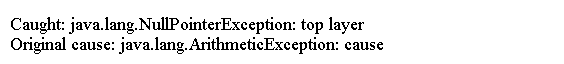Java 异常
Java教程 - Java异常
异常是在运行时在代码序列中出现的异常状况。例如,读取一个不存在的文件。
Java异常是描述异常条件的对象发生在一段代码中。
关键词
Java异常处理通过五个关键字管理: try,catch,throw,throws和finally。
try block包含要监视的程序语句异常。
如果在块中发生异常,则抛出异常。
catch 语句可以捕获异常并以合理的方式处理它。
要手动抛出异常,请使用关键字throw。
任何抛出的异常一个方法必须由一个 throws 子句指定。
任何代码绝对必须是在try块完成之后执行的命令被放在 finally 块中。
语法
要处理一个异常,我们把可能有的代码在try ... catch语句中的异常。
try {
// block of code to monitor for errors
}
catch (ExceptionType1 exOb) {
// exception handler for ExceptionType1
}
catch (ExceptionType2 exOb) {
// exception handler for ExceptionType2
}
可能有异常的程序语句包含在 try 块中。异常处理程序使用 catch 语句进行编码。
这里, ExceptionType 是发生的异常的类型。
例子
在try块和catch子句中封装要监视的代码。
下面的程序包括一个try块和一个catch子句处理由除法生成的ArithmeticException错误:
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int d, a;
try { // monitor a block of code.
d = 0;
a = 42 / d;
System.out.println("This will not be printed.");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) { // catch divide-by-zero error
System.out.println("Division by zero.");
}
System.out.println("After catch statement.");
}
}
此程序生成以下输出:
![]()
例2
一旦抛出异常,程序控制就会从try块转移到catch块中。执行从未从catch返回到try块。
以下代码处理异常并继续。
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 32000; i++) {
try {
b = r.nextInt();
c = r.nextInt();
a = 12345 / (b / c);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Division by zero.");
a = 0; // set a to zero and continue
}
System.out.println("a: " + a);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

Java 异常语句
Java教程 - Java异常语句
为了防止和处理运行时错误,请将代码包含在try块中进行监视。
紧跟在try块之后,包括一个catch子句它指定您希望捕获的异常类型。
Java try catch语句
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try { // monitor a block of code.
int d = 0;
int a = 42 / d;
System.out.println("This will not be printed.");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) { // catch divide-by-zero error
System.out.println("Division by zero.");
}
System.out.println("After catch statement.");
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

多个catch子句
您可以指定两个或多个catch子句,每个捕获不同类型的异常。
当抛出异常时,将按顺序检查每个catch语句,并执行类型与异常类型匹配的第一个。
在执行一个catch语句之后,绕过其他catch语句,并在try/catch块之后继续执行。
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
int a = args.length;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
int b = 42 / a;
int c[] = { 1 };
c[42] = 99;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Divide by 0: " + e);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Array index oob: " + e);
}
System.out.println("After try/catch blocks.");
}
}
当您使用多个catch语句时,异常子类必须在它们的任何超类之前。
上面的代码生成以下结果。
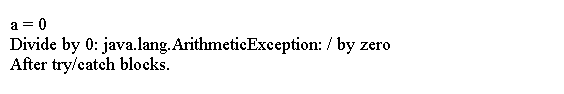
嵌套try语句
try语句可以嵌套。
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
int a = args.length;
int b = 42 / a;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
try { // nested try block
if (a == 1)
a = a / (a - a); // division by zero exception
if (a == 2) {
int c[] = { 1 };
c[4] = 9; // an out-of-bounds exception
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Array index out-of-bounds: " + e);
}
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Divide by 0: " + e);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
![]()
Java throw语句
我们可以在异常情况下抛出异常。
语法
throw的一般形式如下所示:
throw ThrowableInstance;
这里,ThrowableInstance必须是Throwable类型的对象或Throwable的子类。
有两种方法可以获取Throwable对象:在catch子句中使用参数,或者使用new运算符创建一个。
执行流程在throw语句之后立即停止; 任何后续不执行语句。
如何使用Java throws语句?
public class Main {
static void aMethod() {
try {
throw new NullPointerException("demo");
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("Caught inside demoproc.");
throw e; // rethrow the exception
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
aMethod();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("Recaught: " + e);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
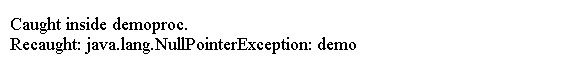
Java throws语句
如果一个方法想抛出一个异常,它必须指定这个行为。
这是包含throws子句的方法声明的一般形式:
type method-name(parameter-list) throws exception-list
{
// body of method
}
exception-list是一个逗号分隔的列表,列出了方法可以抛出的异常。
public class Main {
static void throwOne() throws IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("Inside throwOne.");
throw new IllegalAccessException("demo");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
throwOne();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
System.out.println("Caught " + e);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
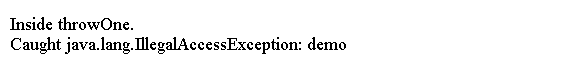
Java finally语句
任何代码,将被执行,不管try块放在一个 finally 阻止。
这是异常处理块的一般形式:
try {
// block of code to monitor for errors
}
catch (ExceptionType1 exOb) {
// exception handler for ExceptionType1
}
catch (ExceptionType2 exOb) {
// exception handler for ExceptionType2
}
// ...
finally {
// block of code to be executed after try block ends
}
finally 创建一个代码块在 try/catch 块完成后执行。
即使没有catch语句与异常匹配, finally 块也将执行。
finally 块可用于关闭文件句柄和释放任何其他资源。finally子句是可选的。
public class Main {
// Through an exception out of the method.
static void methodC() {
try {
System.out.println("inside methodC");
throw new RuntimeException("demo");
} finally {
System.out.println("methodC finally");
}
}
// Return from within a try block.
static void methodB() {
try {
System.out.println("inside methodB");
return;
} finally {
System.out.println("methodB finally");
}
}
// Execute a try block normally.
static void methodA() {
try {
System.out.println("inside methodA");
} finally {
System.out.println("methodA finally");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
methodC();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception caught");
}
methodB();
methodA();
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

