一.SpringFramework介绍
(一)Spring
广义上的 Spring 泛指以 Spring Framework 为基础的 Spring 技术栈。
Spring 已经不再是一个单纯的应用框架,而是逐渐发展成为一个由多个不同子项目(模块)组成的成熟技术,例如 Spring Framework、Spring MVC、SpringBoot、Spring Cloud、Spring Data、Spring Security 等,其中 Spring Framework 是其他子项目的基础。
(二)SpringFramework
Spring Framework(Spring框架)是一个开源的应用程序框架,它提供了很多功能,例如:依赖注入(Dependency Injection)、面向切面编程(AOP)、声明式事务管理(TX)等
二.Spring Ioc容器 和 核心概念
(一)组件和组件管理
注意:组件是映射到应用程序中所有可重用组件的Java对象,应该是可复用的功能对象!
- 组件一定是对象
- 对象不一定是组件

组件可以完全交给Spring 框架进行管理,Spring框架替代了程序员原有的new对象和对象属性赋值动作等!
Spring具体的组件管理动作包含:
- 组件对象实例化
- 组件属性属性赋值
- 组件对象之间引用
- 组件对象存活周期管理
- ......
Spring 充当一个组件容器,创建、管理、存储组件,减少了我们的编码压力,让我们更加专注进行业务编写!
(二)Spring Ioc容器和容器实现
1.Spring Ioc容器介绍
Spring IoC 容器,负责实例化、配置和组装 bean(组件)。
容器通过读取配置元数据来获取有关要实例化、配置和组装组件的指令。配置元数据以 XML、Java 注解或 Java 代码形式表现。
2.Spring Ioc容器的具体接口和实现类
BeanFactory:接口提供了一种高级配置机制,能够管理任何类型的对象,提供了配置框架和基本功能,它是SpringIoC容器标准化超接口!
ApplicationContext:是 BeanFactory 的子接口,添加了更多特定于企业的功能!
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:通过文件系统路径读取 XML 格式的配置文件创建 IOC 容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:通过读取类路径下的 XML 格式的配置文件创建 IOC 容器对象
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:通过读取Java配置类创建 IOC 容器对象
WebApplicationContext:专门为 Web 应用准备,基于 Web 环境创建 IOC 容器对象,并将对象引入存入 ServletContext 域中
Spring框架提供了多种配置方式:XML配置方式、注解方式和Java配置类方式
(三)IoC 和 DI
Ioc (Inversion of Control):控制反转
当应用程序需要使用一个对象时,不再是应用程序直接创建该对象,而是由 IoC 容器来创建和管理,即控制权由应用程序转移到 IoC 容器中,也就是“反转”了控制权
DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入
DI 是指在组件之间传递依赖关系的过程中,将依赖关系在容器内部进行处理,这样就不必在应用程序代码中硬编码对象之间的依赖关系,实现了对象之间的解耦合。在 Spring 中,DI 是通过 XML 配置文件或注解的方式实现的。它提供了三种形式的依赖注入:构造函数注入、Setter 方法注入和接口注入。
三.Spring Ioc实践和应用
(一)Spring Ioc/DI 实现步骤
1.配置
配置元数据,既是编写交给SpringIoC容器管理组件的信息,配置方式有三种:xml,注解,配置类.
2.实例化Ioc容器
提供给 ApplicationContext 构造函数的位置路径是资源字符串地址,允许容器从各种外部资源(如本地文件系统、Java CLASSPATH 等)加载配置元数据。
创建容器 选择合适的容器 实现即可
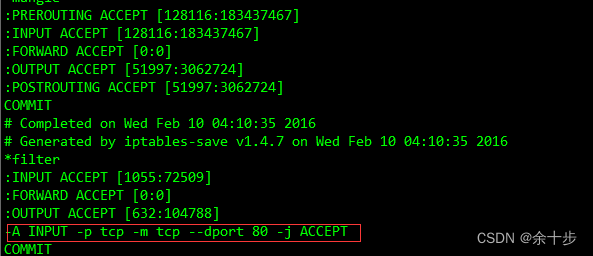
编译后,如果配置文件放在在classes文件里用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public void createIoc() {
//方式1:方式1在源码中使用了方式2
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-03.xml");
//方式2:先创建ioc容器对象,再指定配置文件,再刷新
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
applicationContext1.setConfigLocations("spring-03.xml");//外部配置文件的设置
applicationContext1.refresh();//调用ioc和di的流程
}3.获得Bean组件
ApplicationContext 是一个高级工厂的接口,能够维护不同 bean 及其依赖项的注册表。通过使用方法 T getBean(String name, Class requiredType) ,您可以检索 bean 的实例。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
组件的信息 ioc的配置->applicationContext读取->实例化对象
-->
<bean id="happyComponent" class="com.yan.Ioc_03.HappyComponent"/>
</beans> @Test
public void getBeanFormIoc() {
//创建ioc容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
applicationContext.setConfigLocations("spring-03.xml");
applicationContext.refresh();
//读取ioc容器的组件
//方案1:直接根据beanId获取即可 返回值类型是Objec 需要强转,不推荐
HappyComponent happyComponent1 = (HappyComponent) applicationContext.getBean("happyComponent");
//方案2:根据beanId,同时指定bean的类型Class
HappyComponent happyComponent2 = applicationContext.getBean("happyComponent", HappyComponent.class);
//方案3:直接根据类型获取
//根据Bean的类型 获取,同一类型在IOC容器中只能有一个bean!!!!!!
