目录
- 1.字母大小写全排列
- 1.题目链接
- 2.算法原理详解
- 3.代码实现
- 2.优美的排列
- 1.题目链接
- 2.算法原理详解
- 3.代码实现
- 3.N 皇后
- 1.题目链接
- 2.算法原理详解
- 3.代码实现
1.字母大小写全排列
1.题目链接
- 字母大小写全排列
2.算法原理详解
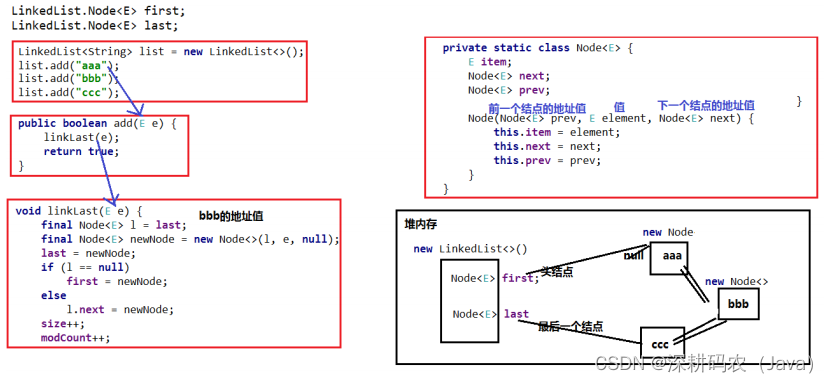
- 本题逻辑与子集大致相同
-
- 思路一:每次盯着一个字符,变或是不变
- 全局变量:
string pathvector<string> ret
DFS()设计- 函数头:
void DFS(string, pos)pos:下一层递归要选的元素
- 函数体:
- 字母可能变/不变,数字一定不需要变
- 递归出口:
pos == nums.size()
- 函数头:
- 回溯:变完函数返回时需要回溯
- 全局变量:
- 思路一:每次盯着一个字符,变或是不变
3.代码实现
class Solution
{
string path;
vector<string> ret;
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string s)
{
DFS(s, 0);
return ret;
}
void DFS(string& s, int pos)
{
if(pos == s.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
char ch = s[pos];
// 不改变
path += ch;
DFS(s, pos + 1);
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,恢复现场
// 改变
if(ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
ch = Change(ch);
path += ch;
DFS(s, pos + 1);
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,恢复现场
}
}
char Change(char ch)
{
if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')
{
ch -= 32;
}
else
{
ch += 32;
}
return ch;
}
};
2.优美的排列
1.题目链接
- 优美的排列
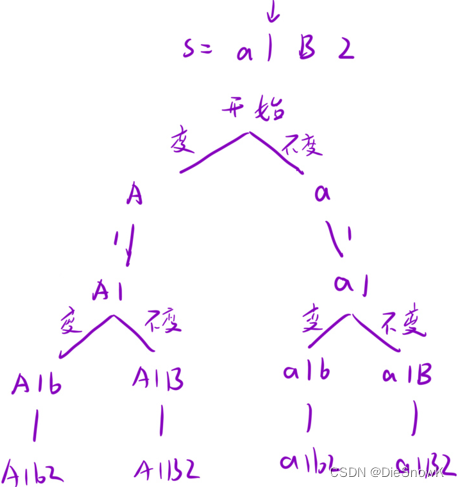
2.算法原理详解
- 思路:对每个位置挨个尝试填入数字
- 全局变量:
int retvector<bool> check-> 剪枝
DFS()设计:void DFS(pos, n)- 剪枝:
- 之前用过的数字不再使用
- 不符合情况的不填入
- 回溯:每层递归返回时回溯
- 全局变量:
3.代码实现
class Solution
{
int ret = 0;
vector<bool> check;
public:
int countArrangement(int n)
{
check.resize(n + 1, false);
DFS(1, n);
return ret;
}
void DFS(int pos, int n)
{
if(pos == n + 1)
{
