三维网格中轴线提取
- 方法介绍
- 实现提取
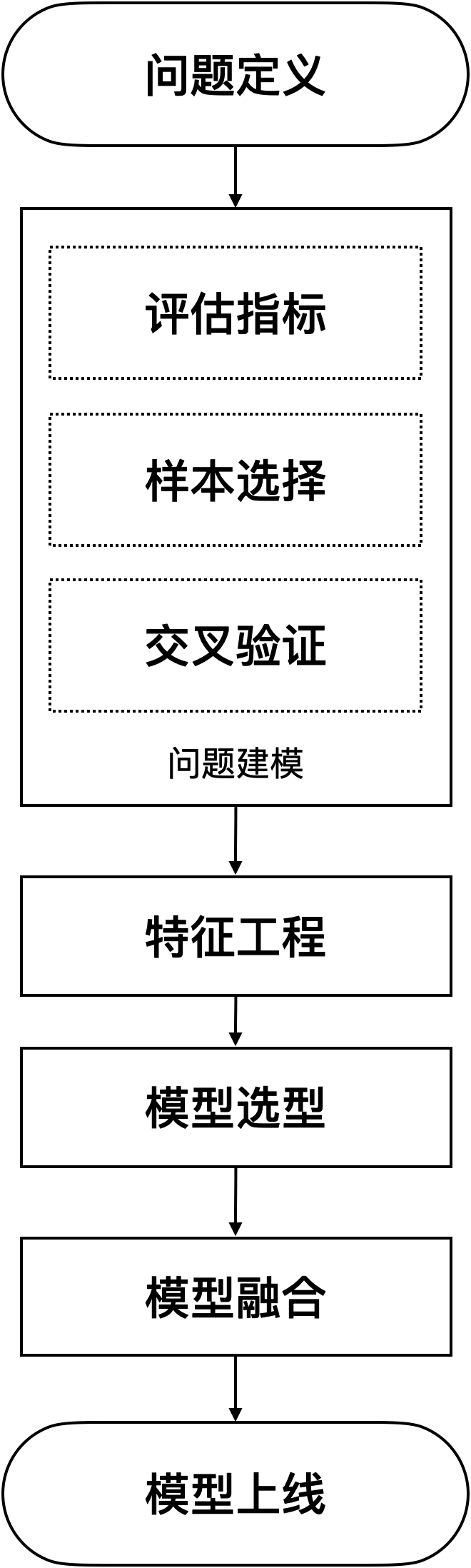
三维网格中轴线提取是计算机图形学和三维建模领域中的一个重要技术,它对于理解三维形状的拓扑结构和几何特性具有重要意义。
方法介绍
以下是几种常见的三维网格中轴线提取方法:
- 基于距离变换的方法
基本原理:首先计算三维网格中每个点到网格边界的距离,形成距离场。然后,根据距离场的分布,通过细化算法提取中轴线。这种方法的核心在于距离变换和细化操作的结合。
步骤:
对三维网格进行距离变换,计算每个点到最近边界的距离。
对距离变换结果进行排序,优先处理距离较小的点。
通过细化算法逐步剥离外层点,直至提取出中轴线。 - 基于中轴球的方法
基本原理:为每个网格端点计算一个中轴球,中轴球的中心即为中轴点。通过计算所有网格端点的中轴球,最终生成中轴网格。
步骤:
估计网格上所有点的法向,以模拟平滑表面。
将模型分割成体素,每个体素具有特定尺寸。
计算每个网格端点的中轴球,包括中轴点和中轴半径。
通过所有中轴点生成中轴网格。 - 基于局部曲面拟合的方法
应用场景:特别适用于处理点云数据,如三维激光扫描数据。
步骤:
对原始点云数据进行预处理,包括配准和去噪。
对点云进行横断面切片处理,得到多个切片点云。
对每个切片点云进行局部曲面拟合,提取切片中心。
将所有切片中心拟合得到整体的中轴线。 - 基于拓扑收缩的方法
基本原理:通过定义一个收缩力函数,控制三维网格内表面的收缩过程,直至收缩成一维的中轴线。
挑战:如何定义收缩力函数以平衡收缩和吸引约束,同时保留骨架线的拓扑性和中间轴的中心位置。 - 基于骨架提取的算法
如Medial Axis Transform (MAT):这类算法通常涉及对三维网格进行骨架化处理,通过逐步剥离外层网格元素,最终得到中轴线或骨架结构。
实现提取
输入:半圆环网格

std::vector<Point> m_points;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> m_faces;
std::unordered_map<int, std::vector<int>> m_adjacency;
std::unordered_set<int> m_boundaryPoints;
std::unordered_set<int> m_skeletonPoints;
std::unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash> m_skeletonEdges;
void buildAdjacencyList() {
for (const auto& face : m_faces) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
int v1 = face[i];
int v2 = face[(i + 1) % 3];
m_adjacency[v1].push_back(v2);
m_adjacency[v2].push_back(v1);
}
}
}
void findBoundaryPoints() {
std::unordered_set<Edge, EdgeHash> edges;
for (const auto& face : m_faces) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
Edge e(face[i], face[(i + 1) % 3]);
if (edges.find(e) != edges.end()) {
edges.erase(e);
}
else {
edges.insert(e);
}
}
}
for (const auto& e : edges) {
m_boundaryPoints.insert(e.v1);
m_boundaryPoints.insert(e.v2);
}
}
void grassfirePropagation() {
// Distance initialization and boundary point queue
std::vector<float> distanceFromBoundary(m_points.size(), std::numeric_limits<float>::max());
std::queue<int> queue;
// Initialize boundary points
for (int idx : m_boundaryPoints) {
distanceFromBoundary[idx] = 0;
queue.push(idx);
}
// Distance update using BFS
while (!queue.empty()) {
int current = queue.front();
queue.pop();
for (int neighborIdx : m_adjacency[current]) {
float newDistance = distanceFromBoundary[current] + distance(m_points[current], m_points[neighborIdx]);
if (newDistance < distanceFromBoundary[neighborIdx]) {
distanceFromBoundary[neighborIdx] = newDistance;
queue.push(neighborIdx);
}
}
}
// Find local maxima (skeleton points)
for (int i = 0; i < m_points.size(); ++i) {
if (m_boundaryPoints.count(i) > 0) continue; // Skip boundary points
bool isLocalMaximum = true;
for (int neighborIdx : m_adjacency[i]) {
if (distanceFromBoundary[neighborIdx] > distanceFromBoundary[i]) {
isLocalMaximum = false;
break;
}
}
if (isLocalMaximum) {
m_skeletonPoints.insert(i);
}
}
}