//如果有多个同类型bean,则会报NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException
//ioc的配置一定是实现类,但是可以根据接口类型获取值
HappyComponent happyComponent3 = applicationContext.getBean(HappyComponent.class);
happyComponent3.doWork();
System.out.println(happyComponent1 == happyComponent2);//true
System.out.println(happyComponent2 == happyComponent3);//true
}(二)基于XML方式
1.组件信息声明配置
通过定义XML配置文件,声明组件类信息,交给 Spring 的 IoC 容器进行组件管理
(1)准备项目
a.创建maven工程(spring-ioc-xml-01)
b.导入SpringIoC相关依赖
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<!--当你引入Spring Context依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>(2)基于无参构造函数
<bean 一个组件信息 一个组件对象
id 组件的标识 方便后期读取
class 组件的类的全限定符
将一个组件类,声明两个组件信息,默认是单例模式,会实例化两个组件对象
a.准备组件类
public class HappyComponent {
}b.编写xml配置文件
<bean id="happyComponent1" class="com.yan.Ioc_01.HappyComponent"/>
<bean id="happyComponent2" class="com.yan.Ioc_01.HappyComponent"/>要求当前组件类必须包含无参数构造函数!
(3)基于静态工厂方法实例化
a.准备组件类
public class ClientService {
private static ClientService clientService = new ClientService();
private ClientService() {
}
public static ClientService createInstance() {
return clientService;
}
}b.编写配置文件
<!--
静态工厂类如何工厂方法进行ioc配置
id="组件的标识"
class ="工厂类的的全限定"
factory-method=静态工厂方法"
-->
<bean id="clientService" class="com.yan.Ioc_01.ClientService" factory-method="createInstance"/>
(4)基于基于静态工厂方法实例化
a.准备组件类
public class DefaultServiceLocator {
private static ClientServiceImpl clientService = new ClientServiceImpl();
public ClientServiceImpl createClientServiceInstance() {
return clientService;
}
}
b.编写配置文件
<!--1.配置工厂类的组件信息-->
<bean id="defaultServiceLocator" class="com.yan.Ioc_01.DefaultServiceLocator"/>
<!--2.
facctory-bean 属性:指定当前容器中工厂Bean的名称
factory-method:指定实例工厂方法名,注意实例方法必须是非static
-->
<bean id="clientService2" factory-bean="defaultServiceLocator" factory-method="createClientServiceInstance"/>2.组件依赖注入配置
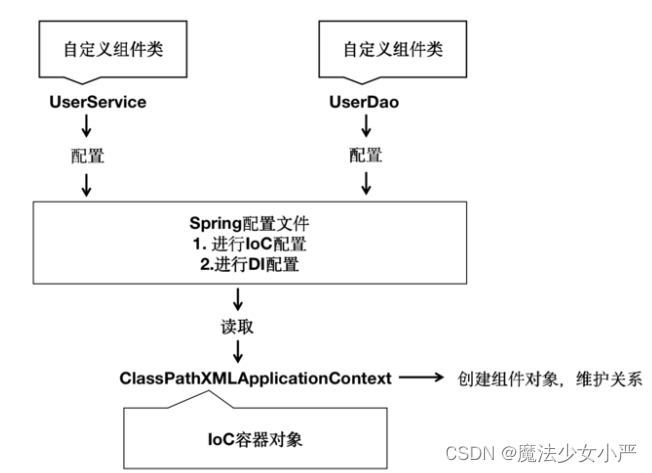
通过配置文件,实现IoC容器中Bean之间的引用(依赖注入DI配置)
主要涉及注入场景:基于构造函数的依赖注入和基于 Setter 的依赖注入
(1)基于构造函数的依赖注入(单个构造参数)
springioc容器是一个高级容器,内部有缓存,先创建对象,再进行属性赋值
引用和被引用的组件,必须全部在ioc容器
a.准备实体类
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private int age;
private String name;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}b.编写配置文件
<!--单个构造参数注入-->
<!--步骤1 将他们都存在ioc容器-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.UserDao"/>
<bean id="userService" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.UserService">
<!--步骤2 构造参数传值 di的配置
<constructor-arg 构造参数传值的di配置
value = 直接属性值 String name="二狗子" int age="18"
ref = 引用其他的bean id值
-->
<constructor-arg ref="userDao"/>
</bean>(2) 基于构造函数的依赖注入(多构造参数解析)
a.准备实体类
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private int age;
private String name;
public UserService(int age, String name, UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}b.编写配置文件
方式一:
<!--多个构造参数注入-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.UserDao"/>
<bean id="userService1" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.UserService">
<!--构造参数的顺序填写-->
<constructor-arg value="18"/>
<constructor-arg value="二狗"/>
