代码解决
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {} }; */ class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { queue<Node*> que; // 定义队列用于层次遍历 if (root != NULL) que.push(root); // 如果根节点不为空,则将根节点加入队列 while (!que.empty()) // 当队列不为空时,继续处理 { int size = que.size(); // 获取当前层的节点数量 Node* node; // 当前处理的节点 Node* prenode; // 前一个处理的节点 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) // 遍历当前层的每一个节点 { if (i == 0) // 如果是当前层的第一个节点 { prenode = que.front(); que.pop(); node = prenode; } else // 如果不是当前层的第一个节点 { node = que.front(); que.pop(); prenode->next = node; // 将前一个节点的 next 指向当前节点 prenode = prenode->next; } if (node->left) que.push(node->left); // 如果该节点有左子节点,将其加入队列 if (node->right) que.push(node->right); // 如果该节点有右子节点,将其加入队列 } prenode->next = NULL; // 当前层的最后一个节点的 next 设为 NULL } return root; // 返回根节点 } };测试代码
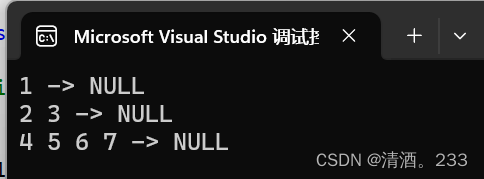
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {} }; class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return NULL; // 如果根节点为空,直接返回 NULL queue<Node*> que; // 定义队列用于层次遍历 que.push(root); // 将根节点加入队列 while (!que.empty()) // 当队列不为空时,继续处理 { int size = que.size(); // 获取当前层的节点数量 Node* prenode = NULL; // 前一个处理的节点,初始化为 NULL for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) // 遍历当前层的每一个节点 { Node* node = que.front(); // 从队列中取出一个节点 que.pop(); // 将该节点从队列中移除 if (prenode != NULL) { prenode->next = node; // 将前一个节点的 next 指向当前节点 } prenode = node; // 更新前一个节点为当前节点 if (node->left) que.push(node->left); // 如果该节点有左子节点,将其加入队列 if (node->right) que.push(node->right); // 如果该节点有右子节点,将其加入队列 } prenode->next = NULL; // 当前层的最后一个节点的 next 设为 NULL } return root; // 返回根节点 } }; // 辅助函数:创建一个测试树 Node* createTestTree() { Node* root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(3); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->left = new Node(6); root->right->right = new Node(7); return root; } // 辅助函数:打印树的每一层 void printTreeByLevel(Node* root) { Node* levelStart = root; while (levelStart != NULL) { Node* current = levelStart; levelStart = NULL; while (current != NULL) { cout << current->val << " "; if (!levelStart) { if (current->left) levelStart = current->left; else if (current->right) levelStart = current->right; } current = current->next; } cout << "-> NULL" << endl; } } int main() { Solution solution; Node* root = createTestTree(); root = solution.connect(root); printTreeByLevel(root); // 打印连接后的树的每一层 return 0; }