1.概述
用一个已经创建的实例作为原型,通过复制该原型对象来创建一个和原型对象相同的新对象
2.结构
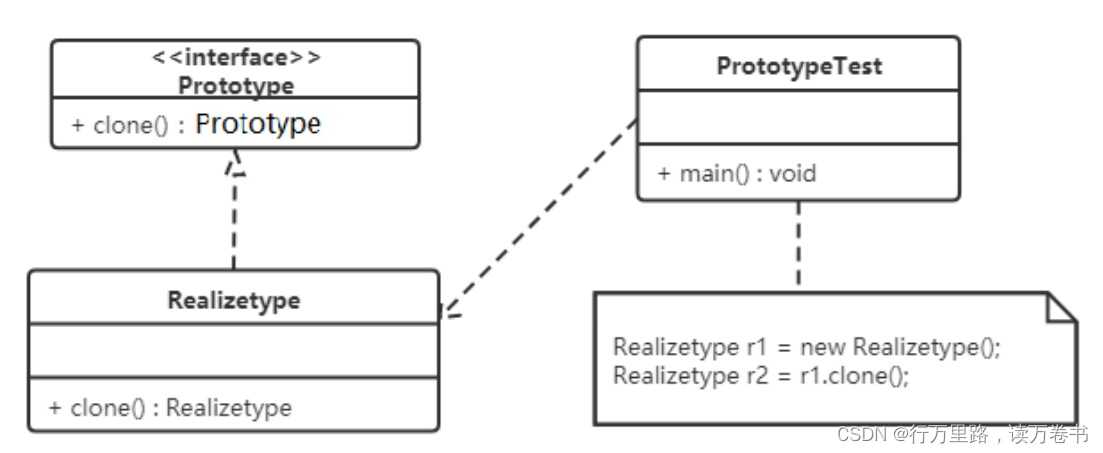
原型模式包含如下角色:
- 抽象原型类:规定了具体原型对象必须实现的的 clone() 方法。
- 具体原型类:实现抽象原型类的 clone() 方法,它是可被复制的对象。
- 访问类:使用具体原型类中的 clone() 方法来复制新的对象。
接口类图如下:
3.实现
原型模式的克隆分为浅克隆和深克隆。
浅克隆:创建一个新对象,新对象的属性和原来对象完全相同,对于非基本类型属性,仍指向原有属性所指向的对象的内存地址。
深克隆:创建一个新对象,属性中引用的其他对象也会被克隆,不再指向原有对象地址。
Java中的Object类中提供了 clone() 方法来实现浅克隆。 Cloneable 接口是上面的类图中的抽象原型类,而实现了Cloneable接口的子实现类就是具体的原型类。代码如下:
package com.itheima.pattern.prototype.demo;
/**
* @program: design-patterns
* @ClassName Realizetype
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-01-14 20:10
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class Realizetype implements Cloneable {
public Realizetype() {
System.out.println("具体的原型对象创建完成!");
}
@Override
protected Realizetype clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
System.out.println("具体原型复制成功!");
return (Realizetype) super.clone();
}
}
package com.itheima.pattern.prototype.demo;
/**
* @program: design-patterns
* @ClassName Client
* @description: 测试类
* @author:
* @create: 2023-01-14 20:12
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// 创建一个原型对象
Realizetype realizetype = new Realizetype();
// 调用Realizetype类中的clone方法进行对象的克隆
Realizetype realizetype1 = realizetype.clone();
System.out.println("原型对象和克隆出来的对象是否为同一个对象?" + (realizetype == realizetype1));
}
}
4.案例
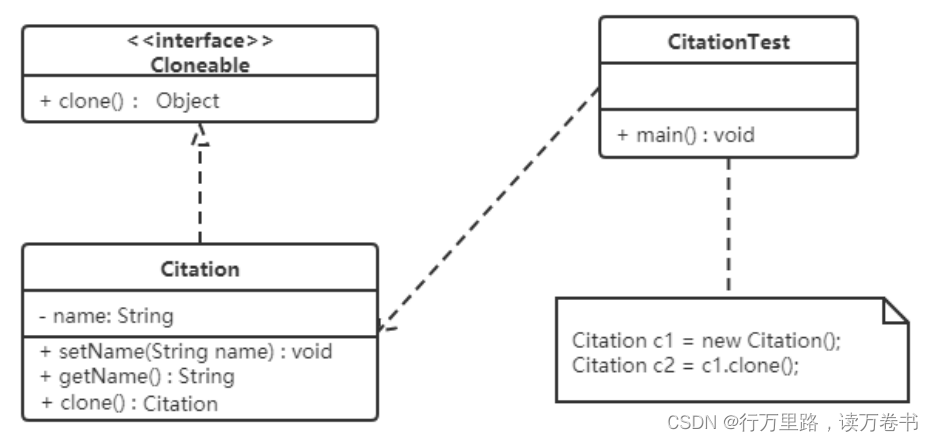
用原型模式生成“三好学生”奖状
同一学校的“三好学生”奖状除了获奖人姓名不同,其他都相同,可以使用原型模式复制多个“三好学生”奖状出来,然后在修改奖状上的名字即可。
类图如下:
代码如下:
//奖状类
public class Citation implements Cloneable {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return (this.name);
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(name + "同学:在2020学年第一学期中表现优秀,被评为三好学
生。特发此状!");
}
@Override
public Citation clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Citation) super.clone();
}
}
//测试访问类
public class CitationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Citation c1 = new Citation();
c1.setName("张三");
//复制奖状
Citation c2 = c1.clone();
//将奖状的名字修改李四
c2.setName("李四");
c1.show();
c2.show();
}
}
4.使用场景
- 对象的创建非常复杂,可以使用原型模式快捷的创建对象。
- 性能和安全要求比较高。
5.扩展(深克隆)
将上面的“三好学生”奖状的案例中Citation类的name属性修改为Student类型的属性。代码如下:
package com.itheima.pattern.prototype.test1;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @program: design-patterns
* @ClassName Student
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-01-14 20:25
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class Student implements Serializable {