<constructor-arg ref="userDao"/>
</bean>方式二:
<!--多个构造参数注入-->
<bean id="userService1" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.UserService">
<!--构造参数的名字进行填写,不用考虑顺序 name=构造参数的名字-->
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"/>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="二狗"/>
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>方式三:
<!--多个构造参数注入-->
<bean id="userService1" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.UserService">
<!--构造参数的下角标进行填写,不用考虑顺序 index=构造参数的下角标 从左到右 从0开始 -->
<constructor-arg index="0" name="age" value="18"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" name="name" value="二狗"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>(3)基于Setter方法依赖注入
a.准备实体类
public class SimpleMovieLister {
private MovieFinder movieFinder;
private String movieName;
public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {
this.movieFinder = movieFinder;
}
public void setMovieName(String movieName) {
this.movieName = movieName;
}
}b.编写配置文件
<!--触发setter方法进行注入-->
<bean id="movieFinder" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.MovieFinder"/>
<bean id="simpleMovieLister" class="com.yan.Ioc_02.SimpleMovieLister">
<!--
namev->属性名 setter方法的去set和首字母小写的值,调用set方法
setMovieFinder -> movieFinder
value | ref 二选一 value-"直接属性值" ref-"其他bean的Id"
-->
<property name="movieFinder" ref="movieFinder"/>
<property name="movieName" value="消失的她"/>
</bean>3. 组件的作用域和周期方法配置
(1)周期方法
a.周期方法概念
我们可以在组件类中定义方法,然后当IoC容器实例化和销毁组件对象的时候进行调用!这两个方法我们成为生命周期方法!
类似于Servlet的init/destroy方法,我们可以在周期方法完成初始化和释放资源等工作。
b.周期方法声明
public class BeanOne {
//周期方法要求: 方法命名随意,但是要求方法必须是 public void 无形参列表
public void init() {
// 初始化逻辑
System.out.println("初始化!");
}
}public class BeanTwo {
public void cleanup() {
// 释放资源逻辑
System.out.println("销毁!");
}
}c.周期方法的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beans>
<!--
init-method=初始化方法
destroy-method=销毁方法
spring ioc容器就会在对应的时间结点回调对应的方法,我们可以在其中写对应的业务
-->
<bean id="beanOne" class="com.yan.Ioc_04.BeanOne" init-method="init"/>
<bean id="beanTwo" class="com.yan.Ioc_04.BeanTwo" destroy-method="cleanup"/>
</beans>
</beans>(2)组件作用域
a.作用域概念
`<bean` 标签声明Bean,只是将Bean的信息配置给SpringIoC容器!
在IoC容器中,这些标签对应的信息转成Spring内部 BeanDefinition 对象,BeanDefinition 对象内,包含定义的信息
SpringIoC容器可以可以根据BeanDefinition对象反射创建多个Bean对象实例,具体创建多少个Bean的实例对象,由Bean的作用域Scope属性指定!
b.作用域可选值
singleton:在 IOC 容器中,这个 bean 的对象始终为单实例,默认值,在IOC 容器初始化时创建对象
prototype:这个 bean 在 IOC 容器中有多个实例,获取 bean 时创建对象
c.作用域配置
<!--bean的作用域
准备两个引用关系的组件类即可!!
-->
<!-- scope属性:取值singleton(默认值),bean在IOC容器中只有一个实例,IOC容器初始化时创建对象 -->
<!-- scope属性:取值prototype,bean在IOC容器中可以有多个实例,getBean()时创建对象 -->
<bean id="happyMachine8" scope="prototype" class="com.atguigu.ioc.HappyMachine">
<property name="machineName" value="happyMachine"/>
</bean>
<bean id="happyComponent8" scope="singleton" class="com.atguigu.ioc.HappyComponent">
<property name="componentName" value="happyComponent"/>
</bean>4.FactoryBean
(1)简介
用于配置复杂的Bean对象,可以将创建过程存储在FactoryBean 的getObject方法!
FactoryBean 接口提供三种方法:
T getObject()
返回此工厂创建的对象的实例。该返回值会被存储到IoC容器!
