SpringBoot启动流程分析之ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件发布(四)
目录:
文章目录
- SpringBoot启动流程分析之ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件发布(四)
- 构建环境
- 1、创建ConfigurableEnvironment对象
- 2、配置环境
- 2.1、配置属性源
- 2.2、配置配置文件
- 3、发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
- 4、将环境绑定到SpringApplication
- 5、将配置属性源绑定到Environment
- 六、SpringApplication.run调用两次
args参数封装执行完成以后,就是构建环境Environment,下面分析其运行流程。
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String…)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
try {
// 开始分析...
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 其余代码忽略了...
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
构建环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
1、创建ConfigurableEnvironment对象
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
//如果你通过SpringApplication对象的setEnvironment()方法设置了环境,则直接返回该环境
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
//根据webApplicationType选择
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment(); //标准的servlet环境
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment(); //标准的响应式web环境
default:
return new StandardEnvironment(); //标准环境
}
}
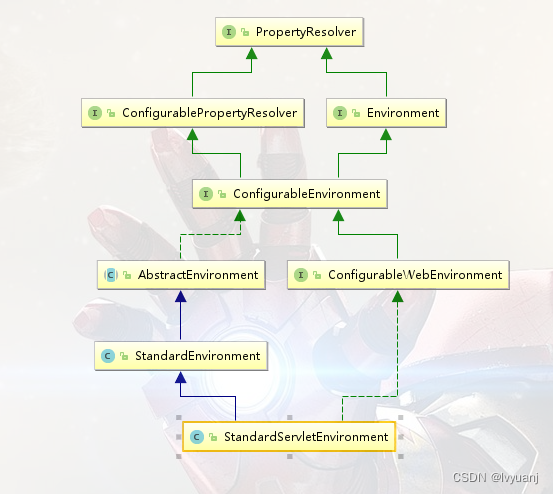
从UML类图看出:StandardServletEnvironment 继承StandardEnvironment 实现ConfigurableWebEnvironment
StandardEnvironment 继承AbstractEnvironment 中构造函数中customizePropertySources()
在StandardServletEnvironment 中有重写:
/** Servlet context init parameters property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletContextInitParams";
/** Servlet config init parameters property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletConfigInitParams";
/** JNDI property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "jndiProperties";
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
StandardEnvironment重写:
/** System environment property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/** JVM system properties property source name: {@value}. */
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
返回的标准servlet环境如下:
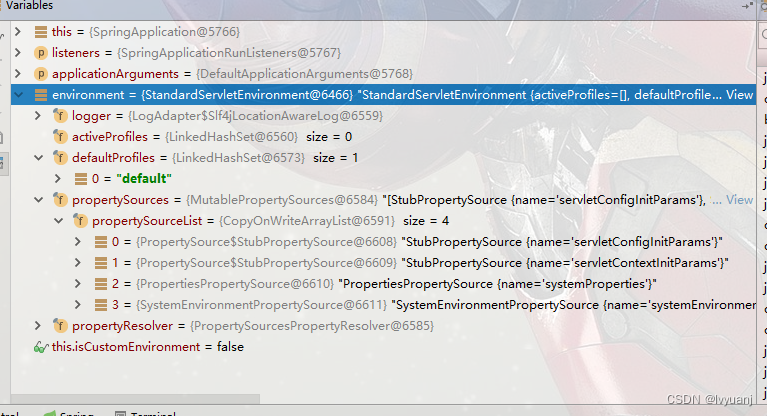
StandardServletEnvironment {
activeProfiles=[],
defaultProfiles=[default],
propertySources=[
StubPropertySource {name='servletConfigInitParams'},
StubPropertySource {name='servletContextInitParams'},
PropertiesPropertySource {name='systemProperties'},
SystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'}
]
}
2、配置环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 开始分析
