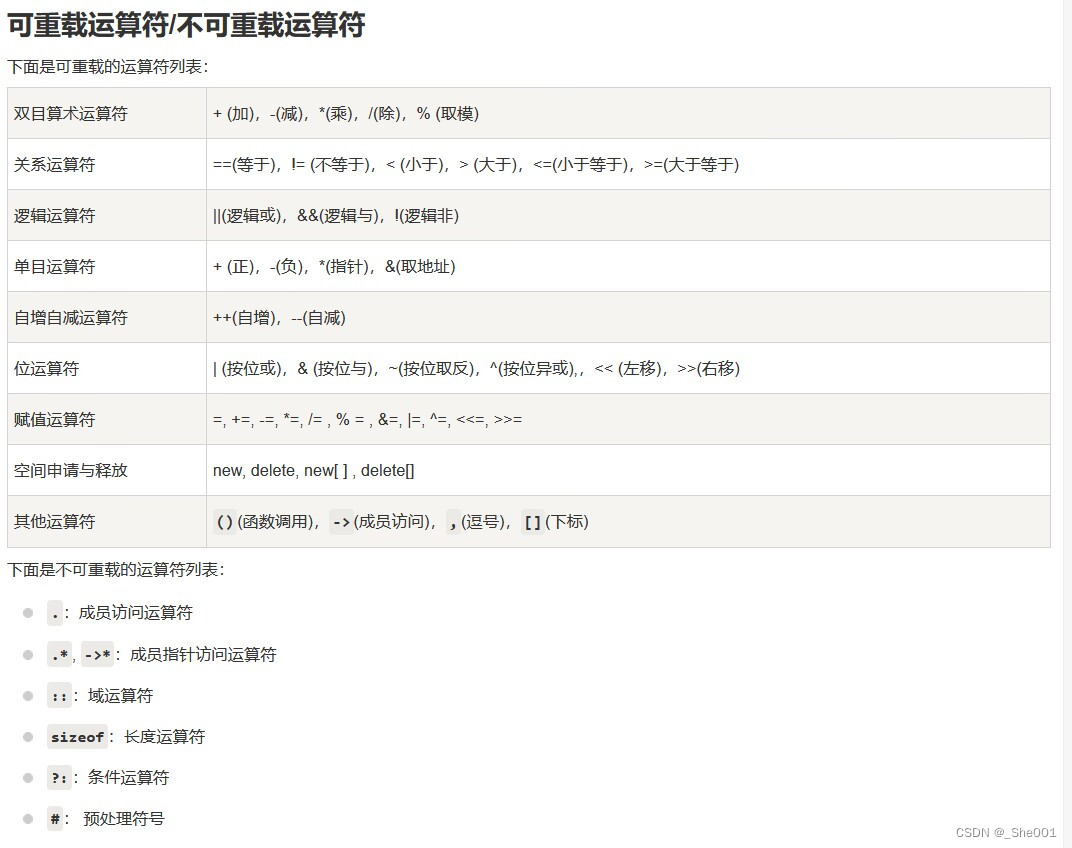
public: /* 不可重载运算符 */
/************************************
*下面是不可重载的运算符列表:
*
* .:成员访问运算符
* .*, ->*:成员指针访问运算符
* :::域运算符
* sizeof:长度运算符
* ?::条件运算符
* #: 预处理符号
**************************************/
};
#endif // PEOPLE_H
People.cpp
#include "people.h"
People::People(string name, string sex, int age)
:m_name(name),m_sex(sex),m_age(age)
{
}
void People::Print() /*打印参数信息*/
{
cout << "\t姓名:" << m_name
<< "\t性别:" << m_sex
<< "\t年龄:" << m_age
<< endl;
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "people.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*** 双目运算符之四则运算 ***/
People people1("张三","男",18);
People people2("李四","女",19);
/*** 调用四则运算 ***/
People people3;
people3 = people1 + people2;
people3 = people1 - people2;
people3 = people1 * people2;
people3 = people1 / people2;
people3 = people1 % people2;
/*** 调用四则高阶运算 ***/
people3 = people1 + 10;
people3 = people1 + string("老师"); /* 过度 */
/*** 调用赋值运算符 ****/
people3 = people1; /*本质:people3.operator =(people1); */
people3 += people1; /*本质:people3.operator +=(people1);*/
people3 -= people1;
people3 *= people1;
people3 /= people1;
people3 %= people1;
people3 = "王老师";
people3 = 58;
people3.Print();
people1.Print();
/*** 调用逻辑运算符 ****/
cout << "people3和people3是否相等:" << (people3 == people3 ? "==" : "!=") << endl;
cout << "people3和people1是否相等:" << (people3 == people1 ? "==" : "!=") << endl;
cout << "people3和people1是否相等:" << (people3 != people1 ? "!=" : "==") << endl;
/*** 调用高阶逻辑运算符 ****/
cout << "people3和 老师 是否相等:" << (people3 == "王老师" ? "==" : "!=") << endl;
/*** 单目运算符: ++,-- ***/
#if 0
int value = 10;
/**** 前置 ****自己 和 返回值都是 自增1*/
// cout << "++value = " << ++(++value) << endl;
// cout << "value = " << value << endl;
/**** 后置 ****返回当前,自己自增 1*/
cout << "value++ = " << (value++)++ << endl;
cout << "value = " << value << endl;
#else
People people4("张三","男",16);
/**** 前置 ****/
// cout << (--(--(--people4))).m_age << endl;;
// people4.Print();
/**** 后置 ****/
cout << (people4++).m_age << endl;;
cout <<(people4).m_age << endl;;
#endif
/*** 单目运算符: << , >> , & , | ^ ***/
#if 0
int value = 1; /* 0x01 ==== 0000 0011*/
cout << "value << 1 = " << (value << 1) << endl;
cout << "value = " << value << endl;
#else
People people5("张三","男",1); /* 0x01 ==== 0000 0100*/
cout << "(people5 >> 2).m_age = " << (people5 >> 2).m_age << endl;
cout << "people5.m_age = " << people5.m_age << endl;
cout << "(people5 & 0).m_age = " << (people5 & 0).m_age << endl;
cout << "people5.m_age = " << people5.m_age << endl;
/**** 高阶 << 运算符 ****/
//cin >> people5; 输入
cout << people5 << endl;; //输出
#endif
People people;
people(); /* 调用仿函数 */
cout << "是否相等:" << (people(10,20) == true ? "相等" : "不相等") << endl;
people[3] = 5; /* 相当于 people.addr[3] = 5 ,解读当前想要操作的是int addr[3]*/
cout << "people[3] = " << people[3] << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < people["max"];i++)
{
cout << people[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
/**** 去操作其他类的直接操作 -> ***/
people->language = 100;
cout << "语文成绩:" << people->language << endl;