boolean isSingleton()
如果此 FactoryBean 返回单例,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。此方法的默认实现返回 true (注意,lombok插件使用,可能影响效果)
Class getObjectType()
返回 getObject() 方法返回的对象类型,如果事先不知道类型,则返回 null
(2)配置
a.准备实现类
public class JavaBean {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "JavaBean{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}package com.yan.Ioc_05;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
/**
* 制造JavaBean的工厂的bean对象
* <p>
* 步骤:
* 1.实现FactoryBean接口<返回值泛型>
*/
public class JavaBeanFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<JavaBean> {
private String name;
@Override
public JavaBean getObject() throws Exception {
//使用自己的方式实例化对象
JavaBean javaBean = new JavaBean();
javaBean.setName(name);
return javaBean;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return JavaBean.class;
}
//默认单例
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return FactoryBean.super.isSingleton();
}
}
b.配置实现类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--id:getObject方法返回的对象的标识-->
<!--Class:factoryBean标准化工厂方法-->
<!--工厂bean的标识 &id值 &javaBean-->
<bean id="javaBean" class="com.yan.Ioc_05.JavaBeanFactoryBean">
<!--
要给javaBean的name赋值,需要在JavaBeanFactoryBean的方法中给javaBean赋值
此位置是给JavaBeanFactoryBean配置的
-->
<property name="name" value="二狗"/>
</bean>
</beans>(3)FactoryBean和BeanFactory区别
FactoryBean 是 Spring 中一种特殊的 bean,可以在 getObject() 工厂方法自定义的逻辑创建Bean!是一种能够生产其他 Bean 的 Bean。FactoryBean 在容器启动时被创建,而在实际使用时则是通过调用 getObject() 方法来得到其所生产的 Bean。因此,FactoryBean 可以自定义任何所需的初始化逻辑,生产出一些定制化的 bean。
BeanFactory 是 Spring 框架的基础,其作为一个顶级接口定义了容器的基本行为,例如管理 bean 的生命周期、配置文件的加载和解析、bean 的装配和依赖注入等。BeanFactory 接口提供了访问 bean 的方式,例如 getBean() 方法获取指定的 bean 实例。它可以从不同的来源(例如 Mysql 数据库、XML 文件、Java 配置类等)获取 bean 定义,并将其转换为 bean 实例。同时,BeanFactory 还包含很多子类(例如,ApplicationContext 接口)提供了额外的强大功能。
(三)基于注解方式
和 XML 配置文件一样,注解本身并不能执行,注解本身仅仅只是做一个标记,具体的功能是框架检测到注解标记的位置,然后针对这个位置按照注解标记的功能来执行具体操作。
本质上:所有一切的操作都是 Java 代码来完成的,XML 和注解只是告诉框架中的 Java 代码如何执行。
1.Bean注解的标记和扫描
(1)导入依赖pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<!--当你引入Spring Context依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>(2)准备组件
public class XxxController {
}
public class XxxDao {
}
public class XxxService {
}
(3)添加注解
标记注解 @Component @Controller @Repository @Service
@Controller
public class XxxController {
}
@Repository("ergou")
public class XxxDao {
}
@Service
public class XxxService {
}(4)配置文件确定扫描范围
普通配置包扫描
base-package:指定容器取哪些包下查找注解类 ioc容器
多个包用逗号相隔开
指定包,相当于指定了子包中的所有类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--
1.普通配置包扫描
base-package:指定容器取哪些包下查找注解类 ioc容器
多个包用逗号相隔开
指定包,相当于指定了子包中的所有类
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.yan.Ioc_01"/>
</beans>指定包,但排除注解
<!-- context:exclude-filter标签:指定排除规则 -->
<!-- type属性:指定根据什么来进行排除,annotation取值表示根据注解来排除 -->
<!-- expression属性:指定排除规则的表达式,对于注解来说指定全类名即可 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.yan">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
</context:component-scan>仅扫描指定的组件
仅扫描 = 关闭默认规则 + 追加规则
use-default-filters属性:取值false表示关闭默认扫描规则
context:include-filter标签:指定在原有扫描规则的基础上追加的规则
<context:component-scan base-package="com.yan.Ioc_01" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
</context:component-scan>(5)组件BeanName问题
现在使用注解后,每个组件仍然应该有一个唯一标识。
默认情况:
类名首字母小写就是 bean 的 id
使用value属性指定:
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
}当注解中只设置一个属性时,value属性的属性名可以省略:
@Service("smallDog")
public class SoldierService {
}2.组件的作用域和周期注解
(1)注解
@Scope:不指定@Scope的情况下,所有的bean都是单实例的bean
singleton 在 IOC 容器中,这个 bean 的对象始终为单实例 IOC 容器初始化时创建对象 默认
prototype 这个 bean 在 IOC 容器中有多个实例 获取 bean 时
@PostConstruct 注解 :指定初始化方法
@PreDestroy 注解:指定销毁方法
(2)配置
@Scope(scopeName = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)//单例 默认值
@Component
public class JavaBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
//周期方法命名随意 但必须public void
System.out.println("初始化方法------");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("销毁方法-----");
}
}3.Bean属性赋值(引用类型自动装配)
(1)自动装配
a前提
参与自动装配的组件(需要装配、被装配)全部都必须在IoC容器中
b.注解
@Autowired注解
在成员变量上直接标记@Autowired注解即可,不需要提供setXxx()方法
boolean required() default true;必须有对应类型的组件
boolean required() false; 佛性装配,可以没有对应的组件 后面可能会出现空指针报错
同一类型有多个对应的组件,Autowired会报错
解决方法:
方法一:
使用@Autowired和 @Qualifier(value = "xxxxx")
用Qualifier 注释指定获得bean的id,不能单独使用,必须配合Autowired
方法二:
使用@Resource注解
Autowired (required=true) + Qualifier(value=userServiceImpl) = Resource(name="userServiceImpl")
如果没有指定name,先根据属性名查找IoC中组件xxxService
如果没有指定name,并且属性名没有对应的组件,会根据属性类型查找
