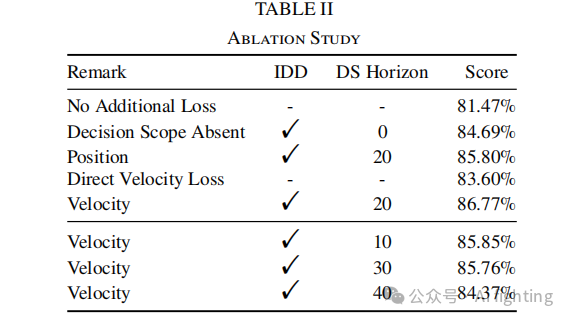
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
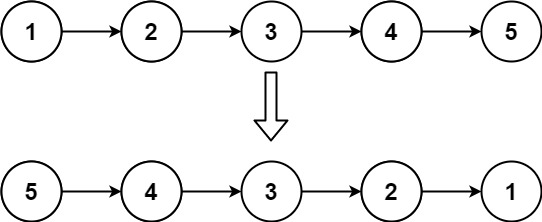
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
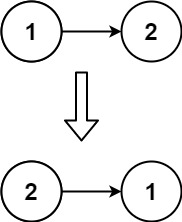
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
迭代法:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *pre = nullptr;
while(cur){
ListNode* nextNode = cur->next; // 暂存当前节点的下一个节点
cur->next = pre; // 反转当前节点的指针
pre = cur; // 移动 prev 指针到当前节点
cur = nextNode; // 移动 curr 指针到下一个节点
}
return pre;
}
};初始状态
cur指针初始化为链表的头节点,表示当前正在处理的节点。pre指针初始化为nullptr,表示前一个节点,在反转过程中将用来链接当前节点。
示例:
链表 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5。
初始状态:
head 指向 1,链表为 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr
cur = head 指向 1
pre = nullptr
第一轮循环:
nextNode = cur->next 指向 2
cur->next = pre 使 1->next 指向 nullptr
pre 变为 1
cur 变为 nextNode(2)
链表状态: 1 -> nullptr(pre指向反转后的部分)
第二轮循环:
nextNode = cur->next 指向 3
cur->next = pre 使 2->next 指向 1
pre 变为 2
cur 变为 nextNode(3)
链表状态: 2 -> 1 -> nullptr
第三轮循环:
nextNode = cur->next 指向 4
cur->next = pre 使 3->next 指向 2
pre 变为 3
cur 变为 nextNode(4)
链表状态: 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> nullptr
第四轮循环:
nextNode = cur->next 指向 5
cur->next = pre 使 4->next 指向 3
pre 变为 4
cur 变为 nextNode(5)
链表状态: 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> nullptr
第五轮循环:
nextNode = cur->next 指向 nullptr
cur->next = pre 使 5->next 指向 4
pre 变为 5
cur 变为 nextNode(nullptr)
链表状态: 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> nullptr
完成反转
当 cur 变为 nullptr 时,循环结束。
返回 pre,它指向反转后的链表头节点(5)。
递归法:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return newHead;
}
};
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr):
当链表为空或仅有一个节点时,直接返回 head。
实例:
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL。
- 第一次调用
head指向节点1。- 调用
reverseList(head->next),即递归进入head = 2的情况。
- 第二次调用
head指向节点2。- 再次调用
reverseList(head->next),进入head = 3的情况。
- 继续递归调用
- 继续类似步骤,递归进入
head = 3、head = 4、head = 5的情况。
- 继续类似步骤,递归进入
- 最后一次调用(终止条件)
head指向节点5,而head->next为nullptr。- 根据终止条件,直接返回节点
5作为新的头节点newHead。
递归回溯阶段(反转指针)
-
回溯到
head = 4newHead仍然是节点5。head->next->next = head,即5->next = 4,链表变成5 -> 4 -> NULL。head->next = nullptr,断开4 -> 5的原指针。
-
回溯到
head = 3head->next->next = head,即4->next = 3,链表变成5 -> 4 -> 3 -> NULL。head->next = nullptr,断开3 -> 4的原指针。
-
回溯到
head = 2head->next->next = head,即3->next = 2,链表变成5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> NULL。head->next = nullptr,断开2 -> 3的原指针。
-
回溯到
head = 1head->next->next = head,即2->next = 1,链表变成5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL。head->next = nullptr,断开1 -> 2的原指针。
最终返回 newHead,即节点 5,完成整个链表的反转。