一,IP进程间的通信方式
共享内存(最高效)
1.是一块内核的预留空间
2.避免了用户空间到内核空间的数据拷贝
1.产生key:ftok函数
功能:将pathname和pid_id转化为key
参数:(路径名,'A')
返回值:成功:key,失败:-1
2.通过key获取ipc对象:shmget函数
功能:申请一个共享内存对象
参数:(key, 1024, IPC_CREAT|0666)
3.共享内存绑定:shmat函数
功能:绑定地址空间
参数:(shmid, NULL, 0)
需要判断
if (p == (void*) - 1)
{
perror(shmid fail);
return -1;
}pause函数 进程阻塞 等一个信号
4.接除绑定:shmdt函数(断开映射现象) shmctl(销毁IPC对象)
功能:解除绑定

发送端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
void handler(int signo)
{
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//step1 产生key值
key_t key = ftok(".",'A');
if(key < 0)
{
perror("ftok fail");
return -1;
}
printf("key = %d\n",key);
//step 2
int shmid = shmget(key, 1024, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
perror("shmget fail");
return -1;
}
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
//step 3 绑定地址空间
void *p = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (p == (void *)-1)
{
perror("shmat fail\n");
return -1;
}
signal(SIGUSR1, handler);
pid_t *q = p;
*q = getpid();
char *s = p;
while(1)
{
printf("s = %s\n",s);
if(strncmp(s,"quit",4) == 0)
break;
pause();
}
//step4 断开连接
if(shmdt(p) < 0)
{
perror("shmdt fail");
return -1;
}
//step5 删除ipc对象
if(shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL) < 0)
{
perror("shmctl fail");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
接收端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//step1 产生key值
key_t key = ftok(".",'A');
if(key < 0)
{
perror("ftok fail");
return -1;
}
printf("key = %d\n",key);
//step 2
int shmid = shmget(key, 1024, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if(shmid < 0)
{
perror("shmget fail");
return -1;
}
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
//step 3 绑定地址空间
void *p = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (p == (void *)-1)
{
perror("shmat fail\n");
return -1;
}
pid_t *q = p;
printf("process a pid = %d\n",*q);
pid_t pid = *q;
while(1)
{
char *s = p;
fgets(s, 1024, stdin);
kill(pid, SIGUSR1);
if(strncmp(s,"quit",4) == 0)
break;
}
//step4 断开连接
if(shmdt(p) < 0)
{
perror("shmdt fail");
return -1;
}
//step5 删除ipc对象
if(shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL) < 0)
{
perror("shmctl fail");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}二,不同主机间进程通信方式
ip地址:标识网络中的一台主机
主机:能进行网络通信功能的机器
端口号:用开标识主机中某一具体(进行网络通信)进程
IP + 端口号:进程在网络中的地址
IP的组成:网络号+主机号
网络号:表示所处网络
主机号:表示能容纳的主机
网络编程
TCP/UDP

TPC协议特点:
1.面向连接 —— 类似于打电话,必须先打通
2.传输可靠 —— 保证数据准确可靠(tpc协议机制内功能)
3.面向字节流
UDP:

特点
1.不可靠
2.无连接
3.数据
类似于广播 wifi 对可靠性不高,需要效率高的内容
具体编程



代码
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h> /* superset of previous */
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("socket fail");
return -1;
}
printf("fd = %d\n", fd);
char buf[1024];
while(1)
{
fgets(buf,1024,stdin);
struct sockaddr_in seraddr;
seraddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
seraddr.sin_port = htons(50002);
seraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.0.177");
sendto(fd, buf, strlen(buf) + 1,0 ,(const struct sockaddr *)&seraddr, sizeof(seraddr));
}
return 0;
}
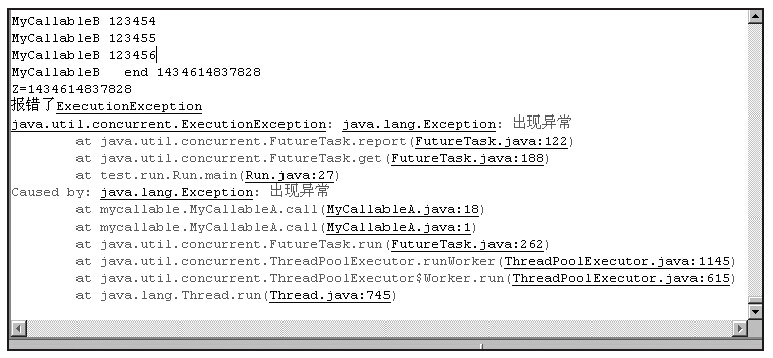
运行结果