ret++;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(!check[i] && (i % pos == 0 || pos % i == 0))
{
check[i] = true;
DFS(pos + 1, n);
check[i] = false; // 回溯,恢复现场
}
}
}
};
3.N 皇后
1.题目链接
- N 皇后
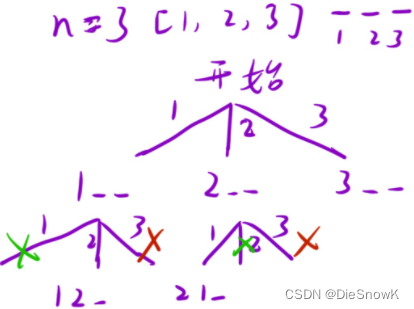
2.算法原理详解
-
本题可以学习二维数组判断行列、主副对角线是否放有数据
-
思路:在每一行找合适的列放置皇后,即每次枚举都是枚举一行
-DFS()设计:void DFS(row)- 决策树
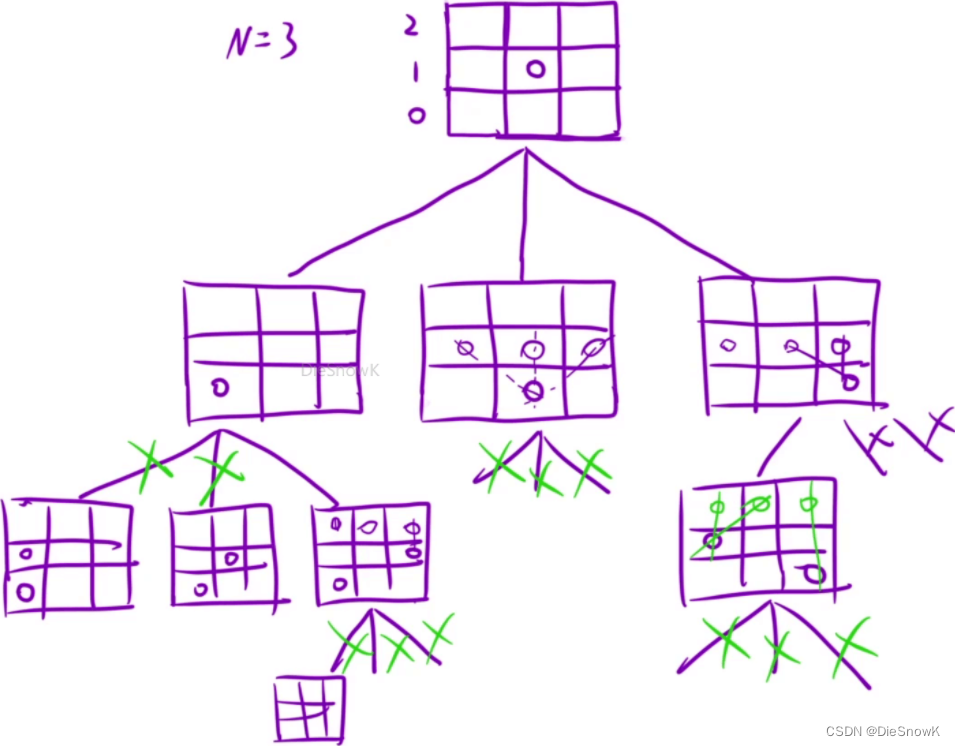
- 决策树
-
如何剪枝?-> 当前这个位置,能否放上皇后?
- 无脑四个循环判断行列、主副对角线 -> ×
- 类似哈希表的策略,需要一定数学理解
- 行不需要剪枝,收递归限制
bool checkCol[n]-> 判断列- 对应下标表示每列是否放置过皇后
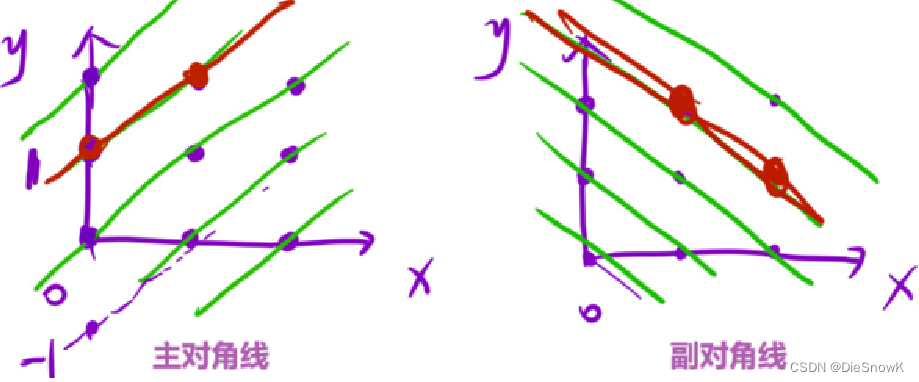
bool checkDig1[2 * n]-> 主对角线y = x + b->y - x = b->b可以唯一标识一个对角线y - x + n = b + n-> 两边加上一个固有偏移量防止下标出现负数
bool checkDig2[2 * n]-> 副对角线y = -x + b->y + x = b->b可以唯一标识一个对角线- 副对角线不需要固定偏移量,因为副对角线的纵截距都大于0
3.代码实现
class Solution
{
int _n = 0;
vector<bool> checkCol;
vector<bool> checkDig1;
vector<bool> checkDig2;
vector<vector<string>> ret;
vector<string> path;
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n)
{
_n = n;
checkCol.resize(n, false);
checkDig1.resize(2 * n, false);
checkDig2.resize(2 * n, false);
path.resize(n, string(n, '.'));
DFS(0);
return ret;
}
void DFS(int row)
{
// 递归出口
if(row == _n)
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 对于每一行,枚举每一列
for(int i = 0; i < _n; i++)
{
// 剪枝
if(!checkCol[i] && !checkDig1[row - i + _n] && !checkDig2[row + i])
{
checkCol[i] = checkDig1[row - i + _n] = checkDig2[row + i] = true;
path[row][i] = 'Q';
DFS(row + 1);
checkCol[i] = checkDig1[row - i + _n] = checkDig2[row + i] = false; // 回溯
path[row][i] = '.';
}
}
}
};