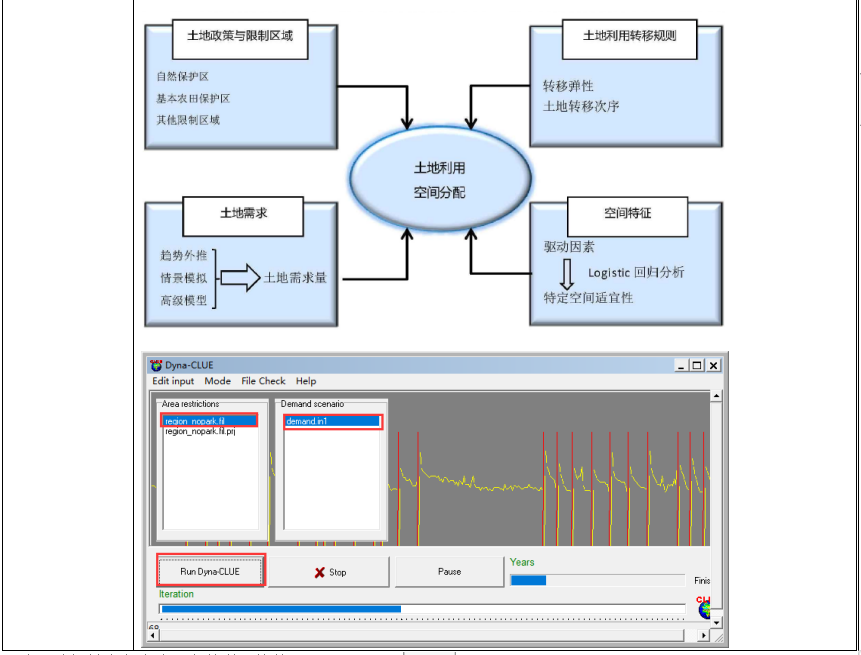
这里我们将介绍一些常用的图像融合方式,并不涉及到诸如CutMix、MixUp、TokenMix、Mosaic、Copy-Paste等图像增强方法。
首先是读取图像,我们这边采用了PIL库进行,那么读进来就应该是一个Image对象。下面介绍Image对象与array的转换方式。
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
img=Image.open(path)
# 从Image读取数据
img=np.array(img,dtype=np.float32)
# 从array转为Image
img=Image.fromarray(img)
有了前置知识后,我们就可以来进行图像融合了。注意,接下来的方法适用于图像大小相等的情况,如果不相等可以重设图像的尺寸。
import numpy as np
import random
from PIL import Image
def combine_images(original_img, augmented_img,combine_choice=None, blend_width=20):
width, height = 640, 640
combine_choice = random.choice(['horizontal', 'vertical',]) if combine_choice==None else combine_choice
if combine_choice == 'randomMix':
o,a=np.array(original_img),np.array(augmented_img)
data = [i for i in range(640 * 640)]
idx = random.sample(data, int(640 * 640 * 0.5))
for k in idx:
i, j = k // 640, k % 640
o[i][j] = a[i][j]
return Image.fromarray(o)
elif combine_choice == 'vertical': # Vertical combination
mask = np.linspace(0, 1, blend_width).reshape(-1, 1)
mask = np.tile(mask, (1, width)) # Extend mask horizontally
mask = np.vstack([np.zeros((height // 2 - blend_width // 2, width)), mask,
np.ones((height // 2 - blend_width // 2 + blend_width % 2, width))])
mask = np.tile(mask[:, :, np.newaxis], (1, 1, 3))
elif combine_choice == 'horizontal':
mask = np.linspace(0, 1, blend_width).reshape(1, -1)
mask = np.tile(mask, (height, 1)) # Extend mask vertically
mask = np.hstack([np.zeros((height, width // 2 - blend_width // 2)), mask,
np.ones((height, width // 2 - blend_width // 2 + blend_width % 2))])
mask = np.tile(mask[:, :, np.newaxis], (1, 1, 3))
elif combine_choice == 'diag1':
mask = np.ones((width, height))
mask[:width // 2, :height // 2] = 0
mask[width // 2:, height // 2:] = 0
mask = np.tile(mask[:, :, np.newaxis], (1, 1, 3))
else:
mask = np.zeros((width, height))
mask[:width // 2, :height // 2] = 1
mask[width // 2:, height // 2:] = 1
mask = np.tile(mask[:, :, np.newaxis], (1, 1, 3))
original_array = np.array(original_img, dtype=np.float32) / 255.0
augmented_array = np.array(augmented_img, dtype=np.float32) / 255.0
blended_array = (1 - mask) * original_array + mask * augmented_array
blended_array = np.clip(blended_array * 255, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
return Image.fromarray(blended_array)
RandomMix将从图像A中随机选择像素点,并由B图像的像素点替代。
Horizontal、Vertical、Diag则是会创造一个水平、垂直、对角线掩膜,用于遮盖A图的部分,并有B图替代。
下面看使用案例。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
combines=['randomMix', 'vertical','horizontal', 'diag1', 'diag2']
def draw(img,idx,title):
plt.subplot(int("15"+str(idx)))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title(title)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
p=r"C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\result1.5\result\original_resized\class0"
img1,img2=Image.open(p+"//0.jpg"),Image.open(p+"//1.jpg")
res=combine_images(img1,img2)
