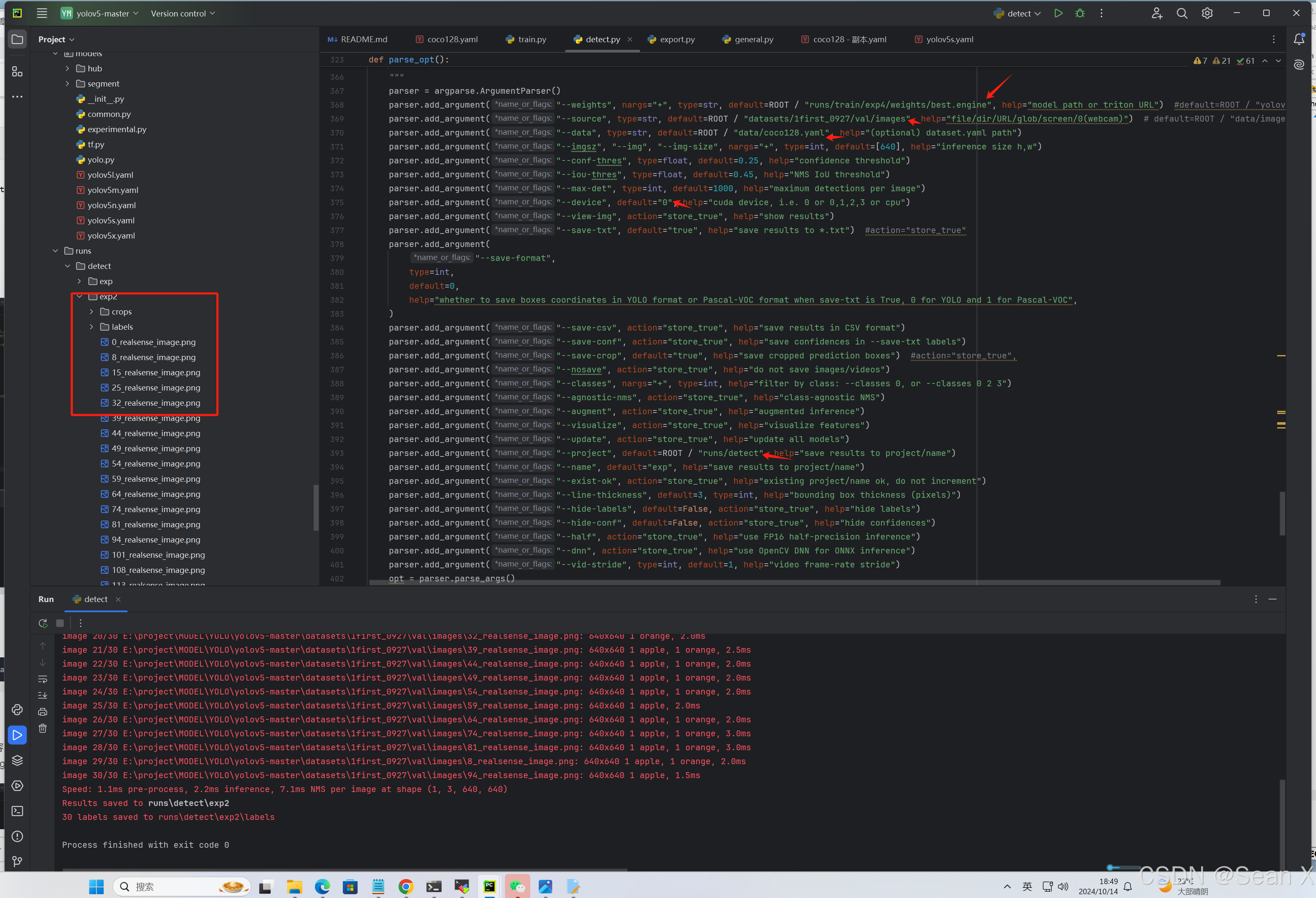
线程的实现方式
- 继承Thread类:void run()方法没有返回值,无法抛异常
- 实现Runnable接口:void run()方法没有返回值,无法抛异常
- 实现Callable接口:V call() throws Exception 返回结果,能够抛异常
实现Callable接口
(1)创建Callable接口的实现类,并实现call()方法,该call()方法将作为线程执行体,并且有返回值。
(2)创建Callable实现类的实例,使用FutureTask类来包装Callable对象,该FutureTask对象封装了该Callable对象的call()方法的返回值。
(3)使用FutureTask对象作为Thread对象的target创建并启动新线程。
(4)调用FutureTask对象的get()方法来获得子线程执行结束后的返回值
任务
四匹马,跑一千米比赛,每匹马的速度通过1~10的随机数来产生,输出哪匹马是冠军
RunTask1.java代码:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
/**
* 跑步任务
*/
public class RunTask1 implements Callable<Long> {
// step/100ms 是否睡着 睡觉时间
// 通过方法形参接收参数
// 定义属性
private int step;
private boolean isSleep;
private int sleepTime;
public RunTask1(int step,boolean isSleep,int sleepTime){
this.step=step;
this.isSleep=isSleep;
this.sleepTime=sleepTime;
}
@Override
public Long call() throws Exception {
int distance=0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(true){
distance+=step;
if (isSleep) {
if (distance == 800) { //跑到800米
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "睡" + sleepTime + "ms");
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
if(distance>=1000){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "跑完" + distance + "米");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
}
}
Test.java代码
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//第一匹马的跑步任务
RunTask1 horse1=new RunTask1(new Random().nextInt(10)+1,true,200);
FutureTask<Long> horseResult = new FutureTask<>(horse1);
Thread t1=new Thread(horseResult,"马1");
//第二匹马的跑步任务
RunTask1 horse2=new RunTask1(new Random().nextInt(10)+1,true,400);
FutureTask<Long> horseResult1 = new FutureTask<>(horse2);
