目录
1.string.h
2.string.cpp
3.test.cpp
4.一些注意点
本篇博客就学习下如何模拟实现简易版的string类,学好string类后面学习其他容器也会更轻松些。
代码实现如下:
1.string.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
namespace lwx {
class string {
private:
char* _str=nullptr;
size_t _size=0;
size_t _capacity=0;
public:
using iterator = char*;
using const_iterator = const char*;
string(const char* s = "");
string(const string& str);
string& operator=(const string& str);
~string();
size_t size()const {
return _size;
}
size_t capacity()const {
return _capacity;
}
char* c_str()const {
return _str;
}
void clear() {
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
string substr(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)const;
iterator begin() {
return _str;
}
iterator end() {
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _str;
}
const_iterator end()const {
return _str + _size;
}
string& operator+=(char c);
string& operator+=(const char* s);
void push_back(char c);
void append(const char* s);
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
void insert(size_t pos, char c);
void insert(size_t pos, const char* s);
size_t find(char c, size_t pos=0)const;
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos=0)const;
void reserve(size_t n) {
if (n > _capacity) {
char* p = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(p, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = p;
_capacity = n;
}
}
char& operator[](size_t n) {
assert(n <= _size);
return _str[n];
}
const char& operator[](size_t n)const {
assert(n <= _size);
return _str[n];
}
public:
static const size_t npos;
};
bool operator==(const string& st, const string& str);
bool operator!=(const string& st, const string& str);
bool operator>=(const string& st, const string& str);
bool operator<=(const string& st, const string& str);
bool operator>(const string& st, const string& str);
bool operator<(const string& st, const string& str);
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const string& str);
istream& operator>>(istream& is, string& str);
}
2.string.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"string.h"
namespace lwx {
const size_t string::npos = -1;
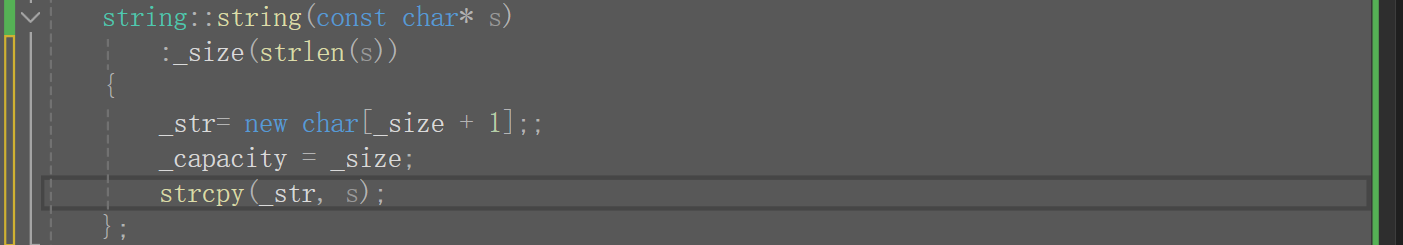
string::string(const char* s)
:_size(strlen(s))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s);
}
string::string(const string& str) {
_size = str._size;
_capacity = str._capacity;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str._str);
}
string& string::operator=(const string& str) {
if (*this != str) {
delete[] _str;
_size = str._size;
_capacity = str._capacity;
_str = new char[_capacity+1];
strcpy(_str, str._str);
}
return *this;
}
string::~string() {
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
void string::push_back(char c) {
if (_size == _capacity) {
reserve(_capacity==0?4:2*_capacity);
}
_str[_size] = c;
_str[_size + 1] = '\0';
_size++;
}
void string::append(const char* s) {
if (_size + strlen(s) > _capacity) {
reserve(2 * _capacity);
}
if (_size + strlen(s) > _capacity)
reserve(_size + strlen(s));
strcpy(_str+_size, s);
_size += strlen(s);
}
string& string::operator+=(char c) {
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* s) {
append(s);
return *this;
}
string string::substr(size_t pos,size_t len) const{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len>_size-pos) {
len = _size - pos;
}
lwx::string sub;
sub.reserve(len+1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sub._str[i] = _str[pos + i];
}
return sub;
}
void string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len ) {
assert(pos <= _size);
if (len >= _size - pos) {
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else {
for (size_t i = 0; i <len; i++) {
_str[pos+i] = _str[pos + len+i];
}
}
_size -= len;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, char c) {
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
reserve(_capacity==0?4:2 * _capacity);
size_t end=_size+1;
while (end > pos) {
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
end--;
}
_str[pos] = c;
_size++;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* s) {
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t n = strlen(s);
if (_size + n > _capacity)
reserve(2 * _capacity);
if (_size + n > _capacity)
reserve(_size + n);
size_t end = _size + n;
while (n > 0) {
_str[end + n] = _str[end];
n--;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
_str[pos + i] = s[i];
}
_size += n;
}
size_t string::find(char c, size_t pos) const{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++) {
if (_str[i] == c)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
