合并有序链表
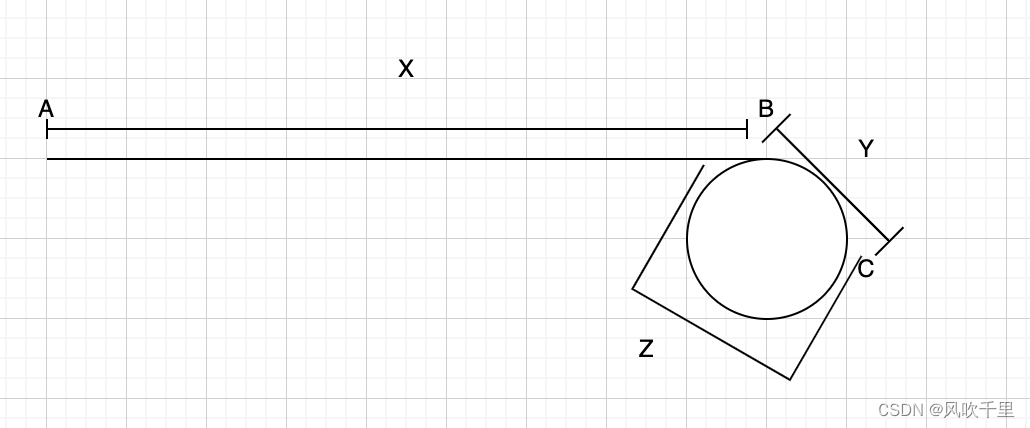
- 图解
- 代码如下
图解
虽然很复杂,但能够很好的理解怎么使用链表,以及对链表的指针类理解
代码如下
Node* merge_list_two_pointer(List& list1, List& list2)
{
Node* new_head1 = list1.head;
Node* new_head2 = list2.head;
Node* sentinel1 = list1.head;
Node* sentinel2 = list2.head;
Node* temp_head1 = NULL;
Node* temp_head2 = NULL;
int flage = 1;
//因为下面是<=,所以以list2优先为空
if (new_head1->data >= new_head2->data)
{
flage = 2;
}
while (new_head1 != NULL && new_head2 != NULL)
{
while (list1.head != NULL && list1.head->data < list2.head->data)
{
temp_head1 = list1.head;
