首先我们肯定先说创建线程
1.继承Thread类
o定义一个类MyThread继承Thread类
o在MyThread类中重写run()方法
o创建MyThread类的对象
o启动线程
package Java.thread;
public class first extends Thread{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
System.out.println("我是小线程"+"名称:"+getName()+",运行结果:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package Java.thread;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("我是主线程");
first f1=new first();
first f2=new first();
f1.start();
f2.start();
Thread.sleep(50);
System.out.println("主线程结果。");
}
}

2.实现Runnable接口
o定义一个类MyRunnable实现Runnable接口
o在MyRunnable类中重写run()方法
o创建MyRunnable类的对象
o创建Thread类的对象,把MyRunnable对象作为构造方法的参数
o启动线程
package Java.thread;
public class second implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
//不能直接获取getname,因为不是继承
System.out.println("我是小线程"+"名称:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",运行结果:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package Java.thread;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("我是主线程");
second s1=new second();
second s2=new second();
Thread t=new Thread(s1,"小线程1");
Thread t1=new Thread(s2,"小线程2");
t.start();
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(50);
System.out.println("主线程结果。");
}
}

使用lambda简化:
package Java.thread;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("我是主线程");
Runnable s1=()->{
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
//不能直接获取getname,因为不是继承
System.out.println("我是小线程"+"名称:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",运行结果:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}};
Thread t=new Thread(s1,"小线程1");
Thread t1=new Thread(s1,"小线程2");
t.start();
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(50);
System.out.println("主线程结果。");
}
}
3.实现Callable接口
- V call() 计算结果,如果无法计算结果,则抛出一个异常
- FutureTask(Callable callable) 创建一个
FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Callable - V get() 如有必要,等待计算完成,然后获取其结果
o定义一个类MyCallable实现Callable接口
o在MyCallable类中重写call()方法
o创建MyCallable类的对象
o创建Future的实现类FutureTask对象,把MyCallable对象作为构造方法的参数
o创建Thread类的对象,把FutureTask对象作为构造方法的参数
o启动线程
o再调用get方法,就可以获取线程结束之后的结果。
package Java.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class thired implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
System.out.println("我是小线程"+"名称:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",运行结果:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
String o="callable";
return o;
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
thired s1=new thired();
thired s2=new thired();
FutureTask f1=new FutureTask(s1);
FutureTask f2=new FutureTask(s2);
Thread t=new Thread(f1,"小线程1");
Thread t1=new Thread(f2,"小线程2");
t.start();
t1.start();
System.out.println("小线程1结果"+f1.get());
System.out.println("小线程2结果"+f2.get());
System.out.println("主线程结果。");
}
}
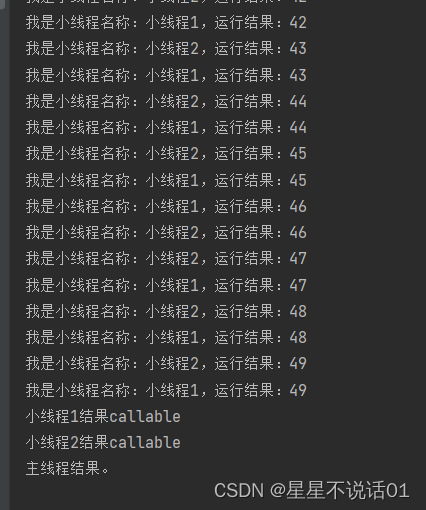
System.out.println(“主线程结果。”); 并不是在所有其他线程都完成之后才执行的,而是取决于 f1.get() 和 f2.get() 的调用顺序和它们的行为。
FutureTask.get() 方法用于获取异步计算的结果。如果计算尚未完成,此方法将阻塞直到它完成。这意味着,如果 f1 或 f2 对应的线程尚未完成其任务,get() 方法将阻塞主线程,直到该任务完成。
主线程会首先等待 f1 完成,然后再等待 f2 完成。
o实现Runnable、Callable接口
o好处: 扩展性强,实现该接口的同时还可以继承其他的类
o缺点: 编程相对复杂,不能直接使用Thread类中的方法
o继承Thread类
o好处: 编程比较简单,可以直接使用Thread类中的方法
o缺点: 可以扩展性较差,不能再继承其他的类
CompletableFuture引入
Future有几个局限,Java1.8就推出了加强版的Future类:CompletableFuture。
来上几个future的局限的代码(部分,下一节重点是completablefuture):
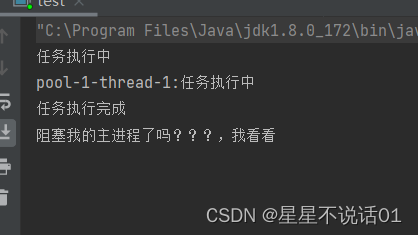
1.阻塞主进程的执行:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//自定义线程池 ,使用自定义的拒绝策略
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));
Callable callable=()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":任务执行中");
Thread.sleep(600);
return "任务执行完成";
};
Future f=threadPoolExecutor.submit(callable);
System.out.println("任务执行中");
System.out.println(f.get());
System.out.println("阻塞我的主进程了吗???,我看看");
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
}
改为completableFuture:
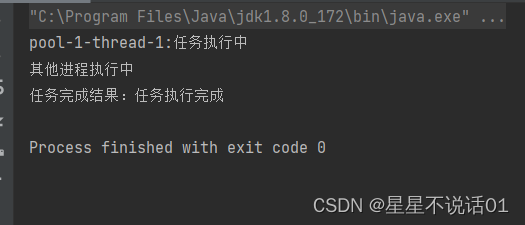
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//自定义线程池 ,使用自定义的拒绝策略
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));
Callable callable=()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":任务执行中");
Thread.sleep(600);
return "任务执行完成";
};
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":任务执行中");
try {
Thread.sleep(600);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "任务执行完成";
},threadPoolExecutor);
//注册一个回调函数来处理结果
completableFuture.thenAccept(re-> {
System.out.println("任务完成结果:"+re);
});
System.out.println("其他进程执行中");
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
}
2.链式调用上:
futuretask不能链式调用,任务2无法用任务1的结果
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//自定义线程池 ,使用自定义的拒绝策略
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));
Future <String> future=threadPoolExecutor.submit(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(60);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "任务1完成";
});
Future <String> future1=threadPoolExecutor.submit(()->{
//我们想要在这个任务中使用 future 的结果,但我们不能直接链式调用
try {
Thread.sleep(60);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "任务2完成";
});
System.out.println(future.get());
System.out.println(future1.get());
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
}
completablefuture:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//自定义线程池 ,使用自定义的拒绝策略
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(60);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "任务1完成";
},threadPoolExecutor);
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1=completableFuture.thenApplyAsync(re->{
//我们想要在这个任务中使用 future 的结果,但我们不能直接链式调用
try {
Thread.sleep(60);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "任务2完成并用了任务1的结果:"+re;
},threadPoolExecutor);
completableFuture.thenAccept(re->{
System.out.println("任务1运行结果:"+re);
});
completableFuture1.thenAccept(re1->{
System.out.println("r任务2运行结果:"+re1);
});
System.out.println("主线程的任务3");
}