@Resource注解属于JDK扩展包,所以不在JDK当中,需要额外引入以下依赖:【高于JDK11或低于JDK8需要引入以下依赖】
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>(2)代码实现
public interface UserService {
public String show();
}
@Controller
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService
{
@Override
public String show() {
return "";
}
}
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired(required = false)
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
public void show() {
//调用业务层show方法
}
}@Controller
public class XxxController {
/**
* 1. 如果没有指定name,先根据属性名查找IoC中组件xxxService
* 2. 如果没有指定name,并且属性名没有对应的组件,会根据属性类型查找
* 3. 可以指定name名称查找! @Resource(name='test') == @Autowired + @Qualifier(value='test')
*/
@Resource
private XxxService xxxService;
//@Resource(name = "指定beanName")
//private XxxService xxxService;
public void show(){
System.out.println("XxxController.show");
xxxService.show();
}
}4.Bean属性赋值(基本类型属性赋值)
@Value 通常用于注入外部化属性
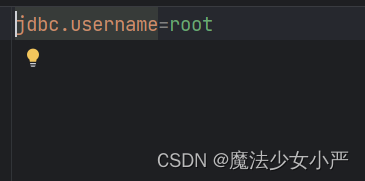
(1)声明配置
创建一个jdbc.properties文件
(2)xml引入外部配置
<!-- 引入外部配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="application.properties" />(3)@Value注解读取配置
${key} 取外部配置key对应的值!
${key:defaultValue} 没有key,可以给与默认值
@Component
public class JavaBean12 {
/**
* 方案1:直接赋值
* 方案2:注解赋值 value
* 引入默认值 @Value(${key:默认值})
*/
private String name = "二狗子";
@Value("19")
private int age;
@Value("${jdbc.username:admin}")//默认值admin
private String username;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "JavaBean{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
'}';
}
}(四)基于配置类方法
配置类
将一个普通的类标记为 Spring 的配置类 @Configuration 注解
包扫描注释配置 @ComponentScan({""})
引用外部的配置文件 @PropertySource(value = "classpath:jdbc.properties")
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
//标注当前类是配置类,替代application.xml
@Configuration
//使用注解读取外部配置,替代 <context:property-placeholder标签
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
//使用@ComponentScan注解,可以配置扫描包,替代<context:component-scan标签
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.yan.components"})
public class MyConfiguration {
}2.实例化IoC容器
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 根据配置类创建 IOC 容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainerAnnotation =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfiguration.class);// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext-IOC容器对象
ApplicationContext iocContainerAnnotation =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//外部设置配置类
iocContainerAnnotation.register(MyConfiguration.class);
//刷新后方可生效!!
iocContainerAnnotation.refresh();
3.@Bean定义组件
需求:将Druid连接池对象存储到IoC容器
需求分析:第三方jar包的类,添加到ioc容器,无法使用@Component等相关注解!因为源码jar包内容为只读模式!
(1)xml实现
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 给bean的属性赋值:引入外部属性文件 -->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
</beans>(2)配置类实现
可以使用方法返回值+@Bean注解
//标注当前类是配置类,替代application.xml
@Configuration
//引入jdbc.properties文件
@PropertySource({"classpath:application.properties","classpath:jdbc.properties"})
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.yan.components"})
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
public DataSource createDataSource(@Value("${jdbc.user}") String username,
@Value("${jdbc.password}")String password,
@Value("${jdbc.url}")String url,
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")String driverClassName){
//使用Java代码实例化
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
//返回结果即可
return dataSource;
}
}(3)@Bean生成BeanName问题
缺省情况下,Bean 名称与方法名称相同
指定@Bean的名称:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean("myThing") //指定名称
public Thing thing() {
return new Thing();
}
}(4)@Bean 初始化和销毁方法指定
public class BeanOne {
public void init() {
// initialization logic
}
}
public class BeanTwo {
public void cleanup() {
// destruction logic
}
}
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init")
public BeanOne beanOne() {
return new BeanOne();
}
@Bean(destroyMethod = "cleanup")
public BeanTwo beanTwo() {
return new BeanTwo();
}
}(5)@Bean Scope作用域
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public Encryptor encryptor() {
// ...
}
}(6)@Bean方法直接的依赖
方式一
直接调用方法返回 Bean 实例,虽然是方法调用,也是通过IoC容器获取对应的Bean
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean
public HappyMachine happyMachine(){
return new HappyMachine();
}
@Bean
public HappyComponent happyComponent(){
HappyComponent happyComponent = new HappyComponent();
//直接调用方法即可!
happyComponent.setHappyMachine(happyMachine());
return happyComponent;
}
}方式二
通过方法参数传递 Bean 实例的引用来解决 Bean 实例之间的依赖关系
可以直接在形参列表接收IoC容器中的Bean!
