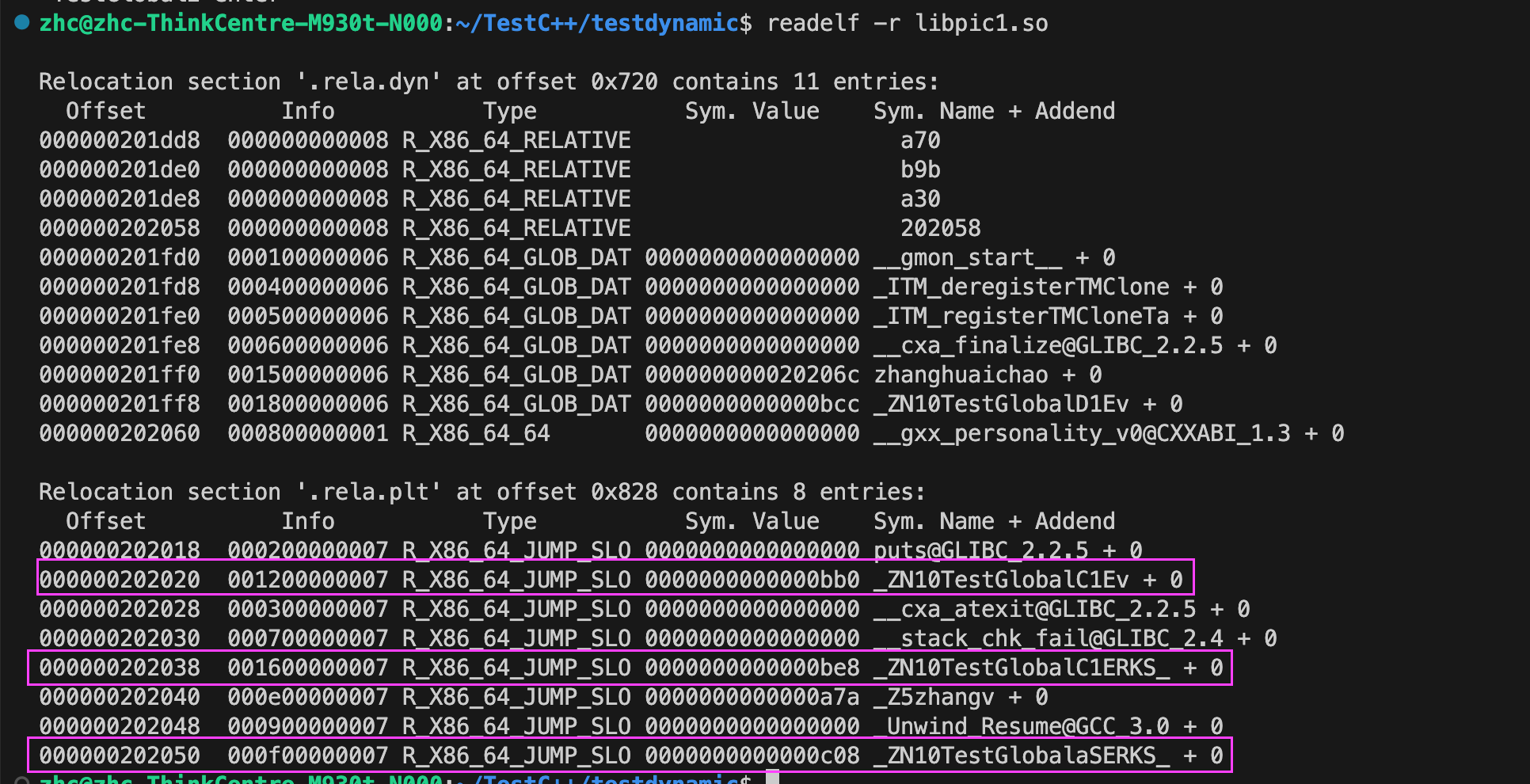
# 导入必要库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns # 用于高级可视化
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
import time # 用于计时
# ======================
# 1. 数据加载与预处理
# ======================
# 加载MNIST数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
# 数据预处理
# 归一化并添加通道维度(CNN需要通道信息)
x_train = x_train.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1)).astype('float32') / 255
x_test = x_test.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1)).astype('float32') / 255
# 将标签转换为one-hot编码
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test)
# ======================
# 2. 构建CNN模型
# ======================
model = keras.Sequential([
# 第一卷积层:32个3x3滤波器,ReLU激活,输入28x28x1
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), # 下采样
# 第二卷积层:64个3x3滤波器,ReLU激活
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
# 全连接层前处理
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dropout(0.5), # 防止过拟合
# 输出层:10个类别,softmax激活
layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
# ======================
# 3. 模型编译与训练
# ======================
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy', # 分类交叉熵
metrics=['accuracy'] # 准确率
)
# 训练配置
epochs = 15
batch_size = 128
validation_split = 0.1 # 使用10%训练数据作为验证集
# 训练模型并记录历史数据
start_time = time.time()
history = model.fit(
x_train, y_train,
epochs=epochs,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_split=validation_split,
verbose=1 # 显示训练进度
)
training_time = time.time() - start_time
# ======================
# 4. 模型评估与可视化
# ======================
# 打印训练信息
print(f"\nTraining completed in {training_time:.2f} seconds")
print(f"Test accuracy: {model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)[1]:.4f}")
# ======================
# 可视化1:训练过程曲线
# ======================
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
# 绘制损失曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'], label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
# 绘制准确率曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# ======================
# 可视化2:混淆矩阵(修正版)
# ======================
# 获取预测结果
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
y_pred_classes = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
y_true = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
# 生成混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred_classes)
# 手动设置类别标签(MNIST 是 0-9)
class_names = [str(i) for i in range(10)]
# 可视化混淆矩阵
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(cm,
annot=True, # 在单元格中显示数值
fmt='d', # 数值格式为整数(适用于混淆矩阵的计数)
cmap='Blues', # 颜色映射(蓝色渐变)
xticklabels=class_names, # X轴标签(类别名称)
yticklabels=class_names) # Y轴标签(类别名称)
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.show()
# ======================
# 可视化3:错误预测样本
# ======================
# 找出预测错误的样本
errors = (y_pred_classes != y_true)
error_samples = x_test[errors]
true_labels = y_true[errors]
pred_labels = y_pred_classes[errors]
# 显示前15个错误样本
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
for i in range(min(15, len(error_samples))):
plt.subplot(3, 5, i + 1)
plt.imshow(error_samples[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap='gray')
plt.title(f"True: {true_labels[i]}, Pred: {pred_labels[i]}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# ======================
# 可视化4:特征图可视化
# ======================
# 获取第一个卷积层的输出
layer_outputs = [layer.output for layer in model.layers[:2]]
activation_model = keras.models.Model(inputs=model.input, outputs=layer_outputs)
activations = activation_model.predict(x_test[0:1])
# 显示第一卷积层的特征图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
first_layer_activation = activations[0]
for i in range(32): # 显示前32个滤波器
plt.subplot(4, 8, i + 1)
plt.imshow(first_layer_activation[0, :, :, i], cmap='viridis')
plt.axis('off')
plt.suptitle('First Convolutional Layer Activations', fontsize=16)
plt.show()运行结果
Epoch 15/15
422/422 [==============================] - 16s 38ms/step - loss: 0.0184 - accuracy: 0.9941 - val_loss: 0.0295 - val_accuracy: 0.9938
Training completed in 343.88 seconds
Test accuracy: 0.9931
313/313 [==============================] - 1s 2ms/step

