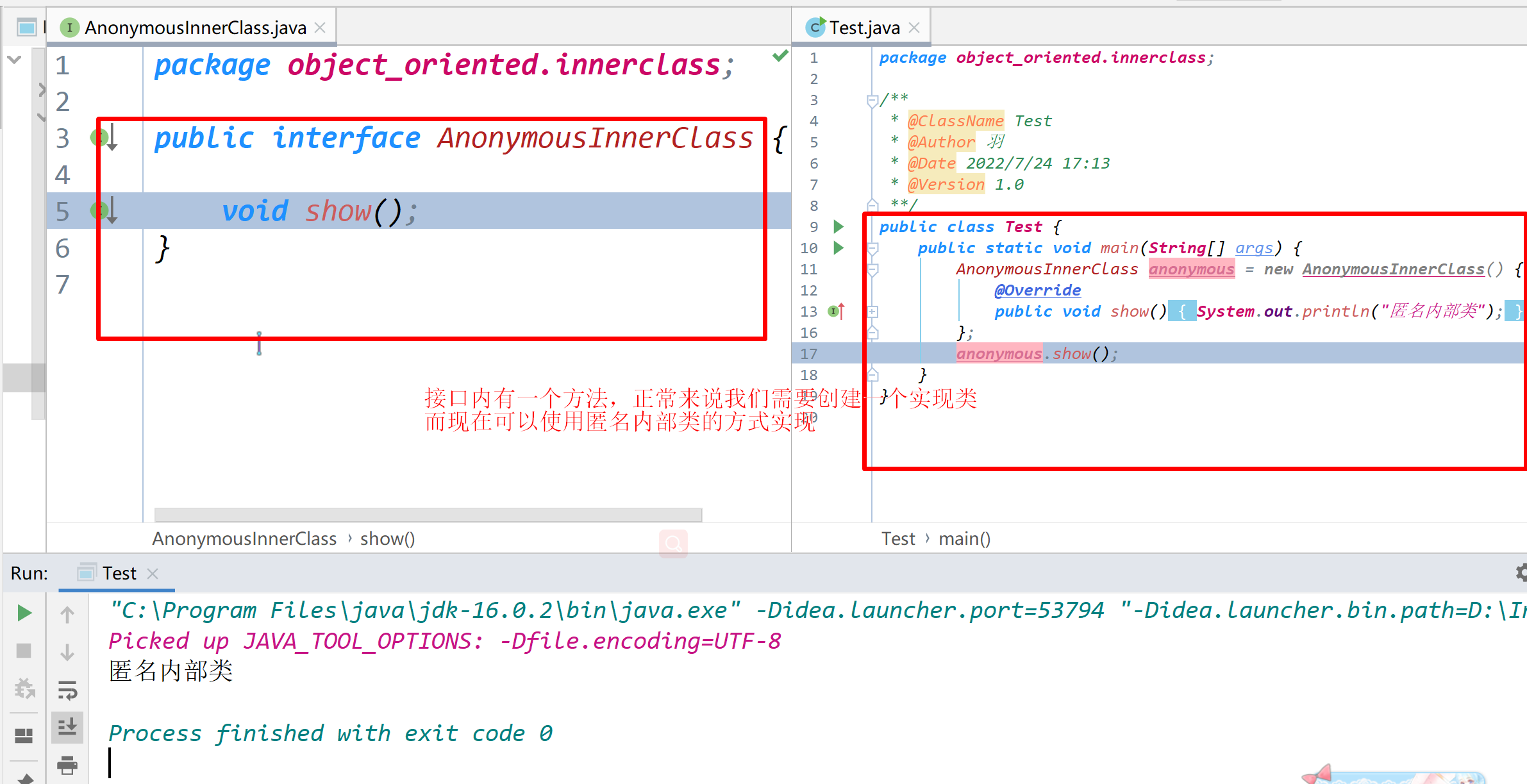
530 .二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
看完题后的思路
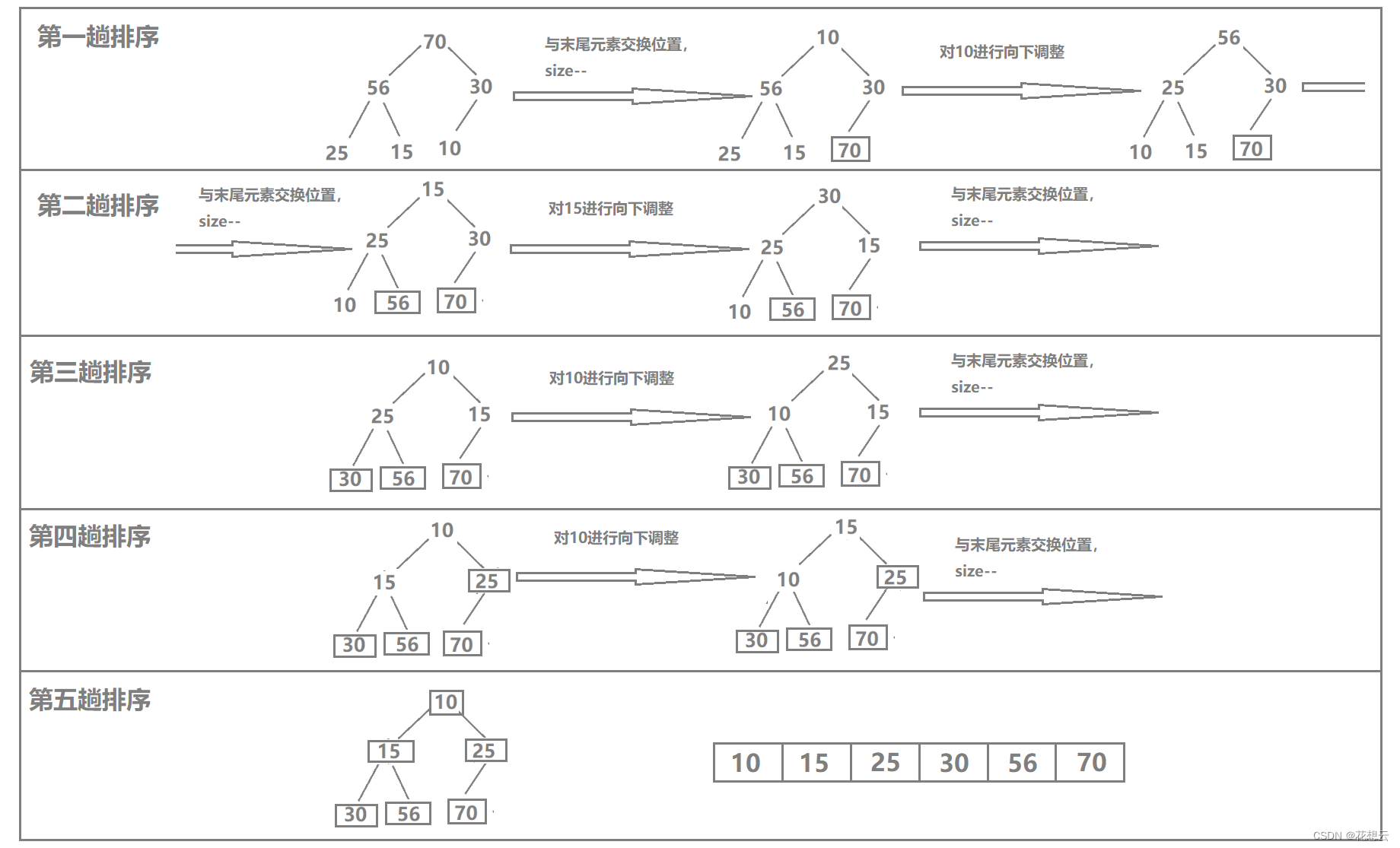
因为是二叉搜索树,所以直接按照二叉搜索树中序遍历,得到递增序列。遍历过程中一个指针指向遍历过的前一个元素
pre=null;
- void f(root)
- if root==null return
- 递归
f(left)
计算差值
pre=root
f(root)
pre可以作为一个全局变量,在操作完元素后赋下一个值
代码
TreeNode pre;
int resgetMinimumDifference=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
getMinimumDifferenceDG(root);
return resgetMinimumDifference;
}
public void getMinimumDifferenceDG(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return;
}
getMinimumDifferenceDG(root.left);
if (pre!=null){
resgetMinimumDifference=Math.min(Math.abs(root.val-pre.val),resgetMinimumDifference);
}
pre=root;
getMinimumDifferenceDG(root.right);
}
复杂度
迭代算法略
收获
本题解决了二叉树中的双指针的写法
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
看完题后的思路