return 0;
}
4.继承
People.h
#ifndef PEOPLE_H
#define PEOPLE_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/** 封装是隐藏实现 **/
class People
{
public:
People(string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0);
public:
string name() const;
void setName(const string &name);
string sex() const;
void setSex(const string &sex);
int age() const;
void setAge(int age);
protected:
string m_name; /*姓名*/
string m_sex; /*性别*/
int m_age; /*年龄*/
};
#endif // PEOPLE_H
People.cpp
#include "people.h"
People::People(string name,string sex,int age)
:m_name(name),m_sex(sex),m_age(age)
{
}
string People::name() const
{
return m_name;
}
void People::setName(const string &name)
{
m_name = name;
}
string People::sex() const
{
return m_sex;
}
void People::setSex(const string &sex)
{
m_sex = sex;
}
int People::age() const
{
return m_age;
}
void People::setAge(int age)
{
m_age = age;
}
Student.h
#ifndef STUDENT_H
#define STUDENT_H
#include "people.h"
class Grade
{
public:
float language; /*语文*/
float math; /*数学*/
float english; /*英语*/
};
class Student : public People
{
public:
Student(string id = "0",string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0);
Student(string id ,float language,float math,float english,string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0);
Student(string id ,Grade grade = {0,0,0},string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0);
/**** 自己实现成员访问运算符 ****/
Grade *operator ->()
{
return &(this->m_grade);
}
string ID() const;
protected:
string m_ID;
Grade m_grade;
};
#endif // STUDENT_H
Student.cpp
#include "student.h"
Student::Student(string id, string name, string sex, int age)
//:m_ID(id),People(name,sex,age),m_grade{0,0,0}
:Student(id,0,0,0,name,sex,age) /*构造函数相互调用*/
{
}
Student::Student(string id, float language, float math, float english, string name, string sex, int age)
:m_ID(id),People(name,sex,age),m_grade{language,math,english}
{
}
Student::Student(string id, Grade grade, string name, string sex, int age)
:Student(id,grade.language,grade.math,grade.english,name,sex,age) /*构造函数相互调用*/
{
}
string Student::ID() const
{
return m_ID;
}
Teacher.h
#ifndef TEACHER_H
#define TEACHER_H
#include "people.h"
class Teacher : public People
{
public:
Teacher(string id = "0",string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0);
string ID() const; /*获取工号*/
protected:
string m_ID;/*工号*/
};
#endif // TEACHER_H
Teachar.cpp
#include "teacher.h"
Teacher::Teacher(string id, string name, string sex, int age)
:m_ID(id),People(name,sex,age)
{
}
string Teacher::ID() const
{
return m_ID;
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "student.h"
#include "teacher.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Student stu("10000","王老师","男",18);
Student stu1("10001",10,20,30,"李白","男",650);
Student xxx;
cout << stu1->english << endl;
cout << stu1->language << endl;
cout << stu1->math << endl;
Teacher teacher("10000","李老师","女",16);
cout << teacher.name() << endl;
cout << teacher.ID() << endl;
return 0;
}
/****** 案例 *******
* 人类
* 学生类 和 老师类
* ****************/