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
//是否添加转换服务,后面在必要时转换环境
if (this.addConversionService) {
// 格式化转换器
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
//配置属性源,包括默认配置和命令行配置,默认配置使用SpringApplication的setDefaultProperties(Map<String, Object> defaultProperties)方法设置
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
//设置配置文件
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
2.1、配置属性源
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#configurePropertySources
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
//得到属性源,即返回的标准环境中的propertySources
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
//判断默认配置是否为空,不为空就添加到source里即propertySources,name为defaultProperties
//通过application.setDefaultProperties(defaultProperties);设置
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
//判断原始args参数长度是否大于0,addCommandLineProperties 默认为true
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
//通过commandLineArgs得到配置
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
//new一个CompositePropertySource,是PropertySource的子类,所以构造方法里传一个name知道啥意思了吧,前面介绍过PropertySource了
//该类中有一个Set<PropertySource<?>>
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(
new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
//用composite替换原 source中name为commandLineArgs的配置
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
//不存在就new一个SimpleCommandLinePropertySource实例添加
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
2.2、配置配置文件
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 开始分析
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
environment.getActiveProfiles(); // ensure they are initialized
// But these ones should go first (last wins in a property key clash)
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
//设置ActiveProfiles
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
可以看到得到的配置文件就是配置项spring.profiles.active配置的。会判断this.activeProfiles是否为空,如果你是通过context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles(profiles)方法设置的,那就直接返回了。
org.springframework.core.env.AbstractEnvironment#getDefaultProfiles
public String[] getDefaultProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(doGetDefaultProfiles());
}
protected Set<String> doGetDefaultProfiles() {
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
if (this.defaultProfiles.equals(getReservedDefaultProfiles())) {
String profiles = getProperty(DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
setDefaultProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.defaultProfiles;
}
}
public void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.clear();
for (String profile : profiles) {
validateProfile(profile);
this.defaultProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
3、发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners#environmentPrepared
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}
事件的具体发布过程: 由于listener具体是实现类:EventPublishingRunListener
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent 的具体实现前面有讲解:
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 重点是由于getApplicationListeners 方法,通过获取具体对应的简体类, 后面进行
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
调用的堆栈信息:
at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:93)
at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:71)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.doInvokeListener(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:172)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.invokeListener(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:165)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:139)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:127)
at org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener.environmentPrepared(EventPublishingRunListener.java:75)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners.environmentPrepared(SpringApplicationRunListeners.java:53)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.prepareEnvironment(SpringApplication.java:340)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:304)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1213)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1202)
at cn.wingsing.RegisterApplication.main(RegisterApplication.java:14)
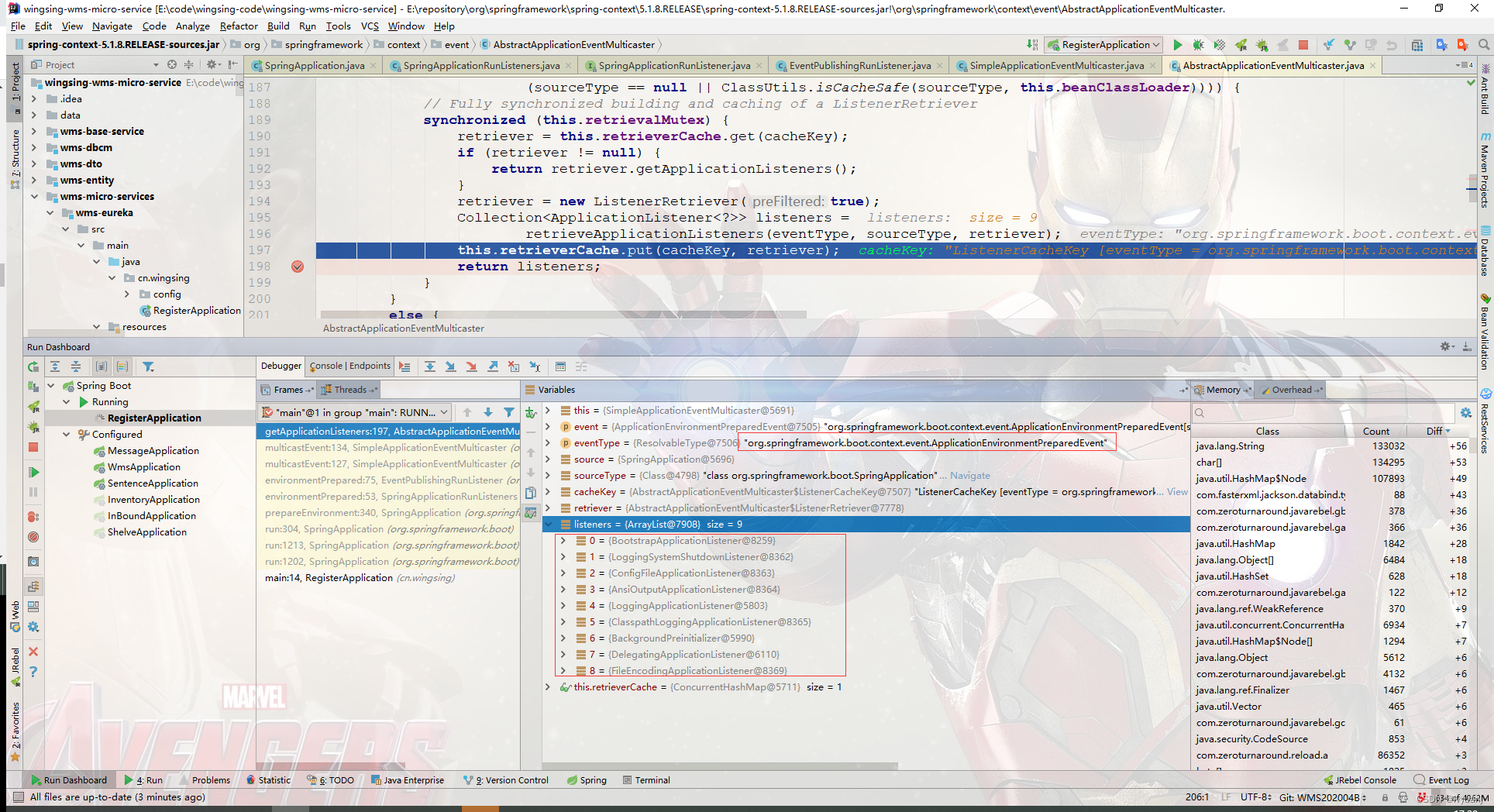
调用监听实现类:
BootstrapApplicationListener
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent
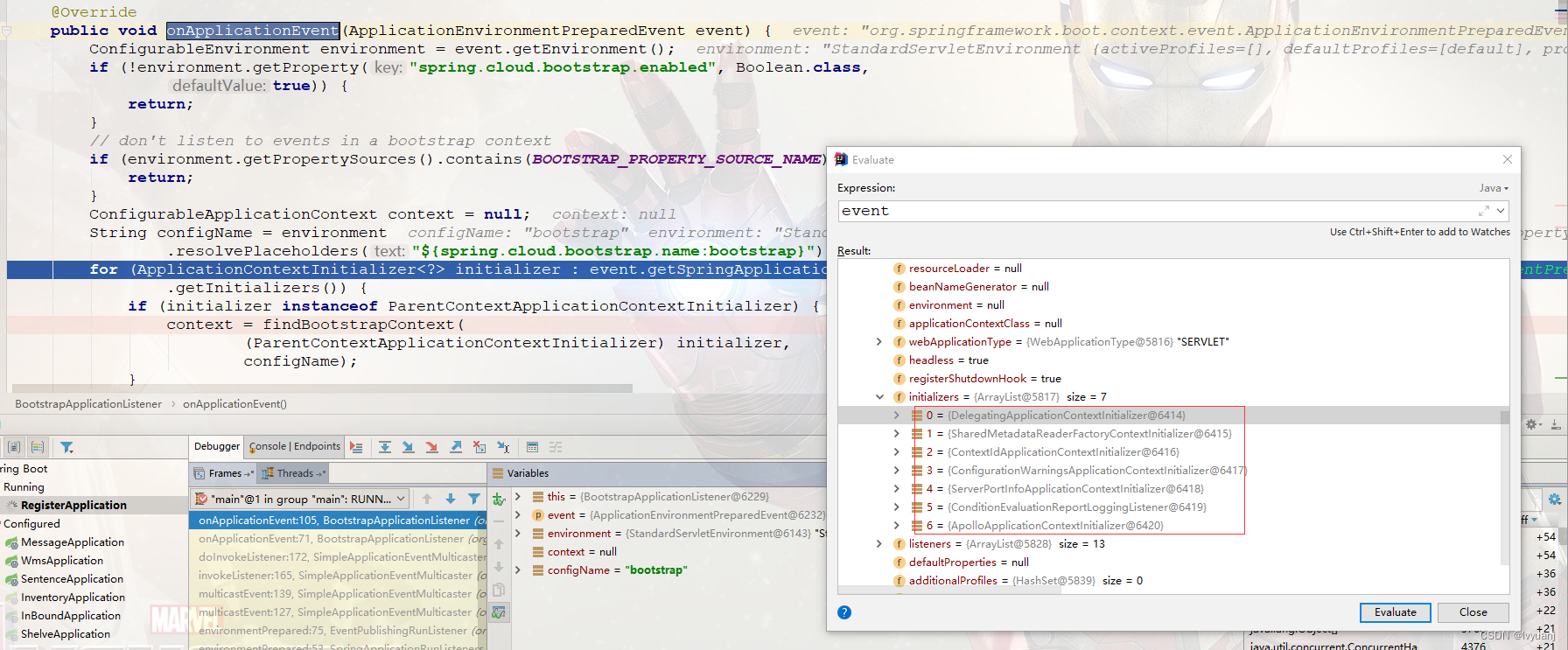
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener#bootstrapServiceContext
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, final SpringApplication application,
String configName) {
StandardEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new StandardEnvironment();
MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment
.getPropertySources();
for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrapProperties) {
bootstrapProperties.remove(source.getName());
}
String configLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:}");
Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>();
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName);
// if an app (or test) uses spring.main.web-application-type=reactive, bootstrap
// will fail
// force the environment to use none, because if though it is set below in the
// builder
// the environment overrides it
bootstrapMap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "none");
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation);
}
bootstrapProperties.addFirst(
new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap));
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (source instanceof StubPropertySource) {
continue;
}
bootstrapProperties.addLast(source);
}
// TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader?
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder()
.profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF)
.environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don't use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE);
final SpringApplication builderApplication = builder.application();
if (builderApplication.getMainApplicationClass() == null) {
// gh_425:
// SpringApplication cannot deduce the MainApplicationClass here
// if it is booted from SpringBootServletInitializer due to the
// absense of the "main" method in stackTraces.
// But luckily this method's second parameter "application" here
// carries the real MainApplicationClass which has been explicitly
// set by SpringBootServletInitializer itself already.
builder.main(application.getMainApplicationClass());
}
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) {
// If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the
// Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the
// LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a
// way to switch those off.
builderApplication
.setListeners(filterListeners(builderApplication.getListeners()));
}
builder.sources(BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class);
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
// gh-214 using spring.application.name=bootstrap to set the context id via
// `ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer` prevents apps from getting the actual
// spring.application.name
// during the bootstrap phase.