plt.figure(figsize=(20,6))
for i,j in enumerate(combines):
draw(combine_images(img1,img2,j),i+1,j)
plt.show()
我们选择两张不同的图像A,B,进行操作后的结果如下图所示:

ISH变换
将高分辨率图像的I分量替换低分辨率的图像,在保留结构纹理的同时获取色彩信息。
def IHS(data_low, data_high, alpha=0.7):
Trans = np.matrix([
[1. / 3., 1. / 3., 1. / 3.],
[-2 ** 0.5 / 6, -2 ** 0.5 / 6, 2 * 2 ** 0.5 / 6],
[1 / 2 ** 0.5, -1 / 2 ** 0.5, 0]
])
Itrans = np.matrix([
[1, -1 / 2 ** 0.5, 1 / 2 ** 0.5],
[1, -1 / 2 ** 0.5, -1 / 2 ** 0.5],
[1, 2 ** 0.5, 0]
])
data_high = data_high.transpose()
data_low = data_low.transpose()
data_high = data_high.reshape(3, 640 * 640)
data_low = data_low.reshape(3, 640 * 640)
AIHS = np.dot(Trans, np.matrix(data_high))
BIHS = np.dot(Trans, np.matrix(data_low))
BIHS[0, :] = BIHS[0, :] * (1 - alpha) + AIHS[0, :] * (alpha)
RGB = np.array(np.dot(Itrans, BIHS))
RGB = RGB.reshape((3, 640, 640))
return RGB.transpose()
注意,ISH变换需要较长的运行时间,而且在性能上可能提升不大。
元素乘法/加法
我们从Beta分布中选取随机数来进行元素乘法(加法):
def get_ab(beta):
if np.random.random() < 0.5:
a = np.float32(np.random.beta(beta, 1))
b = np.float32(np.random.beta(1, beta))
else:
a = 1 + np.float32(np.random.beta(1, beta))
b = -np.float32(np.random.beta(1, beta))
return a, b
# 如果传进来的是Image,需要转成array
def add(img1, img2, beta):
a, b = get_ab(beta)
img1, img2 = img1 * 2 - 1, img2 * 2 - 1
out = a * img1 + b * img2
out = (out + 1) / 2
return out
def multiply(img1, img2, beta):
a, b = get_ab(beta)
img1, img2 = img1 * 2, img2 * 2
out = (img1 ** a) * (img2.clip(1e-37) ** b)
out = out / 2
return out
叠置、前后幕等方法
def screen(img1, img2, beta):
img1, img2 = invert(img1), invert(img2)
out = multiply(img1, img2, beta)
return invert(out)
def overlay(img1, img2, beta):
case1 = multiply(img1, img2, beta)
case2 = screen(img1, img2, beta)
if np.random.random() < 0.5:
cond = img1 < 0.5
else:
cond = img1 > 0.5
return np.where(cond, case1, case2)
def darken_or_lighten(img1, img2):
if np.random.random() < 0.5:
cond = img1 < img2
else:
cond = img1 > img2
return np.where(cond, img1, img2)
def swap_channel(img1, img2):
channel = np.random.randint(3)
img1[channel] = img2[channel]
return img1
图像直接相加
def imageAdd(base_img, overlay_img, alpha=0.20):
overlay_img_resized = overlay_img.resize(base_img.size)
base_array = np.array(base_img, dtype=np.float32)
overlay_array = np.array(overlay_img_resized, dtype=np.float32)
blended_array = (1 - alpha) * base_array + alpha * overlay_array
blended_array = np.clip(blended_array, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
blended_img = Image.fromarray(blended_array)
return blended_img
def ImageListAdd(imglist, weight=None):
n=[1/len(imglist)]*len(imglist) if not weight else weight
base_array=np.array(imglist[0],dtype=np.float32)*n[0]
for idx,i in enumerate(imglist[1:]):
i=np.array(i,dtype=np.float32)
base_array+=n[idx+1]*i
blended_array = np.clip(base_array, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
blended_img = Image.fromarray(blended_array)
return blended_img