Java 异常类型
Java教程 - Java异常类型
下图显示了Java异常类型层次结构:
Throwable | | +---Exception. | | | | | +--- RuntimeException | +---Error
异常及其子类用于用户程序应捕获的异常条件。您可以子类化Exception以创建自己的自定义异常类型。
错误定义在正常情况下不期望捕获的异常。 Java运行时系统使用错误以指示运行时环境中的错误。 堆栈溢出是这种错误的一个例子。
未捕获异常
这个小程序包括一个有意造成除以零误差的表达式:
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int d = 0;
int a = 42 / d;
}
}
以下是执行此示例时生成的异常:
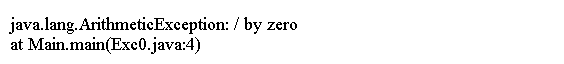
例子
这里是另一个版本的前面的程序,引入相同的错误,但在一个方法与main()分开:
public class Main {
static void subroutine() {
int d = 0;
int a = 10 / d;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
subroutine();
}
}
从默认异常处理程序生成的堆栈跟踪显示如何显示整个调用堆栈:

例2
您可以在println()语句中显示异常描述消息。
例如,catch块可以这样写:
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 32000; i++) {
try {
b = r.nextInt();
c = r.nextInt();
a = 12345 / (b / c);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
a = 0; // set a to zero and continue
}
System.out.println("a: " + a);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

什么是Java的内置异常
子类化RuntimeException的异常不需要包含在任何方法的throws列表中。这些被称为未检查异常。
java.lang中定义的未检查异常在下表中列出。
| 异常 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| ArithmeticException | 算术错误,如除以零。 |
| ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | 数组索引超出边界。 |
| ArrayStoreException | 分配给不兼容类型的数组元素。 |
| ClassCastException | 投射无效。 |
| EnumConstantNotPresentException | 尝试使用未定义的枚举值。 |
| IllegalArgumentException | 用于调用方法的非法参数。 |
| IllegalMonitorStateException | 非法监视器操作,例如等待解锁的线程。 |
| IllegalStateException | 环境或应用程序状态不正确。 |
| IllegalThreadStateException | 请求的操作与当前线程状态不兼容。 |
| IndexOutOfBoundsException | 一些类型的索引是超出界限的。 |
| NegativeArraySizeException | 使用负尺寸创建的数组。 |
| NullPointerException | 无效引用的使用无效。 |
| NumberFormatException | 字符串到数字格式的转换无效。 |
| SecurityException | 试图违反安全。 |
| StringIndexOutOfBounds | 尝试在字符串的边界之外建立索引。 |
| TypeNotPresentException | 未找到类型。 |
| UnsupportedOperationException | 遇到不支持的操作。 |
检查的异常在下表中列出。
| 异常 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| ClassNotFoundException | 找不到类。 |
| CloneNotSupportedException | 尝试克隆不实现Cloneable接口的对象。 |
| IllegalAccessException | 对类的访问被拒绝。 |
| InstantiationException | 尝试创建抽象类或接口的对象。 |
| InterruptedException | 一个线程已被另一个线程中断。 |
| NoSuchFieldException | 请求的字段不存在。 |
| NoSuchMethodException | 请求的方法不存在。 |
Java自定义异常类
您可以通过定义 Exception 的子类来创建自己的异常类。
异常类没有定义自己的任何方法。它继承由 Throwable 提供的方法。
以下程序创建自定义异常类型。
class MyException extends Exception {
private int detail;
MyException(int a) {
detail = a;
}
public String toString() {
return "MyException[" + detail + "]";
}
}
public class Main {
static void compute(int a) throws MyException {
System.out.println("Called compute(" + a + ")");
if (a > 10)
throw new MyException(a);
System.out.println("Normal exit");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
compute(1);
compute(20);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println("Caught " + e);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

Java链接异常
链接异常允许您将另一个异常与异常相关联。第二个异常描述了第一个异常的原因。
为了允许链接异常,两个构造函数和两个方法被添加到 Throwable 。
Throwable(Throwable causeExc) Throwable(String msg, Throwable causeExc)
这里是一个例子,说明处理链接异常的机制:
public class Main {
static void demoproc() {
NullPointerException e = new NullPointerException("top layer");
e.initCause(new ArithmeticException("cause"));
throw e;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
demoproc();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("Caught: " + e);
System.out.println("Original cause: " + e.getCause());
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。