context.setId("bootstrap");
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context
addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
// It only has properties in it now that we don't want in the parent so remove
// it (and it will be added back later)
bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);
return context;
}
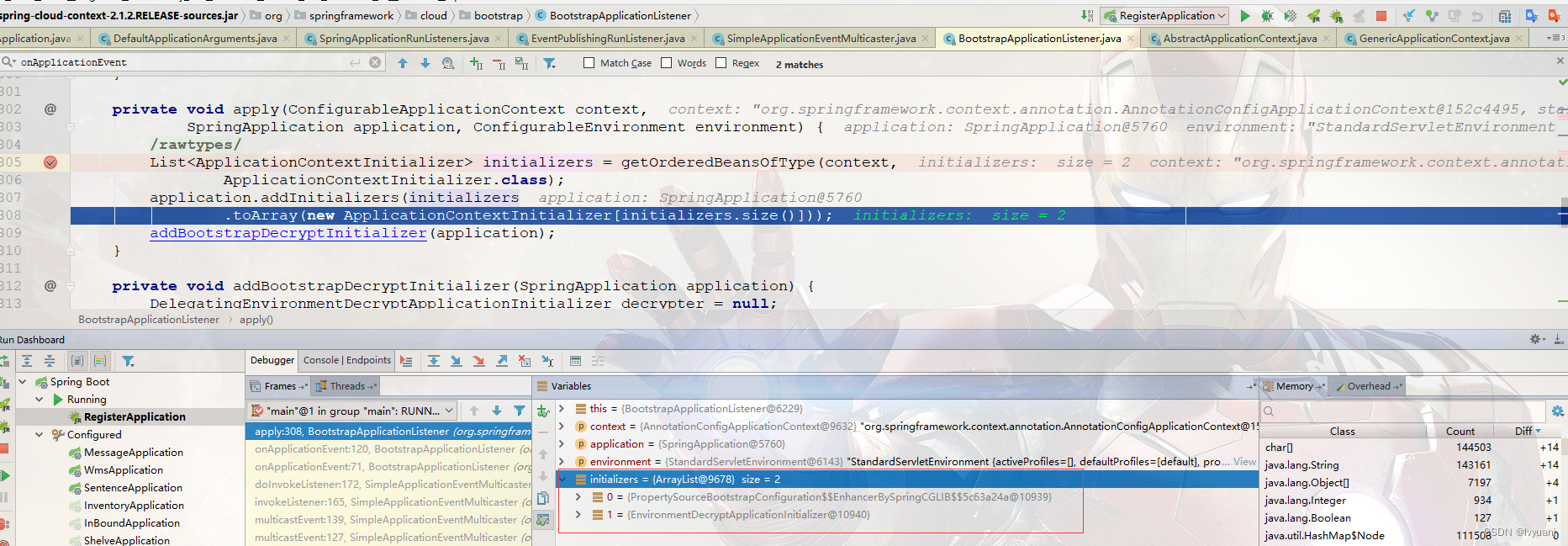
ConfigFileApplicationListener:得到EnvironmentPostProcessor接口的实现类实例,List集合,并添加本身,根据order排序,循环执行postProcessEnvironment方法。
得到的EnvironmentPostProcessor接口实现类有三个,加上ConfigFileApplicationListener,一共四个,如下。
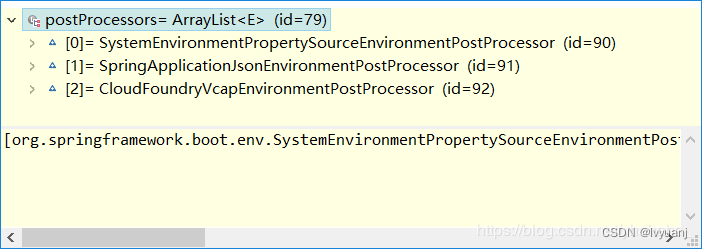
SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor:从标准环境中得到name为systemEnvironment的PropertySource,然后将SystemEnvironmentPropertySource替换为OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource,用于提供从系统环境加载的项对原始属性名的访问。即可以通过原始属性名的到属性值。
SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor:循环数组String[] CANDIDATES={spring.application.json,SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON},确认propertySource中是否存在这两个系统属性,如果存在new一个JsonPropertyValue对象,该类为内部类,将name和value封装,如果不存在返回空,然后过滤是否为空,找到第一个确认是否有这个值,如果有就解析json封装成JsonPropertySource并添加到环境(environment)中,如果不存在不执行任何操作。

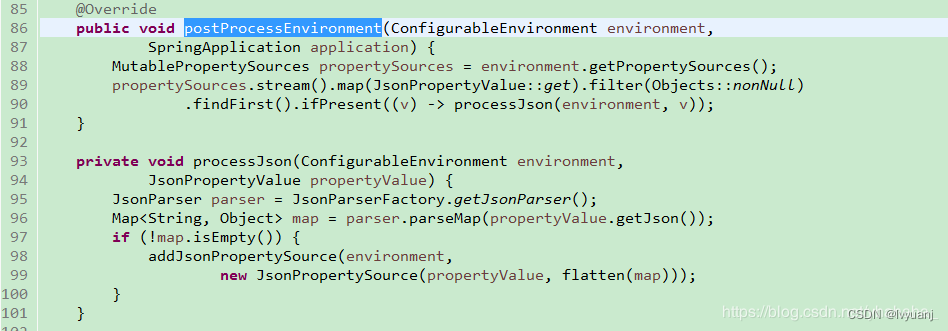

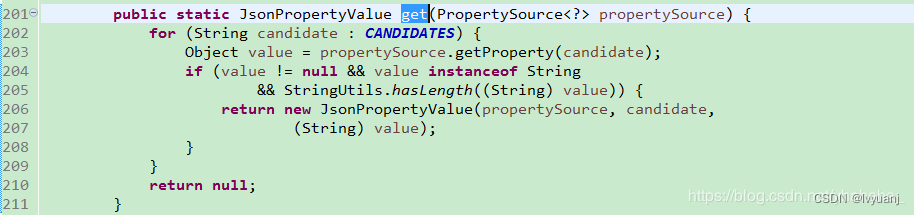
CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor:判断环境中是否存在VCAP_APPLICATION或者VCAP_SERVICES。如果有就添加Cloud Foundry的配置;没有就不执行任何操作。
ConfigFileApplicationListener:得到PropertySourceLoader的实现类PropertiesPropertySourceLoader、YamlPropertySourceLoader,然后加载配置文件,包括application.properties/yml(或yaml)/xml以及application-{dev,prod,test}.properties/yml(或yaml)/xml
AnsiOutputApplicationListener:将spring.output.ansi.enabled的值跟环境自绑定,再根据绑定值配置ANSI输出。
有三个值:
DETECT:尝试检测ANSI着色功能是否可用,默认是这个
ALWAYS:启用ANSI彩色输出
NEVER:禁用ANSI彩色输出
然后根据spring.output.ansi.console-available的值设置System.Console()是否可用。
LoggingApplicationListener:调用initialize()方法完成日志系统的初始化,前面ApplicationStartingEvent事件发布的时候已经调用了beforeInitialize()方法。如果没有配置日志,则使用默认配置,默认情况下,日志输出只写入控制台。如果需要日志文件,logging.path和logging.file属性可以使用。
ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener:在调试级别记录线程上下文类加载器(TCCL)的类路径,对ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent和ApplicationFailedEvent做出反应。
