一、自定义组件
1、自定义组件
自定义组件,最基础的结构如下:
@Component
struct Header {
build() {
}
}提取头部标题部分的代码,写成自定义组件。
1、新建ArkTs文件,把Header内容写好。
2、在需要用到的地方,导入引用即可
@Component
export struct Header {
private title: ResourceStr = ''
build() {
Row() {
Text(this.title)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontSize(24)
}
.width('100%')
.margin({ bottom: 10 })
}
}import { Header } from "../conponents/CommonHeader"
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State
build() { // UI描述,内部声明式UI结构
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Header({ title: "商品列表" })
}
.width('100%')
}
.backgroundColor('#f0f8ff')
.padding(20)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
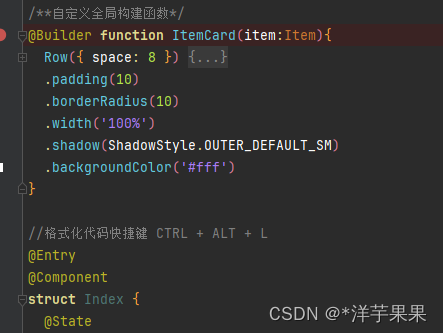
}2、构建函数
如果是仅在该页面内部运用的组件,就可以用构建函数的方式来定义组件
分两类:全局和局部,区别就是写在struct函数外还是内,若是放在struct之内,就不需要些‘function’字段了
这样封装,就保证了代码易读易维护
3、公共样式
类似的,样式也可以这样封装
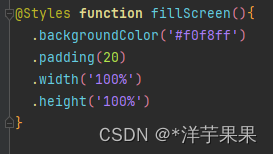

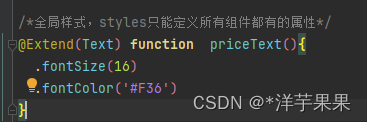
但是Styles只能封装所有组件都有的公共属性,那对于个别的如何处理呢
就需要用到Extend(注意:只能定义成全局的,不能写在struct函数内部)
二、状态管理-装饰器
1、@State
@State装饰器官网文档
@State类似于react中的UseState,只在组件内部使用
@Entry
@Component
struct StatePage {
@State message: string = "hello"
build() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(20)
.onClick(()=>{
this.message = '测试'
})
}.width('100%')
}
}2、@Props
@Prop装饰器官网文档
父组件单向传值给子组件,类似于react里的props参数,可以理解为父组件参数拷贝一份给子组件
子组件数值的变化不会同步到父组件
//子组件
@Component
struct CountDownComponent {
@Prop count: number = 0;
costOfOneAttempt: number = 1;
build() {
Column() {
if (this.count > 0) {
Text(`You have ${this.count} Nuggets left`)
} else {
Text('Game over!')
}
// @Prop装饰的变量不会同步给父组件
Button(`Try again`).onClick(() => {
this.count -= this.costOfOneAttempt;
})
}
}
}
//父组件
@Entry
@Component
struct ParentComponent {
@State countDownStartValue: number = 10;
build() {
Column() {
Text(`Grant ${this.countDownStartValue} nuggets to play.`)
// 父组件的数据源的修改会同步给子组件
Button(`+1 - Nuggets in New Game`).onClick(() => {
this.countDownStartValue += 1;
})
// 父组件的修改会同步给子组件
Button(`-1 - Nuggets in New Game`).onClick(() => {
this.countDownStartValue -= 1;
})
CountDownComponent({ count: this.countDownStartValue, costOfOneAttempt: 2 })
}
}
}3、@Link
变量与其父组件中对应的数据源建立双向数据绑定
可以理解为父组件把地址给子组件,所以改变能够同步
@Link装饰器官网文档
//子组件接收变量
@Link count: number
@Link costOfOneAttempt: number
//调用子组件,因为是引用的方式,所以要加上$
CountDownComponent({ count: $countDownStartValue})4、@Provide 和 @Consume
应用于与后代组件的双向数据同步,应用于状态数据在多个层级之间传递的场景,实现跨层级传递
就是爷爷和孙子之间直接沟通
不需要一级一级的显示传参
@Provide装饰的变量是在祖先组件中,@Consume装饰的变量是在后代组件中
感觉很方便,但一般咱不用,因为比较消耗性能
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Parent {
@Provider() str: string = 'hello';
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.str)
.onClick(() => {
this.str += '0';
})
Child()
}
}
}
@ComponentV2
struct Child {
@Consumer() str: string = 'world';
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.str)
