1.基本概念
队列(
Queue
):也是运算受限的线性表。是一种先进先出(
First In First Out
,简称
FIFO
)的线性表。只允许在表的一端进行插入,而在另一端进行删除。
队首(
front
) :允许进行删除的一端称为队首;
队尾(
rear
) :允许进行插入的一端称为队尾;
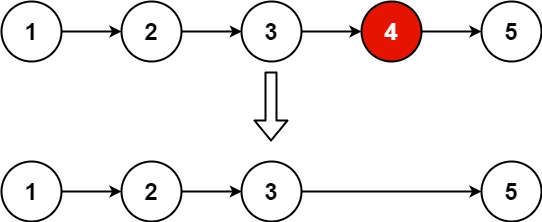
在空队列中依次加入元素
a1, a2,
…
, an
之后,
a1
是队首元素,
an
是队尾元素。显然
退出队列的次序也只能是
a1, a2,
…
, an
,即队列的修改是依先进先出的原则进行的,如
图所示
队列的抽象数据类型定义
ADT Queue{
数据对象:D ={ a
i
|a
i
∈
ElemSet, i=1, 2,
…
, n, n >= 0 }
数据关系:R = {<a
i-1
, a
i
> | a
i-1
, a
i
∈
D, i=2,3,
…
,n }
约定 a1
端为队首,
a
n
端为队尾。
基本操作:
Create
():创建一个空队列;
EmptyQue
():若队列为空,则返回
true
,否则返回
flase
;
InsertQue
(x) :向队尾插入元素
x
;
DeleteQue
(x) :删除队首元素
x
;
} ADT Queue
2.顺序队列
利用一组连续的存储单元(一维数组) 依次存放从队首到队尾的各个元素,称为顺
序队列。
静态顺序队列,其类型定义如下:
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 100
typedef struct{
int data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front;//队首指针
int rear;//队尾指针
}SqQueue;约定: front始终指向队首元素
rear始终指向队尾元素的下一个空位置
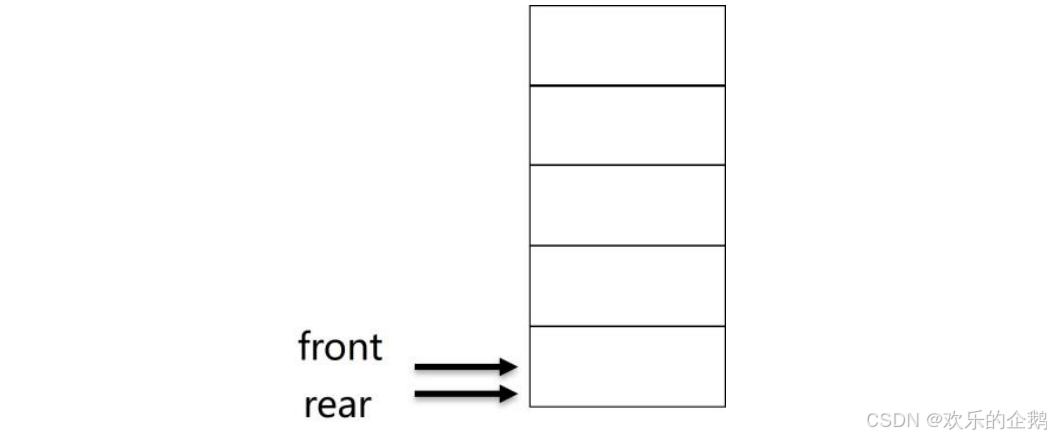
初始化:
front = rear = 0
入队:将新元素插入
rear
所指的位置,然后
rear
加
1
。
出队:删去
front
所指的元素,然后加
1
并返回被删元素。
顺序队列中存在“假溢出”现象。尽管队列中实际元素个
数可能远远小于数组大小,但可能由于尾指针巳超出向量空间
的上界而不能做入队操作。该现象称为假溢出。
为充分利用空间,克服上述“假溢出”现象的方法是:将
为队列分配的向量空间看成为一个首尾相接的圆环,并称这种
队列为循环队列
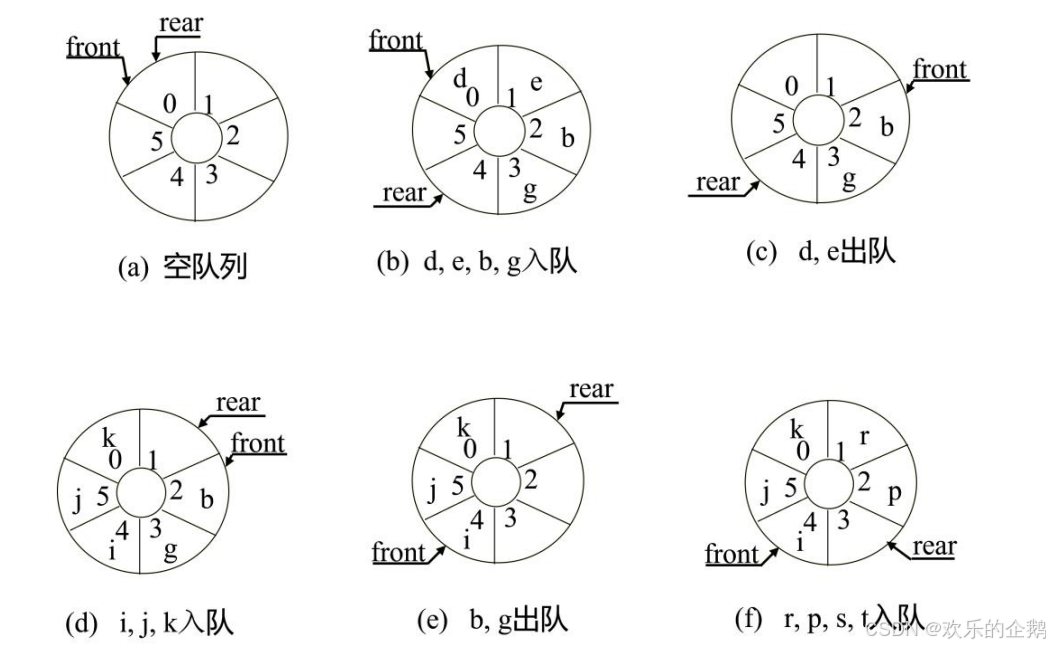
入队:
rear
=
(
rear + 1
)
% MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
出队:
front =
(
front + 1
)
% MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
循环队列中元素个数:
len =
(
rear
–
front + MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
)
% MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 100
typedef struct{
int data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front;//队首指针
int rear;//队尾指针
}SqQueue;
/**
* 约定:front始终指向队首元素
* rear始终指向队尾元素的下一个空位置
*/
SqQueue create_queue() {
SqQueue queue;
queue.front = 0;
queue.rear = 0;
return queue;
}
//将数据元素 e 插入到循环队列 Q 的队尾
bool insert_queue(SqQueue* q, int e) {
//判断队列是否满
if ((q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE == q->front) {
return false;
}
q->data[q->rear] = e;
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return true;
}
//将循环队列 Q 的队首元素出队
bool delete_queue(SqQueue* q, int *e) {
//先判断队列是否空
if (q->rear == q->front) {
return false;
}
*e = q->data[q->front];
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return true;
}
int delete_queue(SqQueue* q) {
int e;
bool ok = delete_queue(q, &e);
return e;
}
int length(const SqQueue* q) {
return (q->rear - q->front + MAX_QUEUE_SIZE) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
}
bool empty(const SqQueue* q) {
return q->front == q->rear;
}
bool full(const SqQueue* q) {