情况1: 如果只有一个,直接指定类型即可,Ioc容器会注入,要求必须有对应类型的组件
情况2: 如果有多个bean,(HappyMachine 名称 ) 形参名称等于要指定的bean名称!
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean
public HappyMachine happyMachine(){
return new HappyMachine();
}
@Bean
public HappyComponent happyComponent(HappyMachine happyMachine){
HappyComponent happyComponent = new HappyComponent();
//赋值
happyComponent.setHappyMachine(happyMachine);
return happyComponent;
}
}4.@Import注解
@Import 注释允许从另一个配置类加载 @Bean 定义
@Configuration
public class ConfigA {
@Bean
public A a() {
return new A();
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(ConfigA.class)
public class ConfigB {
@Bean
public B b() {
return new B();
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigB.class);
// now both beans A and B will be available...
A a = ctx.getBean(A.class);
B b = ctx.getBean(B.class);
}5.三种配置方式总结
(1)XML方式
1. 所有内容写到xml格式配置文件中
2. 声明bean通过<bean标签
3. <bean标签包含基本信息(id,class)和属性信息 <property name value / ref
4. 引入外部的properties文件可以通过<context:property-placeholder
5. IoC具体容器实现选择ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象
(2)XML方式+注解
1. 注解负责标记IoC的类和进行属性装配
2. xml文件依然需要,需要通过<context:component-scan标签指定注解范围
3. 标记IoC注解:@Component,@Service,@Controller,@Repository
4. 标记DI注解:@Autowired @Qualifier @Resource @Value
5. IoC具体容器实现选择ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象
(3)配置类+注解
1. 完全注解方式指的是去掉xml文件,使用配置类 + 注解实现
2. xml文件替换成使用@Configuration注解标记的类
3. 标记IoC注解:@Component,@Service,@Controller,@Repository
4. 标记DI注解:@Autowired @Qualifier @Resource @Value
5. <context:component-scan标签指定注解范围使用@ComponentScan(basePackages = {""})替代
6. <context:property-placeholder引入外部配置文件使用@PropertySource({"classpath:application.properties","classpath:jdbc.properties"})替代
7. <bean 标签使用@Bean注解和方法实现
8. IoC具体容器实现选择AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象
6.Spring5-test5搭建测试环境
整合测试环境作用
好处1:不需要自己创建IOC容器对象了
好处2:任何需要的bean都可以在测试类中直接享受自动装配
(1)导入依赖
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>(2)使用
//@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = {"classpath:spring-context.xml"}) //指定配置文件xml
@SpringJUnitConfig(value = {BeanConfig.class}) //指定配置类
public class Junit5IntegrationTest {
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void testJunit5() {
System.out.println(user);
}
}四.Spring Aop面向切面编程
将重复的代码统一提取,并且[[动态插入]]到每个业务方法
(一)初步实现
1.导入依赖
<!-- spring-aspects会帮我们传递过来aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>2.声明切面类
@Component //保证这个切面类能够放入IOC容器
@Aspect//表示这个类是一个切面类
@Order (10) //指定一个优先级的值,值越小,优先级越高,而后执行,在外圈
public class LogAdvice {
@Before("execution(* com..impl.*.*(..))")
public void start(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("方法开始了");
//1.获取方法属于的类的信息
String simpleName = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
//2.获取方法名称
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();//获取方法名
//3.获取参数列表
Object[] args= joinPoint.getArgs();//获取目标方法参数
}
@After("com.yan.pointcut.MyPointCut.pc()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("方法结束了");
}
@AfterThrowing("com.yan.pointcut.MyPointCut.pc()")
public void error() {
System.out.println("方法报错了");
}
}3.开启aspectj注解支持
(1)xml方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 进行包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xx" />
<!-- 开启aspectj框架注解支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>(2)配置类方式
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.atguigu")
//作用等于 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> 配置类上开启 Aspectj注解支持!