size_t string::find(const char* s, size_t pos) const{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* p = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (p == nullptr) {
return npos;
}
else {
return p - _str;
}
return npos;
}
bool operator==(const string& st, const string& str) {
return strcmp(st.c_str(), str.c_str()) == 0;
}
bool operator!=(const string& st, const string& str) {
return !(st == str);
}
bool operator>=(const string& st, const string& str) {
return !(st < str);
}
bool operator<=(const string& st, const string& str) {
return !(st > str);
}
bool operator>(const string& st, const string& str) {
return strcmp(st.c_str(), str.c_str()) > 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& st, const string& str) {
return !(st > str || st == str);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const string& str) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
os << str[i];
}
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, string& str) {
str.clear();
char c;
c = is.get();
while (c != ' ' && c != '\n') {
str += c;
c = is.get();
}
return is;
}
}3.test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"string.h"
void test_string1()
{
lwx::string s2;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
lwx::string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1[0] = 'x';
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 迭代器 -- 像指针一样的对象
lwx::string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
(*it1)--;
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
// 修改
// 底层是迭代器的支持
// 意味着支持迭代器就支持范围for
for (auto& ch : s1)
{
ch++;
}
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
const lwx::string s3("xxxxxxxxx");
for (auto& ch : s3)
{
//ch++;
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string2()
{
lwx::string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1 += '#';
s1 += "#hello world";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
lwx::string s2("hello world");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.insert(6, 'x');
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.insert(0, 'x');
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
lwx::string s3("hello world");
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
s3.insert(6, "xxx");
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
s3.insert(0, "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
lwx::string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 2);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(5, 20);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(3);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
lwx::string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.find(' ') << endl;
cout << s1.find("wo") << endl;
lwx::string s2 = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/cstring/strstr/?kw=strstr";
//bit::string s2 = "https://blog.csdn.net/ww753951/article/details/130427526";
size_t pos1 = s2.find(':');
size_t pos2 = s2.find('/', pos1 + 3);
if (pos1 != string::npos && pos2 != string::npos)
{
lwx::string domain = s2.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));
cout << domain.c_str() << endl;
lwx::string uri = s2.substr(pos2 + 1);
cout << uri.c_str() << endl;
}
}
void test_string5()
{
lwx::string s1("hello world");
lwx::string s2(s1);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s1[0] = 'x';
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
lwx::string s3("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
s1 = s3;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
s1 = s1;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string6()
{
lwx::string s1("hello world");
lwx::string s2(s1);
lwx::string s3 = s1;
// 构造+拷贝 ->优化直接构造
lwx::string s4 = "hello world";
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 == "hello world") << endl;
cout << ("hello world" == s1) << endl;
//operator<<(cout, s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1 << endl;
std::string ss1("hello world");
cin >> ss1;
cout << ss1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string6();
return 0;
}
4.一些注意点
①我们定义的string类会和库里面有冲突的风险,所以我们可以用命名空间namespace进行封装。
②编写默认构造函数时,我们不能给_str(nullptr)缺省值,因为cout<<(const char*)_str<<endl不会当指针打印,它会自动识别类型,觉得你是想打印字符串,而打印字符串遇到'\0'才会终止,但_str为空指针,这就有解引用空指针问题了。

但标准库里的string不会有这种问题,解决方法:直接给'\0'开一个空间就行了
③在string这里申请空间要多给一个空间用来存放'\0',,但capacity不将'\0'计算其中,空间真实大小=_capacity+1。
④在前面类和对象下我们说到,尽可能的使用初始化列表,但在这里使用比较别捏,三个strlen(),strlen是在运行时计算的,3个O(n),还是很坑的。

那我们改一下,下面这个比上面的运行效率时好多了,但是这种写法是错的。因为我们之前说过,初始化列表会按声明的顺序初始化,先走_str,再走_size,所以我们还得把声明顺序变了才行,但声明顺序变了又不顺我们的习惯(先声明指针),而且过后还要把数据拷贝出来,所以说我们是得尽可能使用初始化列表,但有些东西是初始化列表搞不定的,改该用函数体还是得用,不能说有了初始化列表就不用函数体了。
最终我们可以改成,这样就不用管顺序了。