======================
# 3. 新增功能:随机展示20张测试集样本(调整到模型训练之后)
# ======================
def show_random_samples(model, x_test, y_test, num_samples=20):
"""显示随机测试样本及其预测结果"""
# 确保模型已训练
if not hasattr(model, 'layers'):
raise ValueError("Model must be trained first")
# 生成预测结果
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
y_pred_classes = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
# 获取真实标签
y_true = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
# 随机选择样本
sample_indices = random.sample(range(len(x_test)), num_samples)
# 创建可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 18))
plt.suptitle("Random Handwritten Digit Samples with Predictions\n(Green=Correct, Red=Wrong)",
fontsize=16, y=1.03)
rows, cols = 4, 5
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5, wspace=0.3)
# 使用新版Matplotlib API
cmap = plt.colormaps.get_cmap('RdYlGn') # 修复弃用警告
for i, idx in enumerate(sample_indices):
ax = plt.subplot(rows, cols, i + 1)
img = x_test[idx].squeeze()
# 显示图像
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
# 获取标签信息
true_label = y_true[idx]
pred_label = y_pred_classes[idx]
# 设置标题和颜色
color = 'green' if true_label == pred_label else 'red'
title = f'True: {true_label}\nPred: {pred_label}'
plt.title(title, color=color, fontsize=10, pad=8)
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
混淆矩阵基础结构
1. 矩阵布局(以二分类为例)

2. 关键指标计算

TensorFlow Keras 核心组件
1. 常用层类型

2. 构建模型的三种方式
方式1:顺序模型(Sequential API)
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
model = Sequential([
Dense(128, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)), # 输入层
Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层
])方式2:函数式API(Functional API)
from tensorflow.keras import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense
input_layer = Input(shape=(784,))
hidden = Dense(128, activation='relu')(input_layer)
output = Dense(10, activation='softmax')(hidden)
model = Model(inputs=input_layer, outputs=output)方式3:子类化模型(Subclassing)
from tensorflow.keras import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
class MyModel(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = Dense(128, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = Dense(10, activation='softmax')
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.dense1(inputs)
return self.dense2(x)
model = MyModel()3. 模型编译与训练
# 编译模型
model.compile(
optimizer='adam', # 优化器(自动调参)
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', # 损失函数(分类任务)
metrics=['accuracy'] # 评估指标
)
# 训练模型
history = model.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
batch_size=32, # 每批样本数
epochs=10, # 训练轮次
validation_split=0.2 # 验证集比例
)