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class MyConfig {
}
(二)获取通知细节信息
1.JointPoint接口
(1)获取方法属于的类的信息
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass()
(2)获取方法名称
joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
(3)获取参数列表
joinPoint.getArgs();
(二)插入位置
使用注解配置 指定插入目标方法的位置
前置 @Before
后置 @AfterReturning
异常 @AfterThrowing
最后 @After
环绕 @Around
try{
前置
目标方法执行
后置
}catch(){
异常
}finally{
最后
}@AfterThrowing注解标记异常通知方法
// @AfterThrowing注解标记异常通知方法
// 在异常通知中获取目标方法抛出的异常分两步:
// 第一步:在@AfterThrowing注解中声明一个throwing属性设定形参名称
// 第二步:使用throwing属性指定的名称在通知方法声明形参,Spring会将目标方法抛出的异常对象从这里传给我们
@AfterThrowing(
value = "execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.api.Calculator.add(int,int))",
throwing = "targetMethodException"
)
public void printLogAfterCoreException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable targetMethodException) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("[AOP异常通知] "+methodName+"方法抛异常了,异常类型是:" + targetMethodException.getClass().getName());
}@AfterReturning注解标记返回通知方法
// @AfterReturning注解标记返回通知方法
// 在返回通知中获取目标方法返回值分两步:
// 第一步:在@AfterReturning注解中通过returning属性设置一个名称
// 第二步:使用returning属性设置的名称在通知方法中声明一个对应的形参
@AfterReturning(
value = "execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.api.Calculator.add(int,int))",
returning = "targetMethodReturnValue"
)
public void printLogAfterCoreSuccess(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object targetMethodReturnValue) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("[AOP返回通知] "+methodName+"方法成功结束了,返回值是:" + targetMethodReturnValue);
}(三)切面表达式语法
固定语法 excution(1 2 3.4.5(6))
1.访问修饰符
public/private
2.方法的返回参数类型
如果不考虑访问修饰符和返回值 这两位整合成 *
3.包的位置
单层模糊:com.yan.service.*
多层模糊:com..impl ..impl 是任意层的impl包
..不能开头
*.. 任意包下
4.类的名称
模糊:*
部分模糊:*Impl
5.方法名 语法和类名一致
6.形参数列表
没有参数()
有具体参数(String)
模糊参数(..)没有参数/多个参数
部分模糊 (String..) 第一个是String
a.查询某包某类下,访问修饰符是公有,返回值是int的全部方法
public int xx.xx.jj.*(..)
b.查询某包下类中第一个参数是String的方法
* xx.xx.jj.*.(String)
c.查询全部包下,无参数的方法!
* *..*.*()
d.查询com包下,以int参数类型结尾的方法
* com..*.*(..int)
e.查询指定包下,Service开头类的私有返回值int的无参数方法
private int xx.xx.service*.*()
(四)重用切点表达式
将切点提取,在增强上进行引用即可!
建议:将切点表达式统一存储到一个类中进行集中管理和维护!
@Component
public class MyPointCut {
@Pointcut("execution(* com..impl.*.*(..))")
public void pc(){}
}@After("com.yan.pointcut.MyPointCut.pc()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("方法结束了");
}(五)环绕通知
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class TxAroundAdvice {
/**
* 环绕通知,需要你在通知中定义目标方法的执行
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint 目标方法(获取目标方法信息,多了一个执行方法)
* @return 目标方法的返回值
*/
@Around("com.yan.pointcut.MyPointCut.pc()")
public Object transsction(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
//保证目标方法被执行
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("开启事务");
//目标方法的返回值一定要返回给外界调用者
result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("结束事务");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("事务回滚");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
System.out.println("释放连接");
}
return result;
}
}(六)切面优先级设置
使用 @Order 注解可以控制切面的优先级:
优先级高的切面:外面
优先级低的切面:里面
@Order(较小的数):优先级高
@Order(较大的数):优先级低
(七)动态代理
代理方式可以解决附加功能代码干扰核心代码和不方便统一维护的问题!
他主要是将附加功能代码提取到代理中执行,不干扰目标核心代码!
在目标类没有实现任何接口的情况下,Spring会自动使用cglib技术实现代理
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
public void getEmpList() {
System.out.print("方法执行!");
}
} @Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
public void testNoInterfaceProxy() {
employeeService.getEmpList();
}目标类有接口,必须使用接口接收ioc容器的中代理组件
Calculator是接口
@SpringJUnitConfig(value = JavaConfig.class)
public class SpringAopTest {
@Autowired
private Calculator calculator;
//如果使用AOP技术,目标类有接口,必须使用接口接收ioc容器的中代理组件
@Test
public void test() {
int add = calculator.add(1, 1);
System.out.println(add);
}
}总结:
a. 如果目标类有接口,选择使用jdk动态代理
a. 如果目标类有接口,选择使用jdk动态代理
c. 如果有接口,接口接值
d. 如果没有接口,类进行接值
五.Spring 声明式事务
(一)概念
声明式事务是指使用注解或 XML 配置的方式来控制事务的提交和回滚。
开发者只需要添加配置即可, 具体事务的实现由第三方框架实现,避免我们直接进行事务操作!
(二)事务控制
1.导入依赖
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<!--当你引入Spring Context依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库驱动 和 连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 声明式事务依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.配置事务管理器
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.yan")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
//@EnableAspectJAutoProxy//开启aspectj
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务注解的支持
public class JavaConfig {
@Value("${yan.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${yan.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${yan.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${yan.password}")
private String password;
//druid连接池实例化
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
return dataSource;
}
//jdbcTemplate
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
public TransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
//内部要进行事务的操作,基于连接池
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager
= new DataSourceTransactionManager();
//需要连接池对象
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}
3.使用声明事务注解@Transactional
@Transactional
位置:方法|类上
方法:当前方法有事务
类:类下所有方法都有事务
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, noRollbackFor = FileNotFoundException.class)
public void changeInfo() throws FileNotFoundException {
studentDao.updateAgeById(236, 1);
throw new FileNotFoundException("FF");
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void getStudentInfo() {
//获取学生信息,不修改
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void changeAge() {
studentDao.updateAgeById(998, 1);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void changeName() {
studentDao.updateNameById("二狗子", 1);
}
}
(三)事务属性
1.只读
对一个查询操作来说,如果我们把它设置成只读,就能够明确告诉数据库,这个操作不涉及写操作。这样数据库就能够针对查询操作来进行优化。
readOnly = true把当前事务设置为只读 默认是false!
