1、promise
1.1 实现resolve和reject
class MyPromise {
// 构造方法
constructor(executor) {
// 初始化值
this.initValue()
// 初始化this指向
this.initBind()
try {
// 执行传进来的函数
executor(this.resolve, this.reject)
} catch (e) {
// 捕捉到错误直接执行reject
this.reject(e)
}
}
initBind() {
// 初始化this
this.resolve = this.resolve.bind(this)
this.reject = this.reject.bind(this)
}
initValue() {
// 初始化值
this.PromiseResult = null // 终值
this.PromiseState = 'pending' // 状态
}
resolve(value) {
// state是不可变的
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 如果执行resolve,状态变为fulfilled
this.PromiseState = 'fulfilled'
// 终值为传进来的值
this.PromiseResult = value
}
reject(reason) {
// state是不可变的
if (this.PromiseState !== 'pending') return
// 如果执行reject,状态变为rejected
this.PromiseState = 'rejected'
// 终值为传进来的reason
this.PromiseResult = reason
}
}测试代码:
const test3 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
throw('fail')
})
console.log(test3) // MyPromise { PromiseState: 'rejected', PromiseResult: 'fail' }
1.2 实现then方法
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 接收两个回调 onFulfilled, onRejected
// 参数校验,确保一定是函数
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ?
onFulfilled : val => val
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ?
onRejected : reason => { throw reason }
if (this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled') {
// 如果当前为成功状态,执行第一个回调
onFulfilled(this.PromiseResult)
} else if (this.PromiseState === 'rejected') {
// 如果当前为失败状态,执行第二哥回调
onRejected(this.PromiseResult)
}
}测试代码:
// 输出 ”success“
const test = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('success')
}).then(res => console.log(res), err => console.log(err)) 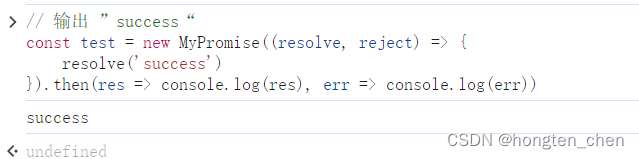
2、call
2.1 实现思路
call() :在使用一个指定的 this 值和若干个指定的参数值的前提下调用某个函数或方法。
let foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar() {
console.log(this.value);
}
bar.call(foo); // 1
上述调用注意两点:
1. call 改变了 this 的指向,指向到 foo;
2. bar 函数执行了;
上述方式等同于:
let foo = {
value: 1,
bar: function() {
console.log(this.value)
}
};
foo.bar(); // 1这个时候 this 就指向了 foo,但是这样却给 foo 对象本身添加了一个属性,所以们用 delete 再删除它即可。
所以我们模拟的步骤可以分为:
-
将函数设为对象的属性;
-
执行该函数;
-
删除该函数;
// 第一步
// fn 是对象的属性名,反正最后也要删除它,所以起什么都可以。
foo.fn = bar
// 第二步
foo.fn()
// 第三步
delete foo.fn2.2 实现
2.2.1 指定this
2.2.2 指定参数
2.2.3 this 参数可以传 null,当为 null 的时候,视为指向 window
// 第三版
Function.prototype.call2 = function (context) {
var context = context || window;
context.fn = this;
let arg = [...arguments].slice(1)
let result = context.fn(...arg)
delete context.fn
return result
}
// 测试一下
var value = 2;
var obj = {
value: 1
}
function bar(name, age) {
console.log(this.value);
return {
value: this.value,
name: name,
age: age
}
}
bar.call2(null); // 2
console.log(bar.call2(obj, 'kevin', 18));
// 1
// Object {
// value: 1,
// name: 'kevin',
// age: 18
// }3、apply
apply 的实现跟 call 类似,只是入参不一样,apply为数组
Function.prototype.apply = function (context, arr) {
var context = Object(context) || window;
context.fn = this;
var result;
if (!arr) {
result = context.fn();
}
else {
result = context.fn(...arr)
}
delete context.fn
return result;
}4、bind
5、debounce > 防抖
防抖: 如果在一定的时间内 (n) 频繁的触发,只会执行最后一次
5.1 js实现
function debounce(func, ms) {
let timeout;
return function () {
let context = this;
let args = arguments;
if (timeout) clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(context, args)
}, ms);
}
}
5.1 hooks实现
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react'
const useDebounce = (fn, ms = 30, deps = []) => {
let timeout = useRef()
useEffect(() => {
if (timeout.current) clearTimeout(timeout.current)
timeout.current = setTimeout(() => {
fn()
}, ms)
}, deps)
const cancel = () => { // 防止内存泄露
clearTimeout(timeout.current)
timeout = null
}
return [cancel]
}
export default useDebounce
// 实际使用
import { useDebounce } from 'hooks'
const Home = (props) => {
const [a, setA] = useState(0)
const [b, setB] = useState(0)
const [cancel] = useDebounce(() => {
setB(a)
}, 2000, [a])
const changeIpt = (e) => {
setA(e.target.value)
}
return <div>
<input type="text" onChange={changeIpt} />
{ b } { a }
</div>
}6、throttle > 节流
节流:每一次触发的时候,会记录与首次触发的一个时间差,如果时间差大于传入的这个时间,则重新计时
6.1 js实现
function throttle(func, ms) {
let previous = 0;
return function() {
let now = Date.now();
let context = this;
let args = arguments;
if (now - previous > ms) {
func.apply(context, args);
previous = now;
}
}
}6.2 hooks实现
mport { useEffect, useRef, useState } from 'react'
const useThrottle = (fn, ms = 30, deps = []) => {
let previous = useRef(0)
let [time, setTime] = useState(ms)
useEffect(() => {
let now = Date.now();
if (now - previous.current > time) {
fn();
previous.current = now;
}
}, deps)
const cancel = () => {
setTime(0)
}
return [cancel]
}
export default useThrottle






![【Qt】[001]-从入门到成神-前言](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5490ffc22c114670ad6460a15fff0176.png)