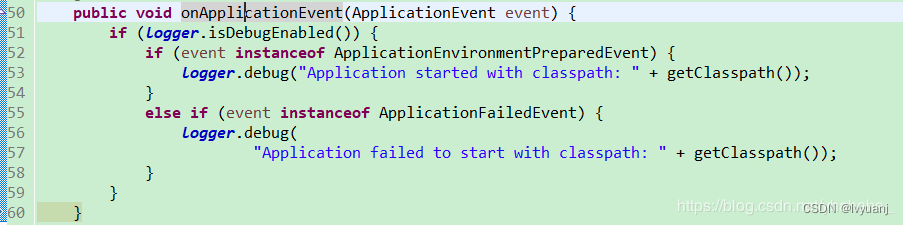
BackgroundPreinitializer:貌似在这一步没做什么事,在ApplicationStartingEvent事件发布的时候已经执行了。
DelegatingApplicationListener:如果是ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,在getListeners方法中会得到配置项"context.listener.classes"设置的listener,得到实例对象添加到多播器multicaster中。否则判断多播器multicaster是否为空,不为空继续广播事件。
FileEncodingApplicationListener:默认情况下不起什么作用,也就是啥都不执行。但是如果spring.mandatory_file_encoding的值和file.encoding属性值不同时会引发报错。
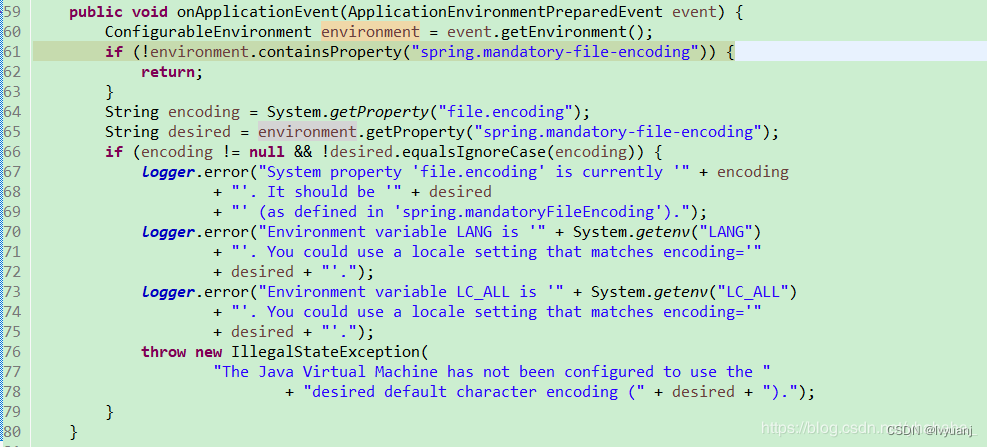
4、将环境绑定到SpringApplication
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 开始分析
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
try {
Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}
5、将配置属性源绑定到Environment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 开始分析
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
public static void attach(Environment environment) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment).getPropertySources();
PropertySource<?> attached = sources.get(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
if (attached != null && attached.getSource() != sources) {
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
attached = null;
}
if (attached == null) {
sources.addFirst(new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources)));
}
}
总结:
整个prepareEnvironment()方法走完以后得到的Environment如下:
StandardServletEnvironment {
activeProfiles=[],
defaultProfiles=[default],
propertySources=[
StubPropertySource {name='servletConfigInitParams'},
StubPropertySource {name='servletContextInitParams'},
PropertiesPropertySource {name='systemProperties'},
SystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'}
]
}
其中ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的发布主要做的就是加载配置文件,初始化日志系统。
六、SpringApplication.run调用两次
"main@1" prio=5 tid=0x1 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:300)
at org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder.run(SpringApplicationBuilder.java:139)
- locked <0x1ba2> (a java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean)
at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.bootstrapServiceContext(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:203)