.onClick(() => {
this.str += '0';
})
}
}
}5、@Observed 和 @ObjectLink
用于在涉及嵌套对象或数组的场景中进行双向数据同步
因为对于非简单类型,比如class、Object或者数组,是需要被@Observed装饰的,否则将观察不到其属性的变化
/**子组件定义包包的类型*/
@Observed
class Bag {
public id: number;
public size: number;
constructor(size: number) {
this.id = NextID++;
this.size = size;
}
}
@Observed
class User {
public bag: Bag;
constructor(bag: Bag) {
this.bag = bag;
}
}
/**子组件*/
@Component
struct ViewA {
label: string = 'ViewA';
//被引用的类需要用ObjectLink装饰
@ObjectLink bag: Bag;
build() {
Column() {
Text(`ViewA [${this.label}] this.bag.size = ${this.bag.size}`)
.fontColor('#ffffffff')
.backgroundColor('#ff3d9dba')
.width(320)
.height(50)
.borderRadius(25)
.margin(10)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
Button(`ViewA: this.bag.size add 1`)
.width(320)
.backgroundColor('#ff17a98d')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.bag.size += 1;
})
}
}
}
/**父组件*/
@Entry
@Component
struct ViewB {
@State user: User = new User(new Bag(0));
build() {
Column() {
ViewA({ label: 'ViewA #1', bag: this.user.bag })
.width(320)
}
}
}三、页面路由
把所有访问记录存在栈里,类似于出栈入栈,跳转就添加一条记录,回到上一页就是把当前记录弹出栈,就回到了上一页(ps:页面栈的最大容量是32)
如果新访问的页面是栈里存在的,把它挪到栈顶即可,这样节省空间性能
1、跳转
有两种方式:保留访问记录就用pushUrl,如果要销毁记录,就用replaceUrl
import router from '@ohos.router';
class DataModelInfo {
age: number = 0;
}
class DataModel {
id: number = 0;
info: DataModelInfo|null = null;
}
function onJumpClick(): void {
// 在Home页面中
let paramsInfo: DataModel = {
id: 123,
info: {
age: 20
}
};
router.pushUrl({
url: 'pages/Detail', // 目标url
params: paramsInfo // 添加params属性,传递自定义参数
}, (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(`跳转失败, ${err.code}, ${err.message}`);
return;
}
console.info('跳转成功!');
})
}2、回到上一页
返回用即可
import router from '@ohos.router';
//回退到指定的home页
router.back({
url: 'pages/Home'
});
//不传参,即是回退到上一页
//router.back();3、综合小案例
跳转到对应页面

如果新建页面时,选择的是新建page,则自动配置路径,若是选择ArkTs,则是没有的
import router from '@ohos.router';
class RouterInfo {
url: string
title: string
constructor(url: string, title: string) {
this.url = url;
this.title = title
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = '页面列表'
private routers: RouterInfo[] = [
new RouterInfo("pages/Shopping", "商品"),
new RouterInfo("pages/Mine", "我的"),
]
build() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(30)
List({ space: 15 }) {
ForEach(
this.routers,
(router: RouterInfo, index) => {
ListItem() {
this.RouterItem(router, index + 1)
}
}
)
}
}.width('100%')
}
@Builder
RouterItem(r: RouterInfo, i: number) {
Row() {
Text(i + '.').fontSize(20).fontColor(Color.White)
Blank()
Text(r.title).fontSize(20).fontColor(Color.White)
}
.width(120)
.padding(12)
.backgroundColor('#38f')
.borderRadius(20)
.onClick(() => {
router.pushUrl(
{
url: r.url,
params: i
},
router.RouterMode.Single,
err => {
if (err) {
console.log(`跳转失败${err.message}${err.code}`)
}
}
)
})
}
}
写在最后,可结合Harmony_鸿蒙专栏阅读