一.运算符
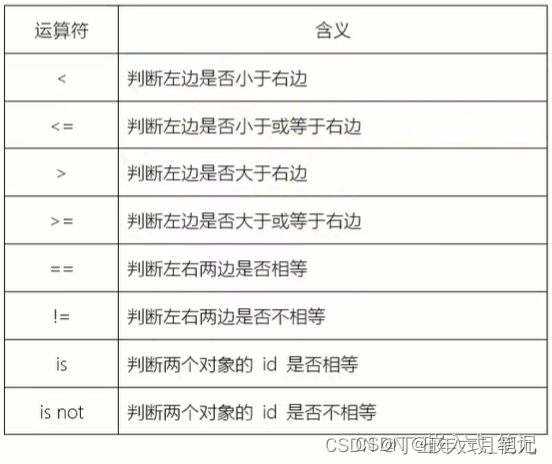
>>> 5<3
False
>>> 5<=3
False
>>> 5>3
True
>>> 5>=3
True
>>> 5==3
False
>>> 5!=3
True与操作and:
>>> 5<3 and 2<4
False>>> 5>3 and 2<4
True二.条件语句
条件分支:

while循环:

temp = input("请输入一个数据:")
guess = int(temp)
i=0
while guess != 8 and i < 3:
i = i + 1
temp = input("哎呀,猜错了,请重新输入吧:")
guess = int(temp)
if guess == 8:
print("我草,你是小甲鱼心里的蛔虫嘛?")
print("哼,猜对了也没有奖励")
else:
if guess > 8:
print("哥,大了大了~~")
else:
print("嘿,小了!小了!!")
print("游戏结束,不玩啦~~")python随机模块random
randint(x,y)函数,参数x,y表示获取随机数的范围:
>>> import random
>>> num = random.randint(1,100)
>>> print(num)
78random模块使用操作系统系统时间作为随机数种子,也就是随机数生成器内部状态:
>>> num = random.randint(1,100)
>>> print(num)
52
>>> num = random.randint(1,100)
>>> print(num)
71
>>> num = random.randint(1,100)
>>> print(num)
95三.数据类型
Python的一些数值类型:整型、布尔类型(True与False)、浮点型、e记法、复数类型等.
e记法(e4相当于10的四次方,e-10相当于10的-10次方)
>>> 1.5e4
15000.0
>>> a=0.0000000001
>>> a
1e-10类型转换:
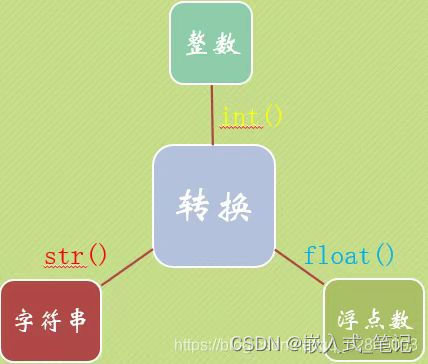
字符型转换为整型:
>>> a = '520'
>>> b = int(a)
>>> print(b)
520type()函数(可查看变量类型)
>>> type(a)
<class 'str'>
>>> type(b)
<class 'int'>isinstance()函数(用来判断两个输入参数类型是否一致)
>>> isinstance(a,str)
True
>>> isinstance(b,int)
True
>>> isinstance(b,str)
Falsepython中的浮点数精度较低
>>> 0.1+0.2
0.30000000000000004
>>> 0.3 == 0.1+0.2
Falsedecimal.Decimal()精确的计算浮点数:
>>> import decimal
>>> a = decimal.Decimal('0.1')
>>> b = decimal.Decimal('0.2')
>>> print(a + b)
0.3







![[leetcode]rotate-array 轮转数组](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/042e573364104ac8b972c8fc728593cc.png)