一般情况下,都是通过类添加事务,类下的所有方法都有事务,查询方法通过再次添加注解,设置为只读模式,提高效率
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@Service
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class EmpService {
// 为了便于核对数据库操作结果,不要修改同一条记录
@Transactional(readOnly = false)
public void updateTwice(……) {
……
}
// readOnly = true把当前事务设置为只读
// @Transactional(readOnly = true)
public String getEmpName(Integer empId) {
……
}
}2.超时时间
事务在执行过程中,有可能因为遇到某些问题,导致程序卡住,从而长时间占用数据库资源。而长时间占用资源,大概率是因为程序运行出现了问题
此时这个很可能出问题的程序应该被回滚,撤销它已做的操作,事务结束,把资源让出来,让其他正常程序可以执行
默认:不超时 -1 设置 timeout= 时间 秒数
超过时间,就会回滚事务和释放异常,报错TransactionTimedOutException
如果类上设置事务属性 ,方法也设置事务注解 方法上的注解会覆盖类上的注解
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
/**
* timeout设置事务超时时间,单位秒! 默认: -1 永不超时,不限制事务时间!
*/
@Transactional(readOnly = false,timeout = 3)
public void changeInfo(){
studentDao.updateAgeById(100,1);
//休眠4秒,等待方法超时!
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
studentDao.updateNameById("test1",1);
}
}
3.事务异常
默认只针对运行时异常回滚,受检异常不回滚
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
/**
* timeout设置事务超时时间,单位秒! 默认: -1 永不超时,不限制事务时间!
* rollbackFor = 指定哪些异常才会回滚,默认是 RuntimeException and Error 异常方可回滚!
* noRollbackFor = 指定哪些异常不会回滚, 默认没有指定,如果指定,应该在rollbackFor的范围内!
*/
@Transactional(readOnly = false,timeout = 3)
public void changeInfo() throws FileNotFoundException {
studentDao.updateAgeById(100,1);
//主动抛出一个检查异常,测试! 发现不会回滚,因为不在rollbackFor的默认范围内!
new FileInputStream("xxxx");
studentDao.updateNameById("test1",1);
}
}rollbackFor属性:指定哪些异常类才会回滚,默认是 RuntimeException and Error 异常方可回滚!
noRollbackFor属性: 回滚异常范围内,控制某个异常不回滚
成功修改,事务不回滚:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, noRollbackFor = FileNotFoundException.class)
public void changeInfo() throws FileNotFoundException {
studentDao.updateAgeById(236, 1);
throw new FileNotFoundException("FF");
}4.事务隔离级别
isolation = 设置事务的隔离级别,mysql默认是repeatable read!
5.事务传播行为
@Transactional 注解通过 propagation 属性设置事务的传播行为。
它的默认值是:Propagation.REQUIRED; 如果父方法有事务,就加入,如果没有就新建自己独立!
REQUIRES_NEW:不管父方法是否有事务,我都新建事务,都是独立的
(1)声明两个业务方法
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
/**
* timeout设置事务超时时间,单位秒! 默认: -1 永不超时,不限制事务时间!
* rollbackFor = 指定哪些异常才会回滚,默认是 RuntimeException and Error 异常方可回滚!
* noRollbackFor = 指定哪些异常不会回滚, 默认没有指定,如果指定,应该在rollbackFor的范围内!
* isolation = 设置事务的隔离级别,mysql默认是repeatable read!
*/
@Transactional(readOnly = false,
timeout = 3,
rollbackFor = Exception.class,
noRollbackFor = FileNotFoundException.class,
isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)
public void changeInfo() throws FileNotFoundException {
studentDao.updateAgeById(100,1);
//主动抛出一个检查异常,测试! 发现不会回滚,因为不在rollbackFor的默认范围内!
new FileInputStream("xxxx");
studentDao.updateNameById("test1",1);
}
/**
* 声明两个独立修改数据库的事务业务方法
*/
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void changeAge(){
studentDao.updateAgeById(99,1);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void changeName(){
studentDao.updateNameById("test2",1);
int i = 1/0;
}
}(2)声明一个整合业务方法
@Service
public class TopService {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@Transactional
public void topService(){
studentService.changeAge();
studentService.changeName();
}
}
(3)添加传播行为测试
@SpringJUnitConfig(classes = AppConfig.class)
public class TxTest {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@Autowired
private TopService topService;
@Test
public void testTx() throws FileNotFoundException {
topService.topService();
}
}
在同一个类中,对于@Transactional注解的方法调用,事务传播行为不会生效,这是因为Spring框架中使用代理模式实现了事务机制,在同一个类中的方法调用并不经过代理,而是通过对象的方法调用,因此@Transactional注解的设置不会被代理捕获,也就不会产生任何事务传播行为的效果