list1.head = list1.head->next;
}
//正常两个有序列表,上面为空,
//456,123456789
if (list1.head == NULL && flage == 2)
{
temp_head1->next = list2.head;
return sentinel2;
}
//特殊情况列表,全大
//123,456
if (list1.head == NULL)
{
temp_head1->next = new_head2;
return sentinel1;
}
if (temp_head1 != NULL)
{
temp_head1->next = new_head2;
}
while (list2.head != NULL && list2.head->data <= list1.head->data)
{
temp_head2 = list2.head;
list2.head = list2.head->next;
}
//正常两个有序列表,下面为空
//123456789,456
if (list2.head == NULL && flage == 1)
{
temp_head2->next = list2.head;
return sentinel1;
}
//特殊情况列表也就是,全小
//456,123
if (list2.head == NULL)
{
//防止89,89这种类型链表跑空
temp_head2->next = list1.head;
return sentinel2;
}
//这里不需要判断这个为空。如果为空,则说明已经到达链表尾部
temp_head2->next = list1.head;
new_head1 = list1.head;
new_head2 = list2.head;
}
}




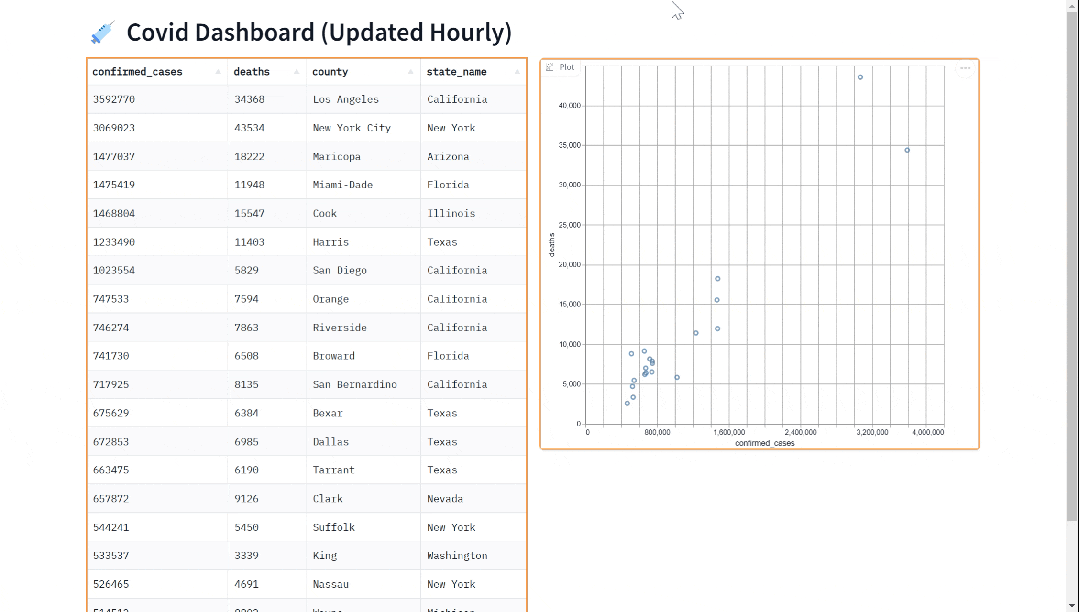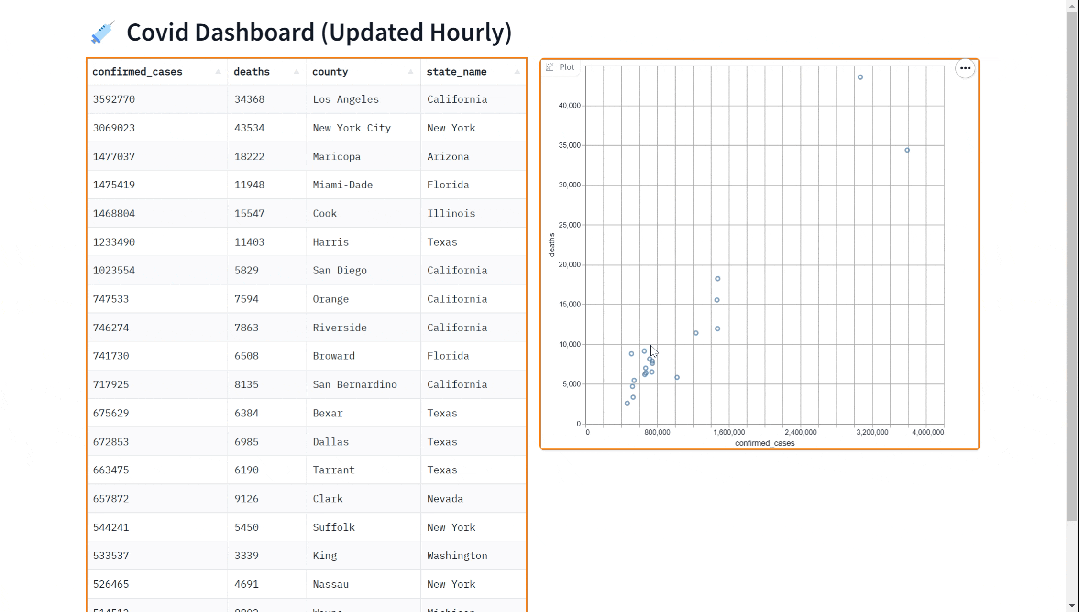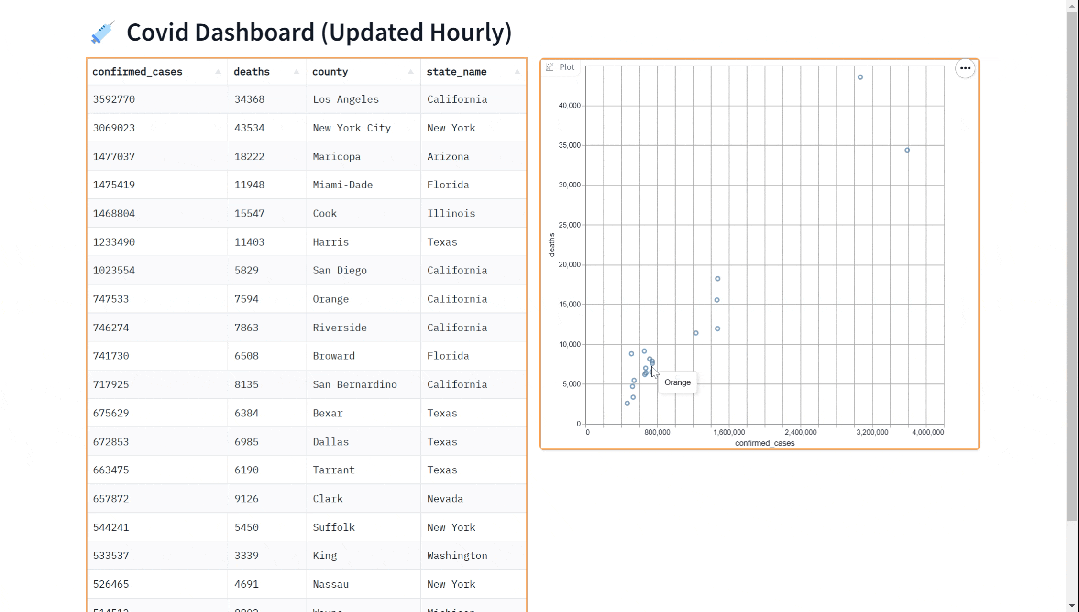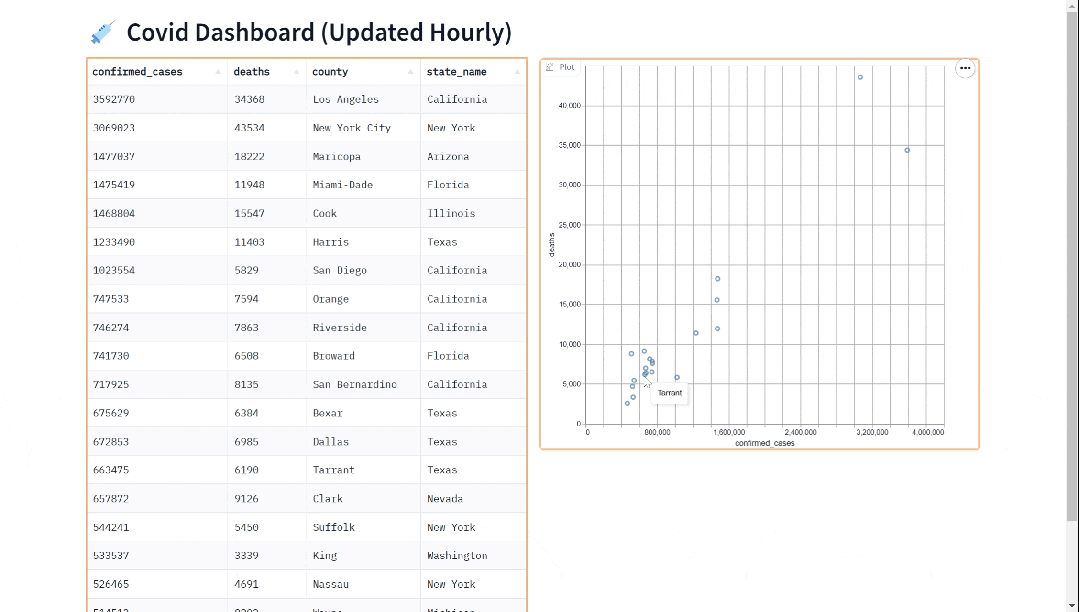


![Nuxt3 [Vue warn]: Hydration node mismatch:【解决方案】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e858816f6b8c43eeb889bad15193e7a6.png)