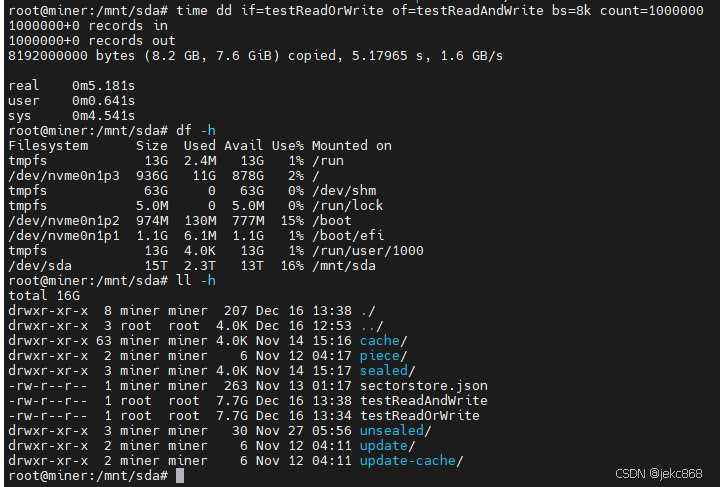
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int pipefd[2];
char buff[1024] = "hello world";
char s[1024];
if(pipe(pipefd)==-1)
{
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}//读端pipefd[0] 写端pipefd[1]
pid_t pid = fork();//创建子进程
if(pid==0)
{
close(pipefd[1]);//先关闭写端
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
read(pipefd[0],s,sizeof(s));
printf("儿子在读取:%s\n",s);//输出读取的数据
}
close(pipefd[0]);//关闭读端
}
else if(pid>0)
{
close(pipefd[0]);//先关闭读端
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
write(pipefd[1],buff,sizeof(buff));
}
close(pipefd[1]);//完成后关闭写端
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}

写端:
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int k = mkfifo("./myfifo",0664);//创建有名管道
if(k==-1)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
int fd1 = open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY);//打开管道
if(fd1==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
char buff[1024];
while(1)//循环写入数据
{
printf("请输入内容:");
int res = read(0,buff,sizeof(buff));//输入从0号描述符读取数据
write(fd1,buff,res);//写入有名管道
}
close(fd1);//关闭有名管道
return 0;
}读端:
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd2 = open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY);//打开管道文件
if(fd2==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
char buff[1024];
while(1)//循环读取数据
{
int res = read(fd2,buff,sizeof(buff));
if(res==0)
{
printf("写入端退出\n");
break;
}
write(1,buff,res);//写入标准输出描述符
}
close(fd2);//关闭管道文件
return 0;
}练习:
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd1 = open("./myfo1",O_WRONLY);
int fd2 = open("./myfo2",O_RDONLY);
if(fd1==-1||fd2==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
char buff[1024];
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)//父进程写入管道1
{
while(1)
{
printf("请输入内容:\n");
int res = read(0,buff,sizeof(buff));
write(fd1,buff,res);//写入管道1
}
}
else if(pid==0)//子进程读取管道2
{
while(1)
{
int res = read(fd2,buff,sizeof(buff));
write(1,buff,res);//读取内容显示出来
}
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd1 = open("./myfo1",O_RDONLY);
int fd2 = open("./myfo2",O_WRONLY);
if(fd1==-1||fd2==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
char buff[1024];
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)//父进程写入管道2
{
while(1)
{
printf("请输入内容:\n");
int res = read(0,buff,sizeof(buff));
write(fd2,buff,res);//写入管道1
}
}
else if(pid==0)//子进程读取管道1
{
while(1)
{
int res = read(fd1,buff,sizeof(buff));
write(1,buff,res);//读取内容显示出来
}
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
#include <myhead.h>
void hander(int tmy)
{
if(tmy==SIGINT)
{
printf("捕获了ctrl+c\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
#if 0
if(signal(SIGINT,SIG_IGN)==SIG_ERR)//忽略ctrl +c信号
{
perror("signal");
return -1;
}
if(signal(SIGINT,SIG_DFL)==SIG_ERR)//默认ctrl +c信号
{
perror("signal");
return -1;
}
#endif
if(signal(SIGINT,hander)==SIG_ERR)//hander将会捕获SIGINT信号作为自己的参数
{
perror("signal");
return -1;
}
int k = 0;
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("唐明宇打呼噜k = %d\n",k);
k++;
}
return 0;
}
#include<myhead.h>
void hander(int tmy)
{
if(tmy==SIGCHLD)
{
printf("捕获了(17)\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
if(signal(SIGCHLD,hander)==SIG_ERR)
{
perror("signal");
return -1;
}
}
else if(pid==0)
{
sleep(1);
exit(0);//成功退出子进程
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
wait(NULL);//阻塞回收子进程资源
return 0;
}
![]()
#include <myhead.h>
void fun(int tmy)
{
sleep(1);
if(SIGSEGV==tmy)
{
printf("内核发送了段错误信号\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(signal(SIGSEGV,fun)==SIG_ERR)//绑定信号
{
perror("signal");
return -1;
}
int *p = NULL;
*p = *p+1;
while(1);
return 0;
}
#include<myhead.h>
void fun(int wly)
{
sleep(1);
if(SIGTSTP==wly)
{
printf("捕获到ctrl+z\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(signal(SIGTSTP,fun)==SIG_ERR)
{
perror("signal");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("wly卷麻了\n");
}
return 0;
}
















![4_使用 HTML5 Canvas API (3) --[HTML5 API 学习之旅]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/b86526d06ca348b4b6d67e878550b764.png#pic_center)