使用中序遍历,if 当前元素!=pre || pre==null ,进行新一轮的计数,上一元素是否是众数,否则 次数值加一
res【】
- void f(root)
- if (root==null) return
- 中序+pre
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> findModeRes = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int count=0;
int maxCount=-1;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
findModeDG(root);
int[] res = new int[findModeRes.size()];
int i=0;
for (Integer integer : findModeRes) {
res[i++]=integer;
}
return res;
}
public void findModeDG(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null){
return;
}
findModeDG(root.left);
// 没有考虑单节点情况
if (pre==null||pre.val!=root.val){
count=1;
}else{
count++;
}
pre=root;
if (count>maxCount){
findModeRes.clear();// 清空 加新的众数
findModeRes.add(root.val);
maxCount=count;
}else if (count==maxCount){
findModeRes.add(root.val);
}
findModeDG(root.right);
}
}
复杂度
本题使用一遍迭代就求出了众数,具体做法为
- 统计元素个数
- 根据元素个数做相应操作
收获
1. 三刷写一遍
2. 求数组众数的最优写法
二叉树的最近公共祖先
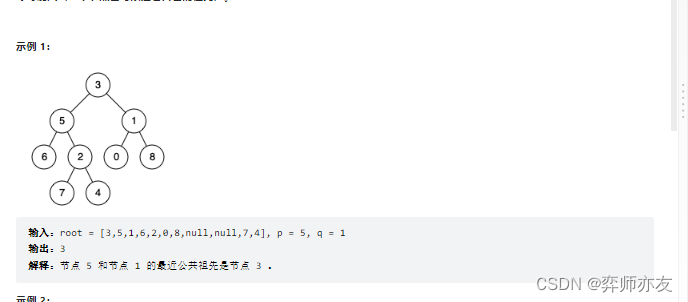
看完题后的思路
从下往上走,使用后续遍历
- node f(root)
- 递归终止条件
if root==null
return null; - 递归逻辑
if(root.val=其中一个){
return root;
}
left=f(左)
right=f(右)
if(左右全为空){
return null}
if (左右只有一个为空){
return 不为空的那个;
}
return 左右的公共节点,就是我
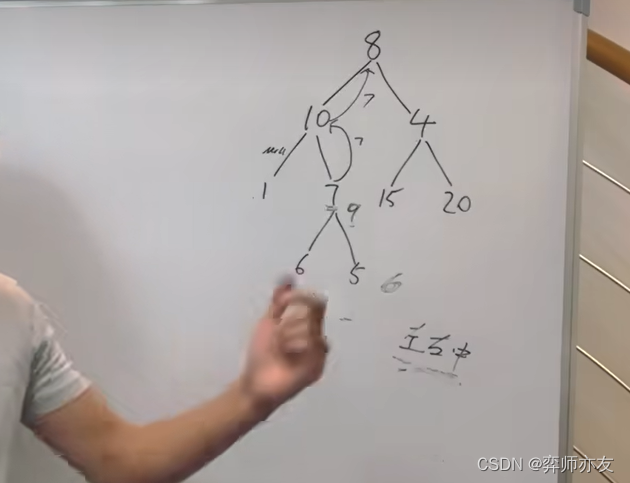
思路
本题既有从上到下,又有从下到上。前序负责从上到下,后续负责从下到上前序是,分别判断每一个节点是不是与目标节点相同,如果相同,终止递归
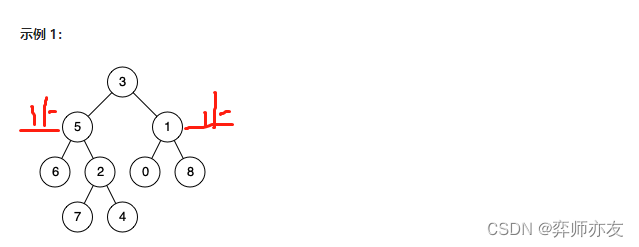
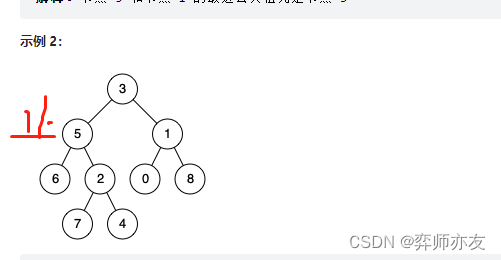
后续时,判断从下到上的返回值,如果两个返回值,则说明我是公共节点,一个返回值,该返回值是公共节点,如果没有返回值,则公共节点为空。
代码
}
//236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root==null){
return null;
}
// 先前序
if (root==p||root==q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left==null&&right==null){
return null;
}
// 有一个空
if (left==null||right==null){
return left!=null ? left : right;
}
//如果左右都不为空,返回自己
return root;
}
复杂度

收获
三刷要再刷一遍
本题的前序负责从上到下,后续负责从下到上很有知道意义