目录
1、初识SpringMVC
1.1 SpringMVC概述
1.2 SpringMVC处理请求原理简图
2、SpringMVC搭建框架
2.1 搭建SpringMVC框架
3、@RequestMapping详解
3.1 @RequestMapping注解位置
3.2 @RequestMapping注解属性
3.3 @RequestMapping支持Ant 风格的路径(了解)
4、@PathVariable 注解
4.1 @PathVariable注解位置
4.2 @PathVariable注解作用
4.3 @PathVariable注解属性
5、REST【RESTful】风格CRUD
5.1 REST的CRUD与传统风格CRUD对比
5.2 REST风格CRUD优势
5.3 实现PUT&DELETE提交方式步骤
5.4 源码解析HiddenHttpMethodFilter
6、SpringMVC处理请求数据
6.1 处理请求参数
6.2 处理请头
6.3 处理Cookie信息
6.4 使用原生Servlet-API
7、SpringMVC处理响应数据
7.1 使用ModelAndView
7.2 使用Model、ModelMap、Map
7.3 SpringMVC中域对象
8、SpringMVC处理请求响应乱码
8.1 源码解析CharacterEncodingFilter
8.2 处理请求与响应乱码
9、解析SpringMVC工作原理
9.1 Controller中方法的返回值问题
9.2 视图及视图解析器源码
10、SpringMVC视图及视图解析器
10.1 视图解析器对象【ViewResolver】
10.2 视图对象【View】
11、视图控制器&重定向&加载静态资源
11.1 视图控制器
11.2 重定向
11.3 加载静态资源
11.4 源码解析重定向原理
第十二章 REST风格CRUD练习
12.1 搭建环境
12.2 实现功能思路
1、初识SpringMVC
1.1 SpringMVC概述
SpringMVC是Spring子框架
SpringMVC是Spring 为【展现层|表示层|表述层|控制层】提供的基于 MVC 设计理念的优秀的 Web 框架,是目前最主流的MVC 框架。
SpringMVC是非侵入式:可以使用注解让普通java对象,作为请求处理器【Controller】。
SpringMVC是用来代替Servlet
Servlet作用
1. 处理请求
将数据共享到域中
2. 做出响应
跳转页面【视图】
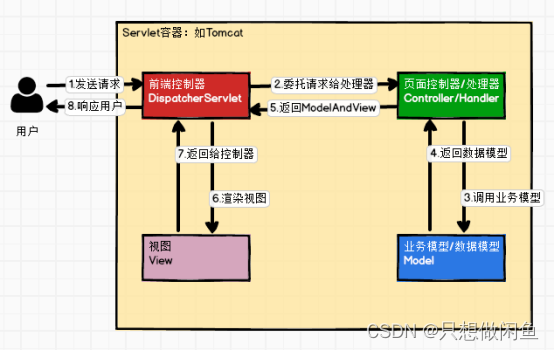
1.2 SpringMVC处理请求原理简图
-
请求:客户端发送请求到服务器。
-
DispatcherServlet【前端控制器】:所有请求都先经过 DispatcherServlet,它是 Spring MVC 的核心控制器,负责统一请求的分发。
-
将请求交给 Controller|Handler:DispatcherServlet 将请求转发给具体的 Controller 或 Handler 处理器。
-
Controller|Handler【请求处理器】:Controller 或 Handler 处理器负责具体的请求处理,可能涉及业务逻辑处理等。
-
处理请求并返回:处理器执行请求处理逻辑,可能会调用 Service 层完成业务逻辑,并返回数据模型。
-
ModelAndView:数据模型包含处理结果的数据,以及视图信息。
-
视图渲染:DispatcherServlet 根据返回的视图信息进行视图渲染,将数据填充到视图中。
-
返回给客户端:渲染后的视图返回给客户端,完成请求响应过程。
2、SpringMVC搭建框架
2.1 搭建SpringMVC框架
创建工程【web工程】
导入jar包
<!--spring-webmvc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 导入thymeleaf与spring5的整合包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--servlet-api-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>编写配置文件
web.xml注册DispatcherServlet
url配置:/
init-param:contextConfigLocation,设置springmvc.xml配置文件路径【管理容器对象】
\<load-on-startup>:设置DispatcherServlet优先级【启动服务器时,创建当前Servlet对象】
springmvc.xml
开启组件扫描
配置视图解析器【解析视图(设置视图前缀&后缀)】
编写请求处理器【Controller|Handler】
使用@Controller注解标识请求处理器
使用@RequestMapping注解标识处理方法【URL】
准备页面进行,测试
3、@RequestMapping详解
@RequestMapping注解作用:为指定的类或方法设置相应URL
3.1 @RequestMapping注解位置
书写在类上面
作用:为当前类设置映射URL
注意:不能单独使用,需要与方法上的@RequestMapping配合使用
书写在方法上面
作用:为当前方法设置映射URL
注意:可以单独使用
3.2 @RequestMapping注解属性
value属性
类型:String[]
作用:设置URL信息
path属性
类型:String[]
作用:与value属性作用一致
method属性
类型:RequestMethod[]
public enum RequestMethod {
GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE
}
作用:为当前URL【类或方法】设置请求方式【POST、DELETE、PUT、GET】
注意:默认情况:所有请求方式均支持,如请求方式不支持,会报如下错误405【Request method 'GET' not supported】
params
类型:String[]
作用:为当前URL设置请求参数
注意:如设置指定请求参数,但URL中未携带指定参数,会报如下错误
400【Parameter conditions "lastName" not met for actual request parameters:】
headers
类型:String[]
作用:为当前URL设置请求头信息
注意:如设置指定请求头,但URL中未携带请求头,会报如下错误
404:请求资源未找到
示例代码
@RequestMapping(value = {"/saveEmp","/insertEmp"},
method = RequestMethod.GET,
params = "lastName=lisi",
headers = "User-Agent=Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/99.0.4844.84 Safari/537.36")
public String saveEmp(){
System.out.println("添加员工信息!!!!");
return SUCCESS;
} @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public @interface PostMapping {}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @interface GetMapping {}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public @interface PutMapping {}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public @interface DeleteMapping {}3.3 @RequestMapping支持Ant 风格的路径(了解)
常用通配符
a) ?:匹配一个字符
b) *:匹配任意字符
c) **:匹配多层路径
示例代码
@RequestMapping("/testAnt/**")
public String testAnt(){
System.out.println("==>testAnt!!!");
return SUCCESS;
}4、@PathVariable 注解
4.1 @PathVariable注解位置
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
书写在参数前面
4.2 @PathVariable注解作用
获取URL中占位符参数
占位符语法:{}
示例代码
<a th:href="@{/EmpController/testPathVariable/1001}">测试PathVariable注解</a><br>
/**
* testPathVariable
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/testPathVariable/{empId}")
public String testPathVariable(@PathVariable("empId") Integer empId){
System.out.println("empId = " + empId);
return SUCCESS;
}
4.3 @PathVariable注解属性
value属性
类型:String
作用:设置占位符中的参数名
name属性
类型:String
作用:与name属性的作用一致
required属性
类型:boolean
作用:设置当前参数是否必须入参【默认值:true】
true:表示当前参数必须入参,如未入参会报如下错误
Missing URI template variable 'empId' for method parameter of type Integer
false:表示当前参数不必须入参,如未入参,会装配null值
5、REST【RESTful】风格CRUD
5.1 REST的CRUD与传统风格CRUD对比
| 功能 | URL | 请求方式 |
| 增 | /insertEmp | POST |
| 删 | /deleteEmp?empId=1001 | GET |
| 改 | /updateEmp | POST |
| 查 | /selectEmp?empId=1001 | GET |
| 功能 | URL | 请求方式 |
| 增 | /emp | POST |
| 删 | /emp/1001 | DELETE |
| 改 | /emp | PUT |
| 查 | /emp/1001 | GET |
5.2 REST风格CRUD优势
REST 风格的 CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete)操作相比传统的 Web 应用程序开发方式具有多方面的优势:
1.提高网站排名:
.排名方式:
竞价排名:通过广告投放等方式,向搜索引擎付费来提高网站在搜索结果中的显示位置。
技术排名:通过搜索引擎的算法对网站内容的相关性、质量等进行评估,从而决定其在搜索结果中的排名位置。
REST 风格的 API 使得网站可以更好地组织和呈现数据,并通过规范的 URL 结构和 HTTP 方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等)来处理请求,这有助于搜索引擎更好地理解和索引网站内容,从而提高技术排名。
2.便于第三方平台对接:
RESTful API 是一种与平台无关的通用接口标准,它基于 HTTP 协议,可以跨平台、跨语言地进行通信。.第三方平台(如移动应用、合作伙伴系统等)可以通过调用 RESTful API 来实现与网站后端的数据交互,实现数据共享、业务整合等功能,从而扩展网站的应用范围和影响力。通过使用 REST 风格的 API 设计,网站可以更好地适应搜索引擎的工作原理,提高在搜索结果中的曝光度;同时,它还可以提供标准化、灵活的接口,方便与其他系统进行集成,从而增强了网站的可扩展性和互操作性。
5.3 实现PUT&DELETE提交方式步骤
注册过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter
设置表单的提交方式为POST
设置参数:\_method=PUT或\_method=DELETE
5.4 源码解析HiddenHttpMethodFilter
public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method";
private String methodParam = DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) == null) {
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(requestToUse, response);
}
/**
* Simple {@link HttpServletRequest} wrapper that returns the supplied method for
* {@link HttpServletRequest#getMethod()}.
*/
private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final String method;
public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) {
super(request);
this.method = method;
}
@Override
public String getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
}6、SpringMVC处理请求数据
使用Servlet处理请求数据
1. 请求参数
String param = request.getParameter();
2. 请求头
request.getHeader();
3. Cookie
request.getCookies();
6.1 处理请求参数
默认情况:可以将请求参数名,与入参参数名一致的参数,自动入参【自动类型转换】
SpringMVC支持POJO入参
要求:请求参数名与POJO的属性名保持一致
示例代码
<form th:action="@{/saveEmp}" method="POST">
id:<input type="text" name="id"><br>
LastName:<input type="text" name="lastName"><br>
Email:<input type="text" name="email"><br>
Salary:<input type="text" name="salary"><br>
<input type="submit" value="添加员工信息">
</form> /**
* 获取请求参数POJO
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/saveEmp",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveEmp(Employee employee){
System.out.println("employee = " + employee);
return SUCCESS;
}@RequestParam注解
作用:如请求参数与入参参数名不一致时,可以使用@RequestParam注解设置入参参数名
属性
value
类型:String
作用:设置需要入参的参数名
name
类型:String
作用:与value属性作用一致
required
类型:Boolean
作用:设置当前参数,是否必须入参
true【默认值】:表示当前参数必须入参,如未入参会报如下错误400【Required String parameter 'sName' is not present】
false:表示当前参数不必须入参,如未入参,装配null值
defaultValue
类型:String
作用:当装配数值为null时,指定当前defaultValue默认值
示例代码
/**
* 获取请求参数
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/requestParam1")
public String requestParam1(@RequestParam(value = "sName",required = false,
defaultValue = "zhangsan")
String stuName,
Integer stuAge){
System.out.println("stuName = " + stuName);
System.out.println("stuAge = " + stuAge);
return SUCCESS;
}
6.2 处理请头
语法:@RequestHeader注解
属性
value
类型:String
作用:设置需要获取请求头名称
name
类型:String
作用:与value属性作用一致
required
类型:boolean
作用:【默认值true】
true:设置当前请求头是否为必须入参,如未入参会报如下错误400【Required String parameter 'sName' is not present】
false:表示当前参数不必须入参,如未入参,装配null值
defaultValue
类型:String
作用:当装配数值为null时,指定当前defaultValue默认值
示例代码
<a th:href="@{/testGetHeader}">测试获取请求头</a>
/**
* 获取请求头
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testGetHeader")
public String testGetHeader(@RequestHeader("Accept-Language")String al,
@RequestHeader("Referer") String ref){
System.out.println("al = " + al);
System.out.println("ref = " + ref);
return SUCCESS;
}
6.3 处理Cookie信息
语法:@CookieValue获取Cookie数值
属性
value
类型:String
作用:设置需要获取Cookie名称
name
类型:String
作用:与value属性作用一致
required
类型:boolean
作用:【默认值true】
true:设置当前Cookie是否为必须入参,如未入参会报如下错误400【Required String parameter 'sName' is not present】
false:表示当前Cookie不必须入参,如未入参,装配null值
defaultValue
类型:String
作用:当装配数值为null时,指定当前defaultValue默认值
示例代码
<a th:href="@{/setCookie}">设置Cookie信息</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/getCookie}">获取Cookie信息</a><br>
/**
* 设置Cookie
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/setCookie")
public String setCookie(HttpSession session){
// Cookie cookie = new Cookie();
System.out.println("session.getId() = " + session.getId());
return SUCCESS;
}
/**
* 获取Cookie
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getCookie")
public String getCookie(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID")String cookieValue){
System.out.println("cookieValue = " + cookieValue);
return SUCCESS;
}
6.4 使用原生Servlet-API
将原生Servlet相关对象,入参即可
@RequestMapping("/useRequestObject")
public String useRequestObject(HttpServletRequest request){}7、SpringMVC处理响应数据
7.1 使用ModelAndView
使用ModelAndView对象作为方法返回值类型,处理响应数据
ModelAndView是模型数据与视图对象的集成对象,源码如下
public class ModelAndView {
/** View instance or view name String. */
//view代表view对象或viewName【建议使用viewName】
@Nullable
private Object view;
/** Model Map. */
//ModelMap集成LinkedHashMap,存储数据
@Nullable
private ModelMap model;
/**
设置视图名称
*/
public void setViewName(@Nullable String viewName) {
this.view = viewName;
}
/**
* 获取视图名称
*/
@Nullable
public String getViewName() {
return (this.view instanceof String ? (String) this.view : null);
}
/**
获取数据,返回Map【无序,model可以为null】
*/
@Nullable
protected Map<String, Object> getModelInternal() {
return this.model;
}
/**
* 获取数据,返回 ModelMap【有序】
*/
public ModelMap getModelMap() {
if (this.model == null) {
this.model = new ModelMap();
}
return this.model;
}
/**
* 获取数据,返回Map【无序】
*/
public Map<String, Object> getModel() {
return getModelMap();
}
/**
设置数据
*/
public ModelAndView addObject(String attributeName, @Nullable Object attributeValue) {
getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue);
return this;
}
}
示例代码
@GetMapping("/testMvResponsedata")
public ModelAndView testMvResponsedata(){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
//设置逻辑视图名
mv.setViewName("response_success");
//设置数据【将数据共享到域中(request\session\servletContext)】
mv.addObject("stuName","zhouxu");
return mv;
}
7.2 使用Model、ModelMap、Map
使用Model、ModelMap、Map作为方法入参,处理响应数据
示例代码
/**
* 使用Map、Model、ModelMap处理响应数据
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/testMapResponsedata")
public String testMapResponsedata(Map<String,Object> map
/* Model model
ModelMap modelMap*/){
map.put("stuName","zhangsan");
// model.addAttribute("stuName","lisi");
// modelMap.addAttribute("stuName","wangwu");
return "response_success";
}
7.3 SpringMVC中域对象
SpringMVC封装数据,默认使用request域对象
session域的使用
方式一
/**
* 测试响应数据【其他域对象】
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/testScopeResponsedata")
public String testScopeResponsedata(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("stuName","xinlai");
return "response_success";
}
方式二
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value = "stuName") //将request域中数据,同步到session域中
public class TestResponseData {
/**
* 使用ModelAndView处理响应数据
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/testMvResponsedata")
public ModelAndView testMvResponsedata(){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
//设置逻辑视图名
mv.setViewName("response_success");
//设置数据【将数据共享到域中(request\session\servletContext)】
mv.addObject("stuName","zhouxu");
return mv;
}
}
8、SpringMVC处理请求响应乱码
8.1 源码解析CharacterEncodingFilter
public class CharacterEncodingFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
//需要设置字符集
@Nullable
private String encoding;
//true:处理请乱码
private boolean forceRequestEncoding = false;
//true:处理响应乱码
private boolean forceResponseEncoding = false;
public String getEncoding() {
return this.encoding;
}
public boolean isForceRequestEncoding() {
return this.forceRequestEncoding;
}
public void setForceResponseEncoding(boolean forceResponseEncoding) {
this.forceResponseEncoding = forceResponseEncoding;
}
public void setForceEncoding(boolean forceEncoding) {
this.forceRequestEncoding = forceEncoding;
this.forceResponseEncoding = forceEncoding;
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String encoding = getEncoding();
if (encoding != null) {
if (isForceRequestEncoding() || request.getCharacterEncoding() == null) {
request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
if (isForceResponseEncoding()) {
response.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
8.2 处理请求与响应乱码
SpringMVC底层默认处理响应乱码
SpringMVC处理请求乱码步骤
1. 注册CharacterEncodingFilter
注册CharacterEncodingFilter必须是第一Filter位置
2. 为CharacterEncodingFilter中属性encoding赋值
3. 为CharacterEncodingFilter中属性forceRequestEncoding赋值
示例代码
<!-- 必须是第一过滤器位置-->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
9、解析SpringMVC工作原理
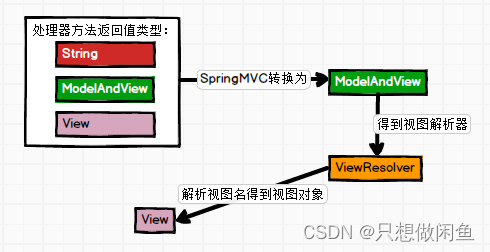
9.1 Controller中方法的返回值问题
无论方法返回是ModelAndView还是String,最终SpringMVC底层,均会封装为ModelAndView对象
- ModelAndView: 这是一种常见的返回类型,它包含了数据模型(Model)和视图名称(View)。在方法中创建一个
ModelAndView对象,并设置数据模型和视图名称,最后返回该对象。Spring MVC会根据ModelAndView中指定的视图名称找到对应的视图,并将数据模型传递给该视图,最终呈现给用户。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("/example")
public ModelAndView handleRequest() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("exampleView");
modelAndView.addObject("message", "Hello, Spring MVC!");
return modelAndView;
}
}
- String: 控制器方法也可以直接返回视图名称的字符串。在这种情况下,Spring MVC会将该字符串解释为视图的逻辑名称,并根据配置的视图解析器(ViewResolver)找到对应的视图。
@Controller public class MyController { @RequestMapping("/example") public String handleRequest(Model model) { model.addAttribute("message", "Hello, Spring MVC!"); return "exampleView"; } }
9.2 视图及视图解析器源码
视图解析器将View从ModelAndView中解析出来
视图解析过程
视图解析器通常根据配置的规则,将控制器方法返回的逻辑视图名称映射到具体的视图资源。这个映射过程可以涉及到前缀、后缀等规则。例如,如果我们配置了一个视图解析器用于解析JSP视图,那么它可能会将逻辑视图名称"exampleView"解析为"/WEB-INF/views/exampleView.jsp"。
视图对象的创建
一旦视图解析器确定了实际的视图资源,它就会创建对应的视图对象。视图对象负责将模型数据渲染到最终的HTML页面中。不同的视图解析器会创建不同类型的视图对象。例如,InternalResourceViewResolver会创建InternalResourceView对象用于解析JSP视图,而ThymeleafViewResolver会创建ThymeleafView对象用于解析Thymeleaf模板引擎视图。
视图的渲染
一旦创建了视图对象,视图解析器就会调用该视图对象的渲染方法,将模型数据传递给视图,并生成最终的HTML内容。这个过程包括将模型中的数据填充到视图中的占位符、执行相应的逻辑等。
示例代码
下面是一个简单的Spring MVC配置,其中包括了一个InternalResourceViewResolver的示例,用于解析JSP视图。
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
registry.viewResolver(resolver);
}
}
在这个配置中,我们创建了一个InternalResourceViewResolver实例,并设置了JSP文件的前缀和后缀。这样,当控制器方法返回的视图名称为"exampleView"时,视图解析器会将其解析为"/WEB-INF/views/exampleView.jsp",并创建相应的InternalResourceView对象进行渲染。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("/example")
public String handleRequest(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello, Spring MVC!");
return "exampleView";
}
}
在这个示例中,handleRequest方法返回了一个字符串"exampleView",这是一个逻辑视图名称。视图解析器会将其解析为"/WEB-INF/views/exampleView.jsp",并最终渲染该JSP视图
10、SpringMVC视图及视图解析器
10.1 视图解析器对象【ViewResolver】
概述:ViewResolver接口的实现类或子接口,称之为视图解析器
作用:将ModelAndView中的View对象解析出来
10.2 视图对象【View】
概述:View接口的实现类或子接口,称之为视图对象
作用:视图渲染
1. 将数据共享域中
2. 跳转路径【转发或重定向】
11、视图控制器&重定向&加载静态资源
11.1 视图控制器
语法:view-controller
步骤
1. 添加\<mvc:view-controller>标签:为指定URL映射html页面
2. 添加\<mvc:annotation-driven>
有20+种功能
配置了\<mvc:view-controller>标签之后会导致其他请求路径都失效,添加\<mvc:annotation-driven>解决
11.2 重定向
语法:return "**redirect:/**xxx.html";
11.3 加载静态资源
由DefaultServlet加载静态资源到服务器
静态资源:html、css、js等资源
tomcat->conf->web.xml关键代码如下:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.catalina.servlets.DefaultServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>debug</param-name>
<param-value>0</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>listings</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
发现问题
DispatcherServlet与DefaultServlet的URL配置均为:/,导致DispatcherServlet中的配置将DefaultServlet配置的/覆盖了【DefaultServlet失效,无法加载静态资源】
解决方案
<!-- 解决静态资源加载问题-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler></mvc:default-servlet-handler>
<!-- 添加上述标签,会导致Controller无法正常使用,需要添加mvc:annotation-driven解决 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>11.4 源码解析重定向原理
创建RedirectView对象【ThymeleafViewResolver的775行代码】
// Process redirects (HTTP redirects)
if (viewName.startsWith(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX)) {
vrlogger.trace("[THYMELEAF] View \"{}\" is a redirect, and will not be handled directly by ThymeleafViewResolver.", viewName);
final String redirectUrl = viewName.substring(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX.length(), viewName.length());
final RedirectView view = new RedirectView(redirectUrl, isRedirectContextRelative(), isRedirectHttp10Compatible());
return (View) getApplicationContext().getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().initializeBean(view, REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX);
}第十二章 REST风格CRUD练习
12.1 搭建环境
导入相关jar包
<!--spring-webmvc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 导入thymeleaf与spring5的整合包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--servlet-api-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
编写配置文件
web.xml
CharacterEncodingFilter
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
DispatcherServlet
springmvc.xml
开启组件扫描
装配视图解析器
装配视图控制器
解决静态资源加载问题
装配annotation-driver
dao&pojo
12.2 实现功能思路
实现添加功能思路
1. 跳转添加页面【查询所有部门信息】
2. 实现添加功能
实现删除功能思路
1. 方式一:直接使用表单实现DELETE提交方式
2. 方式二:使用超链接【a】实现DELETE提交方式
使用Vue实现单击超链接,后提交对应表单
取消超链接默认行为
示例代码
<div align="center" id="app">
<a href="#" @click="deleteEmp">删除</a>
<form id="delForm" th:action="@{/emps/}+${emp.id}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE">
</form>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="static/js/vue_v2.6.14.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{},
methods:{
deleteEmp(){
alert("hehe");
//获取响应表单
var formEle = document.getElementById("delForm");
formEle.submit();
//取消超链接默认行为
event.preventDefault();
}
}
});
</script>