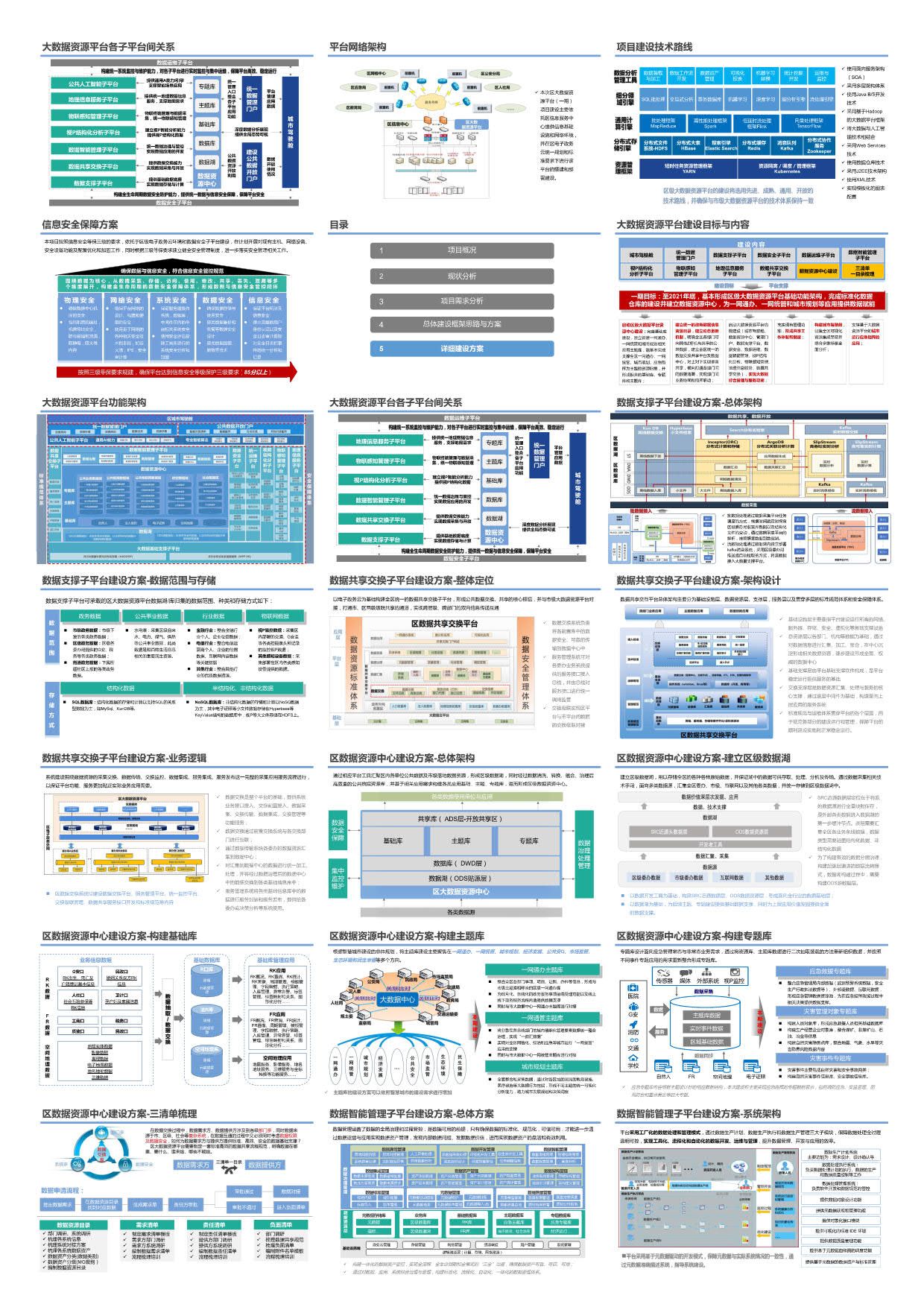
作者:CSDN @ _养乐多_
本文将介绍如何实现一个可视化图片和标签信息的查看器,代码使用python实现。点击下一张和上一张可以切换图片。

文章目录
- 一、脚本界面
- 二、完整代码
一、脚本界面
界面如下图所示,

二、完整代码
使用代码时,需要修改 class_id_to_name 还有 YOLO 格式的图片(images)文件夹路径和标签(labels)文件夹路径。
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageTk
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import os
# 创建类别 ID 到中文名称的映射
class_id_to_name = {
0: "飞机",
1: "船只",
2: "储油罐",
3: "棒球场",
4: "网球场",
5: "篮球场",
6: "跑道场地",
7: "港口",
8: "桥梁",
9: "车辆"
}
def get_image_size(image_path):
# 打开图片文件
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
# 获取图片的宽度和高度
width, height = img.size
return width, height
def read_yolo_labels(label_file, img_width, img_height):
with open(label_file, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
boxes = []
for line in lines:
parts = line.strip().split()
class_id = int(parts[0])
x_center = float(parts[1])
y_center = float(parts[2])
width = float(parts[3])
height = float(parts[4])
# 将 YOLO 格式转换为像素坐标
x_center_px = int(x_center * img_width)
y_center_px = int(y_center * img_height)
width_px = int(width * img_width)
height_px = int(height * img_height)
# 计算矩形框的左上角和右下角点
x1 = int(x_center_px - width_px / 2)
y1 = int(y_center_px - height_px / 2)
x2 = int(x_center_px + width_px / 2)
y2 = int(y_center_px + height_px / 2)
boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2, class_id))
return boxes
def draw_boxes_on_image(image_path, boxes):
# 使用 PIL 加载图片
img = Image.open(image_path)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 定义颜色和线宽
box_color = "yellow" # 选择一个亮色
line_width = 5 # 设置较粗的线宽
# 使用支持中文字符的系统字体
try:
# 尝试使用支持中文的常见系统字体
font = ImageFont.truetype("msyh.ttc", size=24) # 微软雅黑
except IOError:
# 回退到默认字体
font = ImageFont.load_default()
for (x1, y1, x2, y2, class_id) in boxes:
# 绘制矩形框
draw.rectangle([x1, y1, x2, y2], outline=box_color, width=line_width)
# 从 class_id 获取类别名称
class_name = class_id_to_name.get(class_id, "未知")
text = class_name
text_width, text_height = 50, 40 # 设定文本框的宽度和高度
text_x = x1
text_y = y1 - text_height - 5
# 绘制带背景矩形的文本
draw.rectangle([text_x, text_y, text_x + text_width, text_y + text_height], fill=box_color)
draw.text((text_x, text_y), text, fill="black", font=font)
return img
def display_image_with_boxes(image_file, label_file):
# 获取图片尺寸
img_width, img_height = get_image_size(image_file)
# 读取 YOLO 标签
boxes = read_yolo_labels(label_file, img_width, img_height)
