集合
- 1 HashMap 类
- 1.1 HashMap 类概述
- 1.2 HashMap 案例
- 2 TreeMap 类
- 2.1 TreeMap 类概述
- 2.2 TreeMap 案例
- 3 Properties集合
- 3.1 Properties集合概述
- 3.2 Properties基本使用
- 3.3 Properties特有方法
- 3.4 Properties和IO流相结合的方法
- 4 可变参数与不可变集合
- 4.1 可变参数
- 4.2 不可变集合
1 HashMap 类
1.1 HashMap 类概述
- HashMap底层是哈希表结构的
- 没有额外需要学习的特有方法,直接使用Map里面的方法就可以了
- 依赖hashCode方法和equals方法保证 键 的唯一
- 如果 键 要存储的是自定义对象,需要重写hashCode和equals方法(hashCode不同时,则必为不同对象。hashCode相同时,根据equlas()方法不能判断是否为同一对象。)
1.2 HashMap 案例
- 案例需求
- 创建一个HashMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是居住地 (String)。存储多个元素,并遍历。
- 要求保证键的唯一性:如果学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
- 代码实现
学生类
public class Student{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Student,String> hm = new HashMap<>();
Student s1 = new Student("xiaohei",23);
Student s2 = new Student("dapang",22);
Student s3 = new Student("xiaomei",22);
hm.put(s1,"江苏");
hm.put(s2,"北京");
hm.put(s3,"天津");
//第一种:先获取到所有的键,再通过每一个键来找对应的值
Set<Student> keys = hm.keySet();
for (Student key : keys) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "----" + value);
}
System.out.println("===================================");
//第二种:先获取到所有的键值对对象。再获取到里面的每一个键和每一个值
Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : entries) {
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "----" + value);
}
System.out.println("===================================");
//第三种:
hm.forEach( //forEach方法在Map接口的两个实现类中都是可以实现的
(Student key, String value)->{
System.out.println(key + "----" + value);
}
);
}
2 TreeMap 类
2.1 TreeMap 类概述
- TreeMap底层是红黑树结构
- 没有额外需要学习的特有方法,直接使用Map里面的方法就可以了
- 依赖自然排序或者比较器排序,对 键 进行排序
- 如果 键 存储的是自定义对象,需要实现Comparable接口或者在创建TreeMap对象时候给出比较器排序规则
2.2 TreeMap 案例
- 案例需求
- 创建一个TreeMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是籍贯(String),学生属性姓名和年龄,按照年龄进行排序并遍历
- 要求按照学生的年龄进行排序,如果年龄相同则按照姓名进行排序
- 代码实现
(1)自然排序方式
学生类
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//按照年龄进行排序
int result = o.getAge() - this.getAge(); // 从大到小排序,若是从小到大则需要为:int result = this.getAge()- o.getAge();
//次要条件,按照姓名排序。
result = result == 0 ? o.getName().compareTo(this.getName()) : result;
return result;
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建TreeMap集合对象
TreeMap<Student,String> tm = new TreeMap<>();
// 创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("xiaohei",23);
Student s2 = new Student("dapang",22);
Student s3 = new Student("xiaomei",22);
// 将学生对象添加到TreeMap集合中
tm.put(s1,"江苏");
tm.put(s2,"北京");
tm.put(s3,"天津");
// 遍历TreeMap集合,打印每个学生的信息
tm.forEach(
(Student key, String value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---" + value);
}
);
}
(2) 比较器排序
学生类
public class Student{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Student,String> tm = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
int result = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
result = result== 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : result;
return result;
}
});
Student s1 = new Student("xiaohei",23);
Student s2 = new Student("dapang",22);
Student s3 = new Student("xiaomei",22);
tm.put(s1,"江苏");
tm.put(s2,"北京");
tm.put(s3,"天津");
tm.forEach(
(Student key, String value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---" + value);
}
);
}
3 Properties集合
3.1 Properties集合概述
Properties
- 是一个Map体系的集合类
- Properties可以保存到流中或从流中加载
- 属性列表中的每个键及其对应的值都是一个字符串
创建Properties对象的时候不写泛型
3.2 Properties基本使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties prop = new Properties();
//增
prop.put("小龙女","尹志平");
prop.put("郭襄","杨过");
prop.put("黄蓉","欧阳克");
System.out.println(prop);
//删
//prop.remove("郭襄");
//System.out.println(prop);
//改
//put --- 如果键不存在,那么就添加,如果键存在,那么就覆盖.
prop.put("小龙女","杨过");
System.out.println(prop);
//查
//Object value = prop.get("黄蓉");
//System.out.println(value);
//遍历
Set<Object> keys = prop.keySet();
for (Object key : keys) {
Object value = prop.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
System.out.println("========================");
//装的是所有的键值对对象.
Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> entries = prop.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entries) {
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
3.3 Properties特有方法
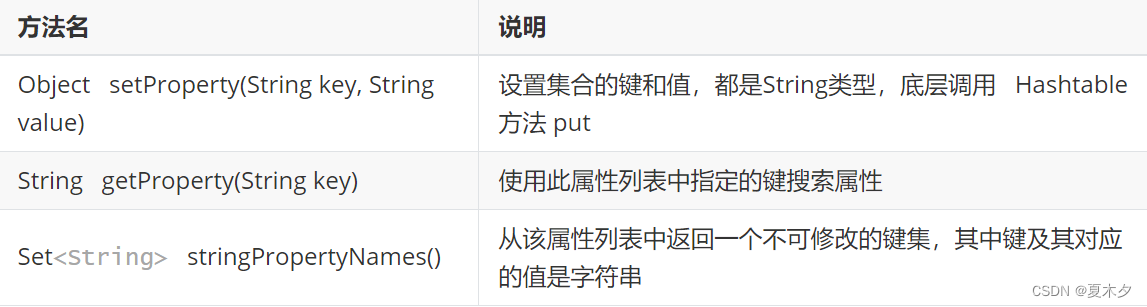
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Object setProperty(String key, String value) --- put
//设置集合的键和值,都是String类型,底层调用 Hashtable方法 put
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("江苏","南京");
prop.setProperty("安徽","南京");
prop.setProperty("山东","济南");
System.out.println(prop);
//String getProperty(String key) --- get
//使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性
String value = prop.getProperty("江苏");
System.out.println(value);
//Set<String> stringPropertyNames() --- keySet
//从该属性列表中返回一个不可修改的键集,其中键及其对应的值是字符串
Set<String> keys = prop.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
3.4 Properties和IO流相结合的方法

读(在同一目录下已存在prop.properties文件)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//读取
Properties prop = new Properties();
//prop.load(new FileReader("prop.properties"));虽然没错但是不建议这样写,因为文件无法关闭
FileReader fr = new FileReader("prop.properties");
//调用完了load方法之后,文件中的键值对数据已经在集合中了.
prop.load(fr);
fr.close();
System.out.println(prop);
}
写
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.put("zhangsan","123");
prop.put("lisi","456");
prop.put("wangwu","789");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("prop.properties");
prop.store(fw,null);//第二个参数是注释,不写的话可以传入null
fw.close();
}
4 可变参数与不可变集合
4.1 可变参数
-
可变参数介绍
- 可变参数又称参数个数可变,用作方法的形参出现,那么方法参数个数就是可变的了
- 方法的参数类型已经确定,个数不确定,我们可以使用可变参数
-
可变参数定义格式
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型… 变量名) { }
示例代码
// 需求:定义一个方法求N个数的和
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum1 = getSum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
System.out.println(sum1);
}
public static int getSum(int number,int... arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum = sum + arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
注意:
- 这里的变量其实是一个数组
- 如果一个方法有多个参数,包含可变参数,可变参数要放在最后
4.2 不可变集合
- 在List、Set、Map接口中,都存在of方法,可以创建一个不可变的集合
- 这个集合不能添加,不能删除,不能修改
- 但是可以结合集合的带参构造,实现集合的批量添加
- 在Map接口中,还有一个ofEntries方法可以提高代码的阅读性
- 首先会把键值对封装成一个Entry对象,再把这个Entry对象添加到集合当中
public static void main(String[] args) {
// static <E> List<E> of(E…elements) 创建一个具有指定元素的List集合对象
//static <E> Set<E> of(E…elements) 创建一个具有指定元素的Set集合对象
//static <K , V> Map<K,V> of(E…elements) 创建一个具有指定元素的Map集合对象
//method1();
//method2();
//method3();
//method4();
}
private static void method4() {
Map<String, String> map = Map.ofEntries(
Map.entry("zhangsan", "江苏"),
Map.entry("lisi", "北京"));
System.out.println(map);
}
private static void method3() {
Map<String, String> map = Map.of("zhangsan", "江苏", "lisi", "北京", "wangwu", "天津");
System.out.println(map);
}
private static void method2() {
//传递的参数当中,不能存在重复的元素。
Set<String> set = Set.of("a", "b", "c", "d","a");
System.out.println(set);
}
private static void method1() {
List<String> list = List.of("a", "b", "c", "d");
System.out.println(list);
//集合的批量添加。
//首先是通过调用List.of方法来创建一个不可变的集合,of方法的形参就是一个可变参数。
//再创建一个ArrayList集合,并把这个不可变的集合中所有的数据,都添加到ArrayList中。
ArrayList<String> list3 = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
System.out.println(list3);
}