1. unordered系列关联式容器
在C++98
中,
STL
提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容器,在查询时效率可达到
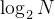 ,即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的节点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11
中,
STL
又提供了
4
个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同,该系列容器使用哈希表进行封装。
,即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的节点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11
中,
STL
又提供了
4
个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同,该系列容器使用哈希表进行封装。
2. unordered_map的介绍
1. unordered_map
是存储
<key, value>
键值对的关联式容器,其允许通过
key
快速的索引到与其对应的value
。
2.
在
unordered_map
中,键值通常用于惟一地标识元素,而映射值是一个对象,其内容与此键关联。键和映射值的类型可能不同。
3.
在内部
,unordered_map
没有对
<kye, value>
按照任何特定的顺序排序
,
为了能在常数范围内找到key
所对应的
value
,
unordered_map
将相同哈希值的键值对放在相同的桶中。
4. unordered_map
容器通过
key
访问单个元素要比
map
快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低。
5. unordered_maps
实现了直接访问操作符
(operator[ ])
,它允许使用
key
作为参数直接访问value。
6.
它的迭代器至少是前向迭代器。
3. unordered_map的使用
1. unordered_map的构造
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|
unordered_map()
|
构造不同格式的
unordered_map
对象
|
2. unordered_map的容量
| 函数声明 |
功能介绍
|
| bool empty() const |
检测
unordered_map
是否为空
|
|
size_t size() const
|
获取
unordered_map
的有效元素个数
|
3. unordered_map的迭代器
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| iterator begin() |
返回
unordered_map
第一个元素的迭代器
|
| iterator end() |
返回
unordered_map
最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器
|
| const_iterator cbegin() const |
返回
unordered_map
第一个元素的
const
迭代器
|
| const_iterator cend() const |
返回
unordered_map
最后一个元素下一个位置的
const
迭代器
|
4. unordered_map的元素访问
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| mapped_type& operator[ ] (const key_type& k) |
返回与
key
对应的
value
,没有返回一个默认值
|
注意:该函数中实际调用哈希桶的插入操作,用参数
key
与
V()
构造一个默认值往底层哈希桶中插入,如果key
不在哈希桶中,插入成功,返回
V()
,插入失败,说明
key
已经在哈希桶中,将key
对应的
value
返回。
5. unordered_map的查询
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|
iterator find(const K& key)
|
返回
key
在哈希桶中的位置
|
|
size_t count(const K& key)
|
返回哈希桶中关键码为
key
的键值对的个数
|
注意:
unordered_map
中
key
是不能重复的,因此
count
函数的返回值最大为
1
6. unordered_map的修改操作
| 函数声明 |
功能介绍
|
| pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& x ) |
向容器中插入键值对
|
| size_type erase ( const key_type& x ) |
删除容器中的键值对
|
|
void clear()
|
清空容器中有效元素个数
|
|
void swap(unordered_map&)
|
交换两个容器中的元
|
7. unordered_map的桶操作
| 函数声明 |
功能介绍
|
|
size_t bucket_count()const
|
返回哈希桶中桶的总个数
|
|
size_t bucket_size(size_t n)const
|
返回
n
号桶中有效元素的总个数
|
|
size_t bucket(const K& key)
|
返回元素
key
所在的桶号
|
4.unordered_map的模拟实现
首先我们要使用哈希表进行封装unordered_map即可,如下是HashTable.cpp的文件,有关哈希表的详细介绍,可以点击了解C++哈希表。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
namespace OpenHash
{
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;
HashNode* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
//将key转换为整型方便取模
template <class K>
struct Hash
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
//模板特化,将string类型转换为整型
template<>
class Hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t ret = 0;
for (auto e : s)
{
ret = ret * 31 + e;
}
return ret;
}
};
//实现迭代器
//因为迭代器的实现需要借助HashTable,所以需要前置定义
template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc = Hash<K>>
class HashTable;
template <class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc = Hash<K>>
struct HashTableIterator
{
typedef typename HashNode<T> Node;
typedef typename HashTableIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunc> Self;
typedef typename HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc> HashTable;
HashTable* _ht;
Node* _node;
HashTableIterator() = default;
HashTableIterator(const Node*& node, const HashTable*& ht)
:_ht(ht)
, _node(node)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
//遍历当前桶
if (_node->_next)
_node = _node->_next;
//找下一个桶
else
{
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
//获取索引值
size_t index = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_table.size();
++index;
while (index < _ht->_table.size() && _ht->_table[index] == nullptr)
++index;
if (index == _ht->_table.size())
_node = nullptr;
else
_node = _ht->_table[index];
}
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template <class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
class HashTable
{
public:
//友元(因为iterator需要用到_table)
template <class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
friend struct HashTableIterator;
typedef typename HashNode<T> Node;
typedef typename HashTableIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunc> iterator;
//构造函数
HashTable()
:_table(vector<Node*>())
, _n(0)
{}
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i])
return iterator(_table[i], this);
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
if (_table.size() == 0)
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
size_t index = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[index];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
return iterator(cur, this);
cur = cur->_next;
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
//第一次插入需要扩容
if (_table.size() == 0)
_table.resize(10);
//不能出现重复数据
if (find(key) != iterator(nullptr, this))
{
return make_pair(find(key), false);
}
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
//桶的个数是一定的,随着元素的不断插入,每个桶中元素的个数不断增多,极端情况下,
//可能会导致一个桶中链表节点非常多,会影响的哈希表的性能,因此在一定条件下需要对
//哈希表进行增容,那该条件怎么确认呢?开散列最好的情况是:每个哈希桶中刚好挂一个
//节点,再继续插入元素时,每一次都会发生哈希冲突,因此,在元素个数刚好等于桶的个数
//时,可以给哈希表增容。
//负载因子到1,需要扩容
if (_n == _table.size())
{
vector<Node*> newtable;
newtable.resize(_table.size() * 2);
//重新映射到新表
for (auto e : _table)
{
Node* cur = e;
while (cur)
{
size_t index = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.size();
cur->_next = newtable[index];
newtable[index] = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
size_t index = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node*& cur = _table[index];
while (cur)
cur = cur->_next;
cur = new Node(key);
return make_pair(iterator(cur, this), true);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
size_t index = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[index], * pre = _table[index];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
//要删除该位置第一个元素
if (cur == pre)
_table[index] = cur->_next;
else
pre->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
_n--;
return true;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table;
size_t _n;//有效数据个数
};
}unordered_map.cpp文件如下
#include"HashTable.cpp"
namespace lbk
{
template<class K,class Hash=OpenHash::Hash<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename OpenHash::HashTable<K,K,SetKeyOfT,Hash>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.find(key);
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.insert(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.erase(key);
}
private:
OpenHash::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
}