// 三好学生上的姓名
private String name;
private String address;
public Student(String name, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
package com.itheima.pattern.prototype.test1;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @program: design-patterns
* @ClassName Citation
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-01-14 20:17
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class Citation implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private Student student;
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
@Override
public Citation clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Citation) super.clone();
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(student.getName() + "同学:在2020学年第一学期中表现优秀,被评为三好学 生。特发此状!");
}
}
package com.itheima.pattern.prototype.test1;
/**
* @program: design-patterns
* @ClassName CitaionTest
* @description: 深克隆
* @author:
* @create: 2023-01-14 20:20
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class CitaionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Citation c1 = new Citation();
Student stu = new Student("张三", "西安");
c1.setStudent(stu);
// 复制奖状
Citation c2 = c1.clone();
//获取c2奖状所属学生对象
Student stu1 = c2.getStudent();
stu1.setName("李四");
// 判断stu对象和stu1对象是否是同一个对象
System.out.println("stu和stu1是同一个对象?" + (stu == stu1));
c1.show();
c2.show();
}
}
运行结果:

说明:
stu对象和stu1对象是同一个对象,就会产生将stu1对象中name属性值改为“李四”,两个Citation(奖状)对象中显示的都是李四。这就是浅克隆的效果,对具体原型类(Citation)中的引用类型的属性进行引用的复制。这种情况需要使用深克隆,而进行深克隆需要使用对象流。
代码如下:
package com.itheima.pattern.prototype.test1;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
/**
* @program: design-patterns
* @ClassName CitaionTest
* @description: 深克隆
* @author:
* @create: 2023-01-14 20:20
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class CitaionTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Citation c1 = new Citation();
Student stu = new Student("张三", "西安");
c1.setStudent(stu);
// 创建对象输出流对象
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\robin\\a.txt"));
// 将c1对象写出到文件中
oos.writeObject(c1);
oos.close();
// 创建对象输入流对象
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\robin\\a.txt"));
// 读取对象
Citation c2 = (Citation) ois.readObject();
Student stu1 = c2.getStudent();
stu1.setName("李四");
// 判断stu对象和stu1对象是否为同一个对象
System.out.println("stu和stu1是同一个对象?" + (stu == stu1));
c1.show();
c2.show();
}
}
运行结果为:

注意:Citation类和Student类必须实现Serializable接口,否则会抛NotSerializableException异常。