package com.bjpowernode.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/*
编程思想:
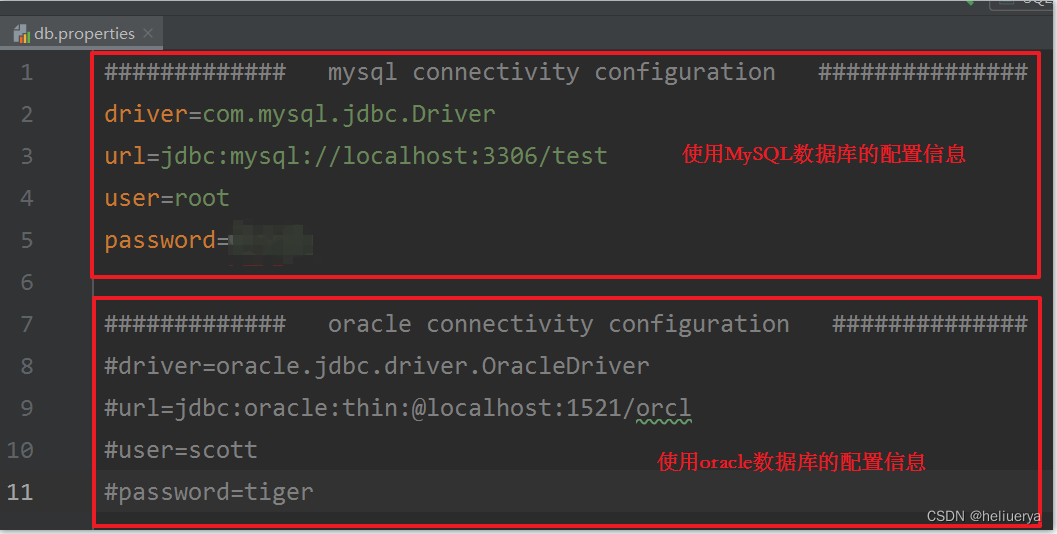
将连接数据库时可变化的4条信息都写到配置文件中,以后需要连接其他数据库的时候,可直接修改配置文件,不用修改java程序。
这4个信息分别是:driver、url、user、password。
*/
public class 通过属性配置文件编写JDBC程序 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//资源绑定器(db.properties必须省略扩展名)
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources\\db");
//通过属性配置文件拿到信息
String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//2.获取连接(这里的url、user、password和上行代码的参数driver都来源于属性配置文件)
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//3.获取数据库操作对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行sql语句
String sql = "select a.ename as '员工',b.ename as '领导' from emp a left join emp b on a.mgr = b.empno";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.处理查询结果集
while(rs.next()){
String ename = rs.getString("员工");
String lname = rs.getString("领导"); //这里是根据查询结果的字段名获取对应值
System.out.println(ename + "," + lname);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//6.释放资源(注意关闭顺序)
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
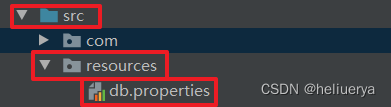
属性配置文件在IDEA中目录所处位置
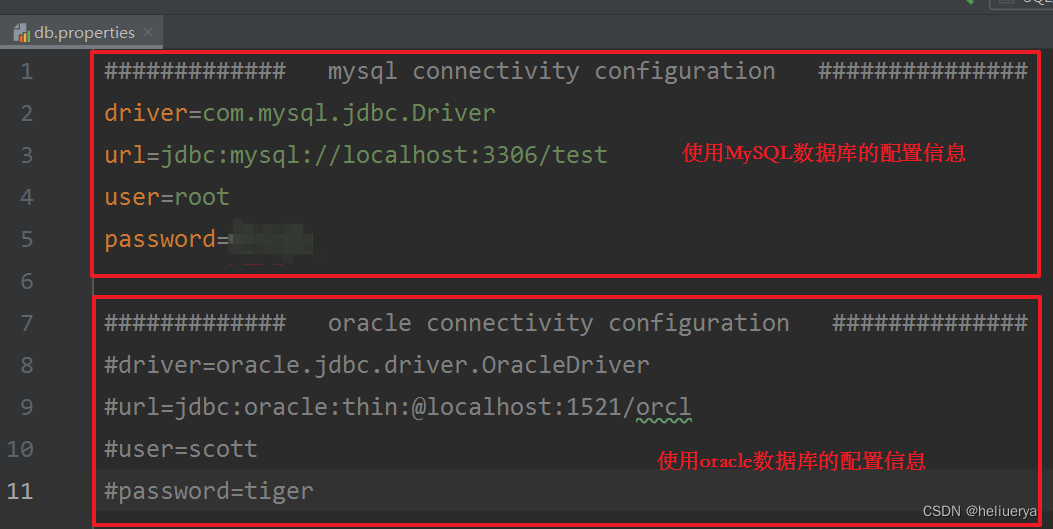
属性配置文件db.properties中的内容