at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:114)
at org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent(BootstrapApplicationListener.java:71)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.doInvokeListener(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:172)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.invokeListener(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:165)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:139)
at org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java:127)
at org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener.environmentPrepared(EventPublishingRunListener.java:75)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners.environmentPrepared(SpringApplicationRunListeners.java:53)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.prepareEnvironment(SpringApplication.java:340)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:304)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1213)
at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1202)
at cn.wingsing.RegisterApplication.main(RegisterApplication.java:14)
以上调用的堆栈信息,调用两次的原因:
第一次调用是服务启动的入库main方法的正常调用;
第二次调用的原因:
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment
中listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
实现的EventPublishingRunListener事件监听的environmentPrepared方法,通过 this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment)); 广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent。
BootstrapApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent的方法监听
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener#bootstrapServiceContext中
// 配置启动的
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder()
.profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF)
.environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don’t use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE); // 注意配置NONE
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run(); 调用了run()方法.
前面讲的过 SpringApplicationBuilder 是SpringApplication的包装类,其实就是SpringApplication.run调用
![正点原子[第二期]Linux之ARM(MX6U)裸机篇学习笔记-24.3,4 SPI驱动实验-I.MX6U SPI 寄存器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/46f172da445f4bc4b1fa67699f80a176.png)