return q->front == (q->rear+1)%MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
}
void test1() {
SqQueue q = create_queue();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
insert_queue(&q, i*2);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
printf("%d,", delete_queue(&q));//2,4,6
}
printf("\n=============\n");
printf("len = %d\n", length(&q));//7
printf("\n=============\n");
SqQueue q1 = create_queue();
printf("empty ? %s\n", empty(&q1) ? "true" : "false");//true
printf("full ? %s\n", full(&q1) ? "true" : "false");//false
printf("\n=============\n");
SqQueue q2 = create_queue();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; i++) {
insert_queue(&q2, i);
}
printf("empty ? %s\n", empty(&q2) ? "true" : "false");//false
printf("full ? %s\n", full(&q2) ? "true" : "false");//true
}3.链式队列
队列的链式存储结构简称为链队列,它是限制仅在表头进行删除操作和表尾进行插入
操作的单链表。
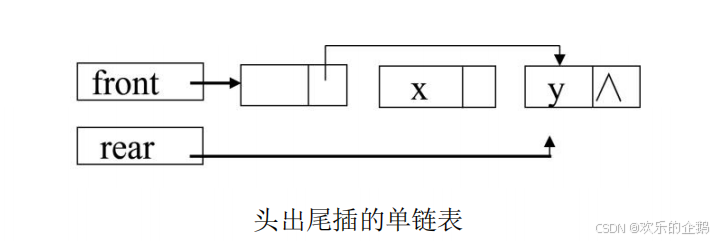
数据元素结点类型定义:
typedef struct QNode {
int data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct{
QNode* front;
QNode* rear;
}LinkQueue;
链队的操作实际上是单链表的操作,只不过是删除在表头进行,插入在表尾进行。插
入、删除时分别修改不同的指针。
typedef struct QNode {
int data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct{
QNode* front;
QNode* rear;
}LinkQueue;
/**
* 创建结点(私有函数)
*/
QNode* node_create(int data, QNode *next) {
QNode* node = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (node != nullptr) {
node->data = data;
node->next = next;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 创建链队列
*/
LinkQueue queue_create() {
LinkQueue q;
q.front = node_create(0, nullptr);
q.rear = q.front;
return q;
}
bool insert_queue(LinkQueue* q, int e) {
if (q == nullptr || q->front == nullptr) {
return false;
}
//创建结点,插入队列尾
QNode* node = node_create(e, nullptr);
q->rear->next = node;
q->rear = node;
return true;
}
bool delete_queue(LinkQueue* q, int* e) {
if (q == nullptr || q->front == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if (q->front == q->rear) {//队列为空,返回false
return false;
}
QNode* p = q->front->next;
q->front->next = p->next;
*e = p->data;
free(p);
return true;
}
int delete_queue(LinkQueue* q) {
int e;
if (false == delete_queue(q, &e)) {
return INT_MIN;
}
return e;
}
bool empty(LinkQueue* q) {
return q->front == q->rear;
}
void test() {
LinkQueue q = queue_create();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
insert_queue(&q, i * i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
printf("%d,", delete_queue(&q));
}
printf("\n=============\n");
}4.队列应用
1. 排队买东西
、打印机服务、医院的挂号系统等等
2. 树的层次遍历
3. 图的广度优先遍历