Thread t2=new Thread(horseResult1,"马2");
//第三匹马的跑步任务
RunTask1 horse3=new RunTask1(new Random().nextInt(10)+1,true,5500);
FutureTask<Long> horseResult2 = new FutureTask<>(horse3);
Thread t3=new Thread(horseResult2,"马3");
//第四匹马的跑步任务
RunTask1 horse4=new RunTask1(new Random().nextInt(10)+1,false,0);
FutureTask<Long> horseResult3 = new FutureTask<>(horse4);
Thread t4=new Thread(horseResult3,"马4");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
//统计比赛结果,一定要等main线程执行,否则, Horse1的线程还没跑完,就输出了winner is Horse2
if((horseResult.get().longValue() < horseResult1.get().longValue()) && (horseResult.get().longValue() < horseResult2.get().longValue()) && (horseResult.get().longValue() < horseResult3.get().longValue())){
System.out.println("winner is "+t1.getName());
}
else if((horseResult1.get().longValue() < horseResult.get().longValue()) && (horseResult1.get().longValue() < horseResult2.get().longValue()) && (horseResult1.get().longValue() < horseResult3.get().longValue())){
System.out.println("winner is "+t2.getName());
}
else if((horseResult2.get().longValue() < horseResult.get().longValue()) && (horseResult2.get().longValue() < horseResult1.get().longValue()) && (horseResult2.get().longValue() < horseResult3.get().longValue())){
System.out.println("winner is "+t3.getName());
}
else if(horseResult3.get().longValue() < horseResult.get().longValue() && (horseResult3.get().longValue() < horseResult1.get().longValue()) && (horseResult3.get().longValue() < horseResult2.get().longValue())){
System.out.println("winner is "+t4.getName());
}
else System.out.println("平局");
}
}
控制台输出,想要结果不一样,可以通过设置哪一匹马会睡眠,从而改变结果,代码还是有不足: