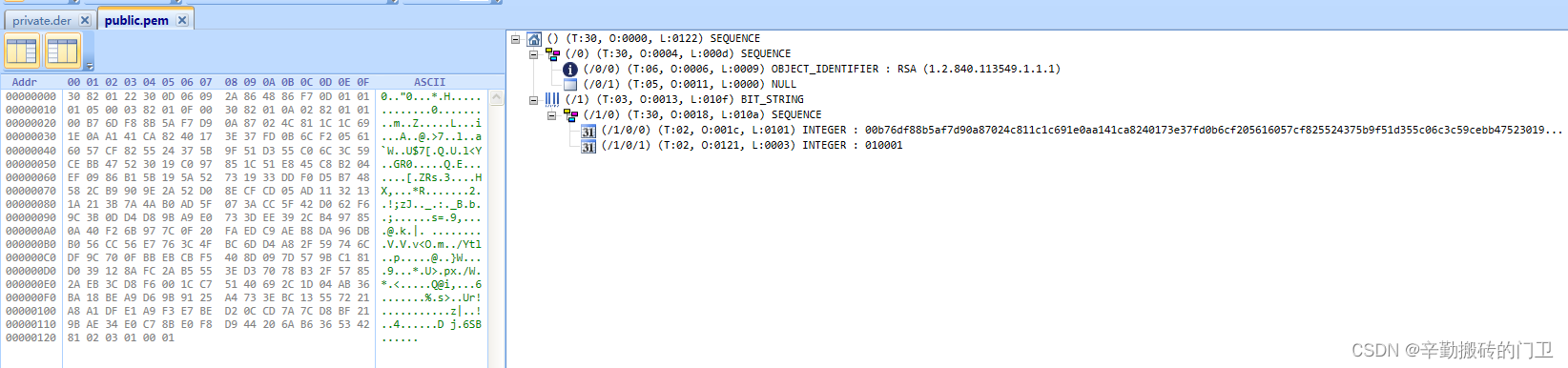
BMI例题如下:
BMI中国计算标准:体质指数(BMI)=体重(kg)÷身高^2(m)
例如:一个人的身高为1.75米,体重为68千克,他的BMI=68/(1.75^2)=22.2(千克/米^2)当BMI指数为18.5~23.9时属正常。
成人的BMI数值标准:
过轻:低于18.5 正常:>=18.5且<24
过重:>=24且<28 肥胖:>=28且<32
非常肥胖:>=32
第1步:在IEDA环境下完成BMI类的代码实现
方案1:通过键盘输入身高,体重或者直接通过构造方法或者BMI类的成员方法初始化身高体重,然后调用方法计算BMI值,并人工判断校验。
package sample;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import static java.lang.Math.abs;
public class BMI {
double height; //身高
double weight; //体重
//设置和得到属性值
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
//构造函数
public BMI(double w, double h) {
weight = w;
height = h;
}
//设置体重和身高
public void setParams(double w, double h) {
weight = w;
height = h;
}
//根据 BMI 值判断健康状况
public String getBMIType() {
double bmi = 0.0;
String result = "";
//设置浮点数输出格式,保留 2 位小数
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
if (weight > 0 && height > 0) {
//计算 BMI
bmi = weight / (height * height);
//2、根据 bmi 判断所属健康分类
if (bmi < 18.5) {
result = "偏瘦";
} else if (bmi < 24) {
result = "正常";
} else if (bmi < 28) {
result = "过重";
}else if (bmi < 32) {
result = "肥胖";
}else {
result = "非常肥胖";
} } else {
return "重量或者身高错误!";
}
System.out.println("bmi 的值是:" + df.format(bmi));
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方案 1
//用户输入体重和身高,调用被测方法,结果输出到屏幕
//得到一个扫描对象,从键盘接收数据
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
double w = 0.0, h = 0.0;
System.out.println("请输入体重(公斤)和身高(米),以等号=结束");
//检测到下一个数为 Double 类型,则返回 True
while (reader.hasNextDouble()) {
w = reader.nextDouble();
h = reader.nextDouble();
}
BMI testobj = new BMI(w, h);
String result = testobj.getBMIType();
String output = "体重:" + w + ",身高:" + h + ",BMI 状况是:" + result;
System.out.println(output);
//设置多个测试用例
BMI tmpobj = new BMI(45.0, 1.6);
String type = tmpobj.getBMIType();
System.out.println(type);
tmpobj.setParams(55, 1.6);
System.out.println(tmpobj.getBMIType());
tmpobj.setParams(68, 1.6);
System.out.println(tmpobj.getBMIType());
tmpobj.setParams(80, 1.6);
System.out.println(tmpobj.getBMIType());
}
}
根据自身实际问题再做修改。
第2步:针对BMI类设计测试用例
| 输入 | BMI值 | 等价类/边界值 | 预期输出 | ||
| 用例编号 | 体重(KG) | 身高(M) | |||
| 1 | 59.95 | 1.80 | 18.5 | 等于边界值18.5 | 正常 |
| 2 | 46.24 | 1.70 | 16 | 输出等价类小于18.5 | 过轻 |
| 3 | 0 | 1.70 | 输入体重边界值0 | 输入有误 | |
| 4 | 48.91 | 1.62 | 18.6 | 输出等价类大于18.5 | 正常 |
| 5 | 69.12 | 1.70 | 23.9 | 输出等价类小于24 | 正常 |
| 6 | 68.55 | 1.69 | 24.0 | 等于边界值24 | 过重 |
| 7 | 71.32 | 1.72 | 24.1 | 输出等价类大于24 | 过重 |
| 8 | 82.56 | 1.72 | 27.9 | 输出等价类小于28 | 过重 |
| 9 | 79.10 | 1.68 | 28.0 | 等于边界值28 | 肥胖 |
| 10 | 80.31 | 1.69 | 28.1 | 输出等价类大于28 | 肥胖 |
| 11 | 93.31 | 1.71 | 31.9 | 输出等价类小于32 | 肥胖 |
| 12 | 88.20 | 1.66 | 32.0 | 等于边界值32 | 非常肥胖 |
| 13 | 88.50 | 1.66 | 32.1 | 输出等价类大于32 | 非常肥胖 |
| 14 | 100.04 | 1.69 | 35.0 | 输出等价类大于32 | 非常肥胖 |
| 15 | 60.00 | 0 | 输入身高边界值0 | 输入有误 | |
| 16 | 200.00 | 1.7 | 69.2 | 无效等价类超出正常体重 | 输入有误 |
| 17 | 60.00 | 2.50 | 9.6 | 无效等价类超出正常身高 | 输入有误 |
| 18 | 60.00 | 0.90 | 74.1 | 无效等价类低于正常身高 | 输入有误 |
设计用例不多,可以再自行增加边界值用例。
第3步
方案2是在方案1的基础上改进,将预期值和计算的BMI值进行比较,实现自动校验。
package sample;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import static java.lang.Math.abs;
public class BMI {
double height; //身高
double weight; //体重
//设置和得到属性值
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
//构造函数
public BMI(double w, double h) {
weight = w;
height = h;
}
//设置体重和身高
public void setParams(double w, double h) {
weight = w;
height = h;
}
//根据 BMI 值判断健康状况
public String getBMIType() {
double bmi = 0.0;
String result = "";
//设置浮点数输出格式,保留 2 位小数
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
if (weight > 0 && height > 0) {
//计算 BMI
bmi = weight / (height * height);
//2、根据 bmi 判断所属健康分类
if (bmi < 18.5) {
result = "偏瘦";
} else if (bmi < 24) {
result = "正常";
} else if (bmi < 28) {
result = "过重";
}else if (bmi < 32) {
result = "肥胖";
}else {
result = "非常肥胖";
} } else {
return "重量或者身高错误!";
}
System.out.println("bmi 的值是:" + df.format(bmi));
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方案 2:脚本自行根据测试用例来设置体重和身高,并自动校验执行结果
//1、创建被测对象
BMI testobj=new BMI(48.91,1.62);
//2、调用被测方法
String actual=testobj.getBMIType();
//3、校验执行结果
String expected="正常";
String output="";
if(actual==expected)
{ output+="pass";
}else
{ output+="Fail,体重:48.91,身高 1.62,Expected:"+expected+",Actual:"+actual;
}output+="\n";
//测试用例 2
testobj.setParams(69.12,1.70); actual=testobj.getBMIType(); expected="正常";
if(actual==expected)
{
output+="pass";
}else
{ output+="Fail,体重:69.12,身高 1.70,Expected:"+expected+",Actual:"+actual;
}output+="\n";
//测试用例 3
testobj.setParams(68.55,1.69); actual=testobj.getBMIType(); expected="过重";
if(actual==expected)
{ output+="pass";
}else
{ output+="Fail,体重:68.55,身高 1.69,Expected:"+expected+",Actual:"+actual;
}output+="\n";
//测试用例 4
testobj.setParams(71.32,1.72); actual=testobj.getBMIType(); expected="过重";
if(actual==expected)
{ output+="pass";
}else
{ output+="Fail,体重:71.32,身高 1.72,Expected:"+expected+",Actual:"+actual;
}output+="\n";
//4、输出结果
System.out.println(output);
}
}
第4步
先另外创建一个TestBMI类,在方案1和方案2基础上做如下改进:
方案3代码如下:
package sample;
import static java.lang.Math.abs;
class TestBMI {
BMI bmiObj; //被测类
//创建被测对象
public void createTestobj(double w, double h) {
bmiObj = new BMI(w, h);
}
//释放被测对象
public void freeTestobj() {
bmiObj = null;
}
//执行结果校验
public boolean verify(String expected, String actual) {
if (expected == actual) { return true;
} else {return false;
}
}
//记录执行过程
public String record(double w, double h, String expected, String actual, boolean testResult) {
String output = "";
if (testResult) { output += "Pass. 体重:" + w + ", 身高:" + h;
} else {output += "Fail. 体重:" + w + ", 身高:" + h +
", Expected:" + expected + ", Actual:" + actual;
}return output;
}
//测试用例 1
public void testGetBMIType1() { createTestobj(48.91, 1.62);
String actual = bmiObj.getBMIType();
boolean testResult = verify("正常", actual);
System.out.println(record(48.91, 1.62, "正常", actual, testResult));
freeTestobj();
}
//测试用例 2
public void testGetBMIType2() { createTestobj(69.12, 1.70);
String actual = bmiObj.getBMIType();
boolean testResult = verify("正常", actual);
System.out.println(record(69.12, 1.70, "正常", actual, testResult));
freeTestobj();
}
//测试用例 3
public void testGetBMIType3() { createTestobj(68.55, 1.69);
String actual = bmiObj.getBMIType();
boolean testResult = verify("过重", actual);
System.out.println(record(68.55, 1.69, "过重", actual, testResult));
freeTestobj();
}
//测试用例 14
public void testGetBMIType4() { createTestobj(71.32, 1.72);
String actual = bmiObj.getBMIType();
boolean testResult = verify("过重", actual);
System.out.println(record(71.32, 1.72, "过重", actual, testResult));
freeTestobj();
}
//主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestBMI test = new TestBMI();
test.testGetBMIType1();
test.testGetBMIType2();
test.testGetBMIType3();
test.testGetBMIType4();
}
}
第5步:BMI类下创建BMITest类进行独立测试
测试结果如下:

代码如下:
package sample;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class BMITest {
BMI testobj; //创建被测类
@Test
public void getBMIType() {
//创建被测对象
testobj=new BMI(48.91,1.62);
String expected="正常";
//System.out.println(testobj.getBMIType());
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType()==expected);
testobj=null;
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Normal() {
//创建被测对象
testobj=new BMI(69.12,1.70);
String expected="正常";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType()==expected);
testobj=null;
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Thin() {
//创建被测对象
testobj=new BMI(68.55,1.69);
String expected="过重";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType()==expected);
testobj=null;
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_SlightlyFat() {
//创建被测对象
testobj=new BMI(71.32,1.72);
String expected="过重";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType()==expected);
//释放对象
testobj=null;
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Fat() {
//创建被测对象
testobj=new BMI(79.1,1.68);
String expected="肥胖";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType()==expected);
testobj=null;
}
}
第6步:BMI类创建BMITest1类,使用Before和After方法进行独立测试
测试结果如下:
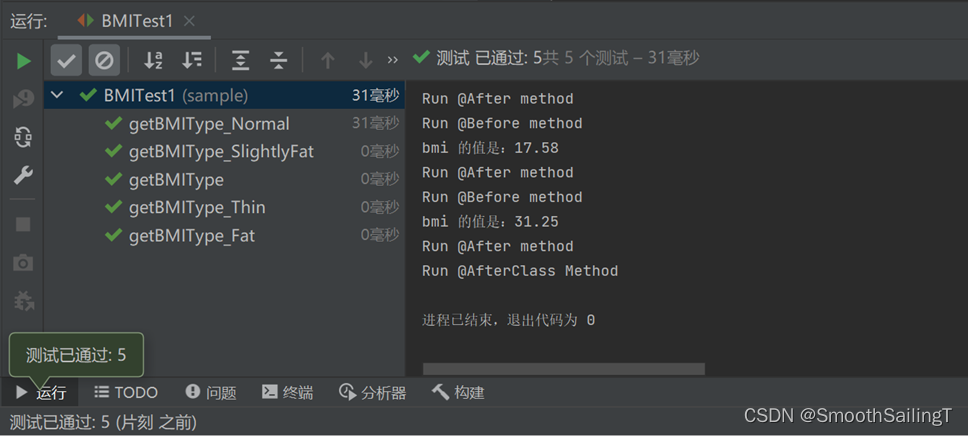
代码如下:
package sample;
import org.junit.*;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class BMITest1 {
BMI testobj;
@Before
public void setUp() {
System.out.println("Run @Before method");
testobj = new BMI();
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
System.out.println("Run @After method");
testobj = null;
}
@BeforeClass
public static void prepareEnvironment() {
System.out.println("Run @BeforeClass Method");
}
@AfterClass
public static void RestoreEnvironment() {
System.out.println("Run @AfterClass Method");
}
@Test
public void getBMIType() {
//创建被测对象
testobj.setParams(55.0, 1.6);
String expected = "正常";
//System.out.println(testobj.getBMIType());
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Normal() {
//赋值被测对象
testobj.setParams(55.0, 1.6);
String expected = "正常";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Thin() {
//赋值被测对象
testobj.setParams(45.0, 1.6);
String expected = "偏瘦";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_SlightlyFat() {
//赋值被测对象
testobj.setParams(55.0, 1.6);
String expected = "正常";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Fat() {
//赋值被测对象
testobj.setParams(80.0, 1.6);
String expected = "肥胖";
//调用测试方法,并校验测试结果
assertTrue(testobj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
}
代码根据需求或用例自行修改。