文章目录
- 一、简介
- 二、实现代码
- 2.1 windows平台
- 2.2 C++标准库
- 三、实现效果
一、简介
有时候总是会用到一些计时的操作,这里也整理了一些代码,包括C++标准库以及window自带的时间计算函数。
二、实现代码
2.1 windows平台
StopWatch.h
#ifndef STOP_WATCH_H
#define STOP_WATCH_H
#ifdef _WIN32
# include <windows.h>
#else
# include <sys/time.h>
#endif
/// <summary>
/// 基于Windows平台提供的函数,进行时间计算
/// </summary>
class StopWatch
{
public:
StopWatch(); // 计时器将自动开始
~StopWatch();
void start();
// 返回启动以来用户经过的时间(以秒为单位)。
double elapsed() const;
private:
#ifdef WIN32
LONGLONG freq_;
LONGLONG start_count_;
#else
timeval start_time_;
#endif
};
#endif
StopWatch.cpp
#include "StopWatch.h"
#include <iostream>
StopWatch::StopWatch() {
start(); //开始计时
}
StopWatch::~StopWatch() {}
void StopWatch::start() {
#ifdef WIN32
LARGE_INTEGER largeInteger;
// 获取高精度性能计数器的频率,这个频率通常以每秒的计数数来衡量。
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&largeInteger);
freq_ = largeInteger.QuadPart;
//获取当前性能计数器的值,它表示自系统启动以来的计数次数。
QueryPerformanceCounter(&largeInteger);
start_count_ = largeInteger.QuadPart;
#else
gettimeofday(&start_time_, 0);
#endif
}
template <class T>
inline T clip_precision(T v, int p) {
float tmp = std::pow(10.0f, p);
return (static_cast<int>(v * tmp) / tmp);
}
double StopWatch::elapsed() const {
#ifdef WIN32
LARGE_INTEGER largeInteger;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&largeInteger);
LONGLONG now_count = largeInteger.QuadPart;
//计算已经经过的时间。
//计算当前计数值与起始计数值之间的差值,然后将其除以频率来得到时间,以秒为单位。
double time = (double)((now_count - start_count_) / static_cast<double>(freq_));
return clip_precision(time, 6); //保留小数的有效位数
#else
timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now, 0);
double time = (now.tv_sec - start_time_.tv_sec) + (now.tv_usec - start_time_.tv_usec) / 1.0e6;
return clip_precision(time, 2);
#endif
}
2.2 C++标准库
std::chrono::steady_clock类型
Timer.h
#pragma once
#define NOMINMAX
#undef min
#undef max
#include <chrono>
#include <stdexcept>
/// <summary>
/// 基于C++标准库时间函数,进行计时(支持跨平台使用)
/// </summary>
class Timer
{
public:
Timer()
: m_start(std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point::min())
{
}
void clear()
{
m_start = std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point::min();
}
bool isStarted() const
{
return (m_start != std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point::min()); //最小时间点
}
void start()
{
//steady_clock 是一个专门用于测量时间间隔的时钟,
//它提供了稳定的、不受系统时间调整影响的时间
m_start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
}
std::int64_t getMs() const
{
if (!this->isStarted()) {
throw std::runtime_error("计时器未启动!");
}
const std::chrono::steady_clock::duration diff = std::chrono::steady_clock::now() - m_start;
return std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(diff).count();
}
private:
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point m_start;
};
std::clock类型
BasicTimer.h
#ifndef TIMER_H
#define TIMER_H
#include <cfloat>
/// <summary>
/// 测量用户进程时间的计时器类, 它只计算处于
/// 运行状态(CPU执行)的时间, 时间信息以秒为单位给出。
/// </summary>
class BasicTimer
{
public:
BasicTimer() : elapsed_(0.0), started_(0.0), interv_(0), running_(false) {}
void start();
void stop();
void reset();
bool is_running() const { return running_; }
double time() const;
int intervals() const { return interv_; }
double precision() const;
private:
double user_process_time() const; //秒
double compute_precision() const; //秒
double elapsed_;
double started_;
int interv_;
bool running_;
static bool failed_;
};
#endif
BasicTimer.cpp
#include "BasicTimer.h"
#include <climits>
#include <ctime>
#include <cfloat>
#include <assert.h>
#include <cmath>
bool BasicTimer::failed_ = false;
template <class T>
inline T basic_timer_clip_precision(T v, int p) {
float tmp = std::pow(10.0f, p);
return (static_cast<int>(v * tmp) / tmp);
}
double BasicTimer::user_process_time() const {
// 与操作系统相关。 返回一个单调增加的时间(以秒为单位)
//(在溢出的情况下可能会回绕,请参阅 max()),
// 如果该时间的系统调用失败,则返回 0.0。
// 如果系统调用失败,则设置静态标志“m_failed”。
std::clock_t clk = std::clock();
assert(clk != (std::clock_t)-1);
if (clk != (std::clock_t)-1) {
return double(clk) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
}
else {
failed_ = true;
return 0.0;
}
}
double BasicTimer::compute_precision() const {
// 动态计算计时器精度(以秒为单位)。
double min_res = DBL_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
double current = user_process_time();
if (failed_)
return -1.0;
double next = user_process_time();
while (current >= next) { // 等到计时器增加
next = user_process_time();
if (failed_)
return -1.0;
}
// 获取所有运行的最小时间差。
if (min_res > next - current)
min_res = next - current;
}
return min_res;
}
double BasicTimer::precision() const {
// 如果计时器系统调用失败,则第一次调用时计算精度返回 -1.0。
static double prec = compute_precision();
return prec;
}
void BasicTimer::start() {
assert(!running_);
started_ = user_process_time();
running_ = true;
++interv_;
}
void BasicTimer::stop() {
assert(running_);
double t = user_process_time();
elapsed_ += (t - started_);
started_ = 0.0;
running_ = false;
}
void BasicTimer::reset() {
interv_ = 0;
elapsed_ = 0.0;
if (running_) {
started_ = user_process_time();
++interv_;
}
else {
started_ = 0.0;
}
}
double BasicTimer::time() const {
if (running_) {
double t = user_process_time();
return basic_timer_clip_precision(elapsed_ + (t - started_), 6);
}
return basic_timer_clip_precision(elapsed_, 6);
}
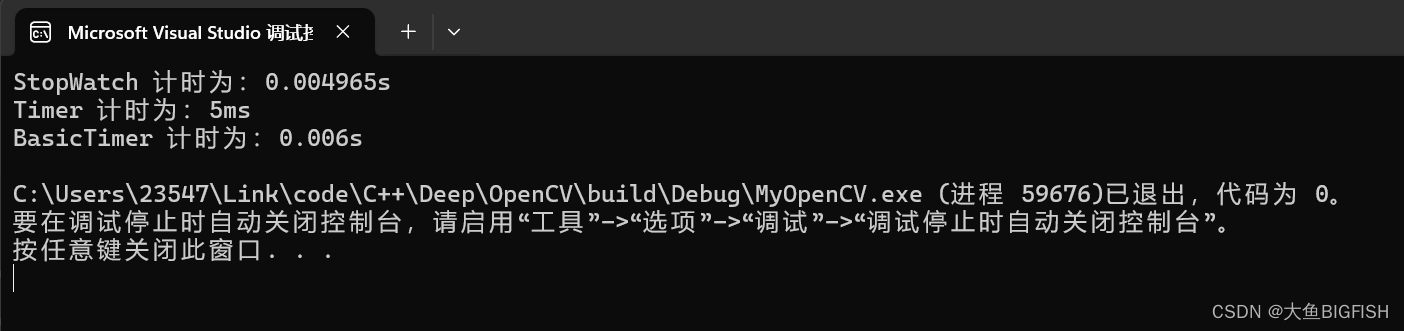
三、实现效果
测试:
#include <iostream>
#include "../StopWatch.h"
#include "../Timer.h"
#include "../BasicTimer.h"
int main()
{
// ------------------------windows平台----------------------
StopWatch stopWatch;
stopWatch.start();
// --------------------C++标准库(支持跨平台)---------------
Timer timer;
timer.start();
BasicTimer basicTimer;
basicTimer.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; ++i)
{
//循环,用于计时
}
// ------------------------输出结果----------------------
std::cout << "StopWatch 计时为:" << stopWatch.elapsed() << "s" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Timer 计时为:" << timer.getMs() << "ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "BasicTimer 计时为:" << basicTimer.time() << "s" << std::endl;
return 0;
}