# 在图片上绘制矩形框
img_with_boxes = draw_boxes_on_image(image_file, boxes)
return img_with_boxes
class ImageViewer:
def __init__(self, root, image_files, label_files):
self.root = root
self.image_files = image_files
self.label_files = label_files
self.current_index = 0
# 设置固定的查看器大小
self.viewer_width = 800
self.viewer_height = 600
# 初始化界面
self.init_ui()
def init_ui(self):
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self.root, width=self.viewer_width, height=self.viewer_height)
self.canvas.pack()
self.prev_button = ttk.Button(self.root, text="上一张", command=self.prev_image)
self.prev_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT)
self.next_button = ttk.Button(self.root, text="下一张", command=self.next_image)
self.next_button.pack(side=tk.RIGHT)
self.update_image()
def update_image(self):
image_file = self.image_files[self.current_index]
label_file = self.label_files[self.current_index]
img_with_boxes = display_image_with_boxes(image_file, label_file)
# 将图片转换为 Tkinter 可用格式
img_with_boxes = img_with_boxes.convert("RGB")
img_tk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img_with_boxes)
# 计算缩放比例
img_width, img_height = img_with_boxes.size
scale = min(self.viewer_width / img_width, self.viewer_height / img_height)
new_width = int(img_width * scale)
new_height = int(img_height * scale)
# 缩放图片
img_resized = img_with_boxes.resize((new_width, new_height), Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
img_tk_resized = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img_resized)
# 清除画布上的内容
self.canvas.delete("all")
# 在画布上显示图片
self.canvas.create_image(self.viewer_width / 2, self.viewer_height / 2, image=img_tk_resized)
# 保持对图像的引用
self.canvas.image = img_tk_resized
def prev_image(self):
if self.current_index > 0:
self.current_index -= 1
self.update_image()
def next_image(self):
if self.current_index < len(self.image_files) - 1:
self.current_index += 1
self.update_image()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 图片和标签文件的路径
image_folder = 'E:\\DataSet\\positive'
label_folder = 'E:\\DataSet\\yolo_labels'
# 获取所有图片和标签文件
image_files = sorted([os.path.join(image_folder, f) for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith('.jpg')])
label_files = sorted([os.path.join(label_folder, f) for f in os.listdir(label_folder) if f.endswith('.txt')])
# 创建 Tkinter 窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("图片标注查看器")
# 启动图像查看器
viewer = ImageViewer(root, image_files, label_files)
root.mainloop()