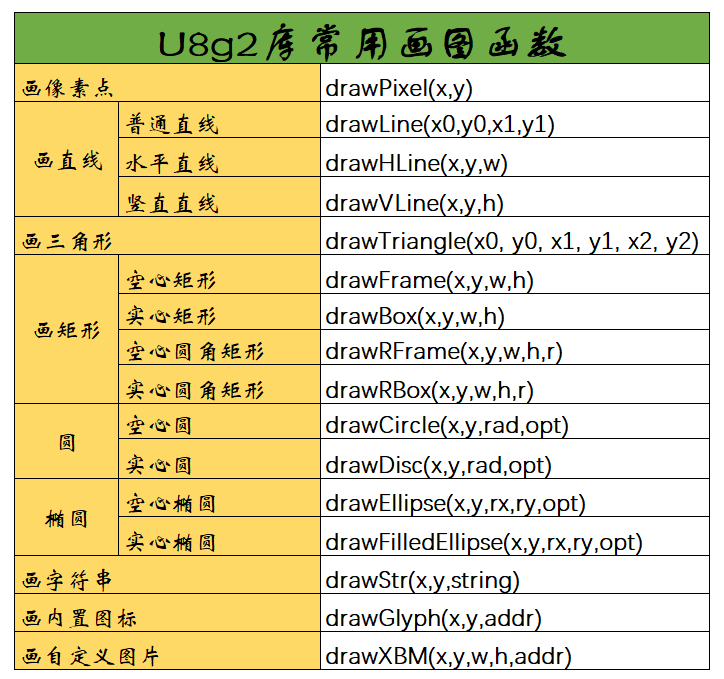
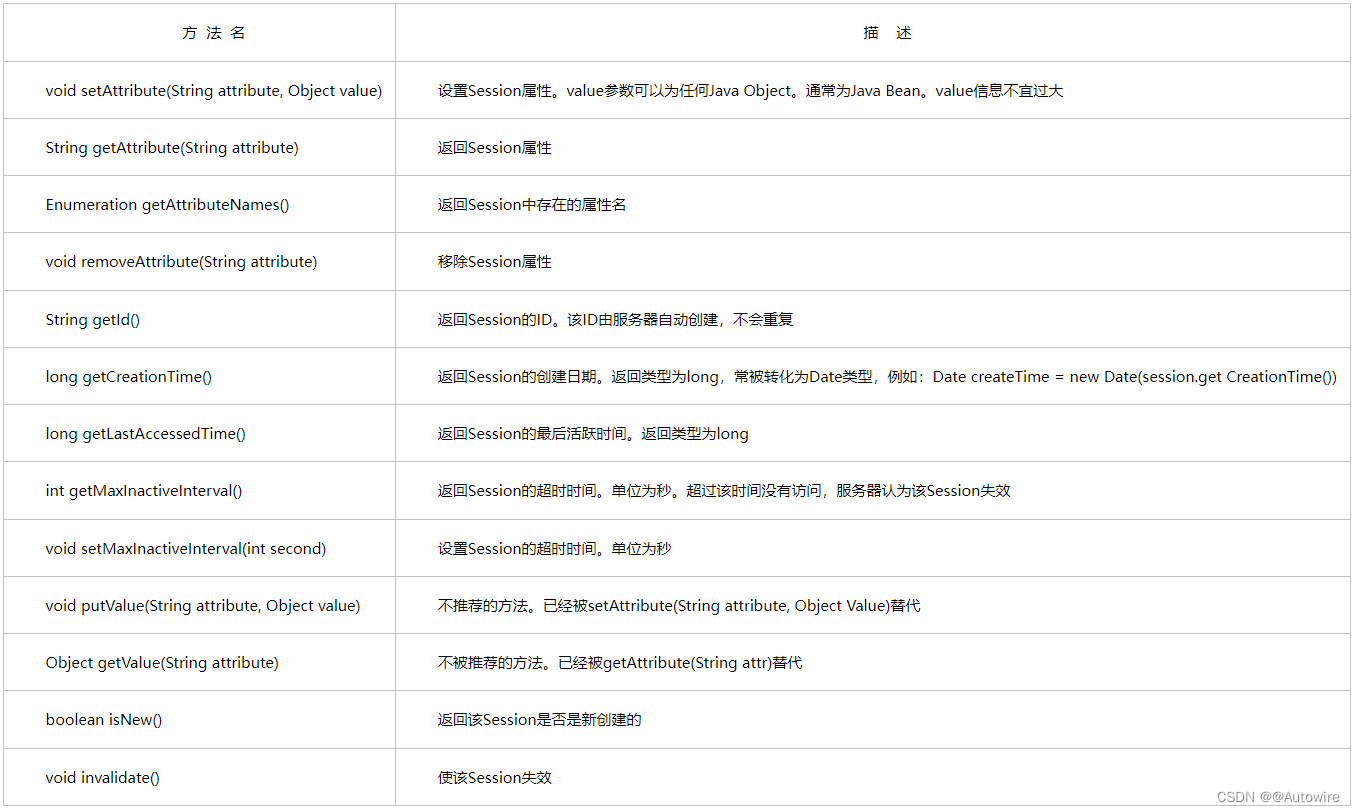
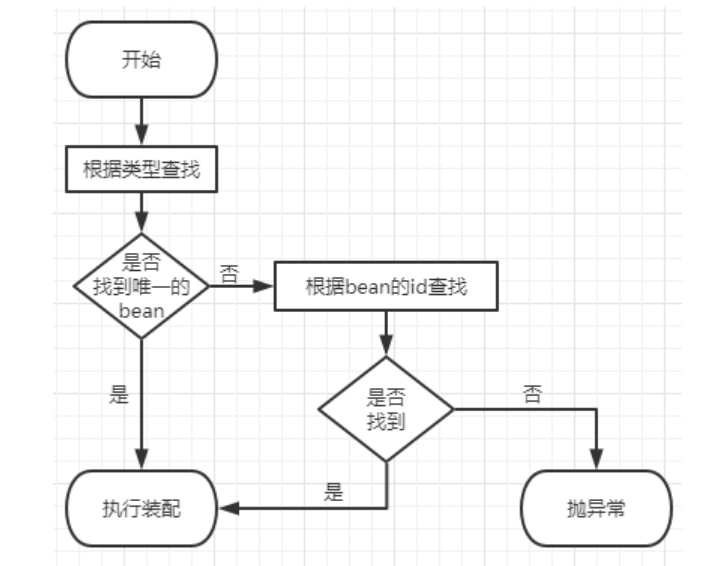
目录
- 1.概述
- 2.代码实现
- 3.应用
本文参考:
LABULADONG 的算法网站
1.概述
(1)拓扑排序 (Topological Sort) 是指将有向无环图 G = (V, E) 中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点 u 和 v,若边<u, v> ∈ E(G),则 u 在线性序列中出现在 v 之前。通常,这样的线性序列称为满足拓扑次序 (Topological Order) 的序列,简称拓扑序列。
(2)下面的左图是一个有向无环图,右图则将左图进行了同构变换,方便观察其拓扑序列。
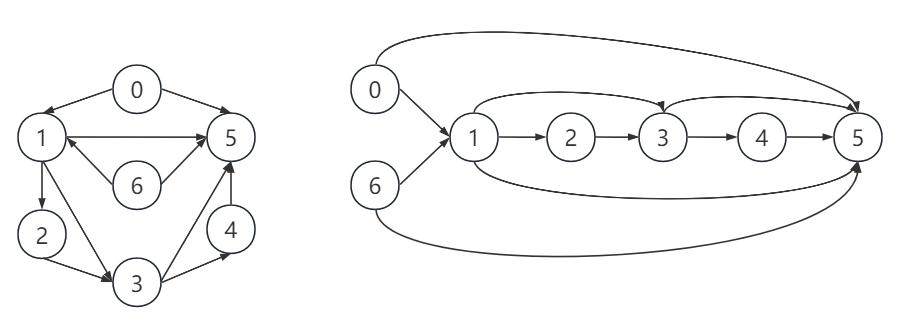
(2)拓扑排序仅针对有向无环图,并且有向无环图的拓扑序列一定存在且不一定唯一。例如上面左图的拓扑排序可以为:
0 6 1 2 3 4 5
或者
6 0 1 2 3 4 5
2.代码实现
(1)当使用邻接矩阵来表示图时,其代码实现如下:
class Solution {
/**
* @param1: 邻接矩阵,adjMatrix[i][j] = 0 表示节点 i 和 j 之间没有边直接相连
* @return: 拓扑序列
* @description: 对用邻接表 adjMatrix 表示的图进行拓扑排序
*/
public static int[] topologicalSort(int[][] adjMatrix) {
// n 表示图中的节点数
int n = adjMatrix.length;
//计算图中每个节点的入度,inDegree[i] = j 表示节点 i 的入度为 j
int[] inDegree = new int[n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (adjMatrix[i][j] != 0) {
inDegree[j]++;
}
}
}
//将入度为 0 的节点加入到队列中
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
//记录拓扑序列
int[] order = new int[n];
//记录遍历节点的顺序
int cnt = 0;
//通过 BFS 算法完成拓扑排序
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队首节点
int cur = queue.poll();
//取出的节点顺序即为拓扑排序的结果
order[cnt] = cur;
cnt++;
//遍历当前节点 cur 所指向的所有节点
for (int next = 0; next < n; next++) {
if (adjMatrix[cur][next] != 0) {
//去掉 cur 指向 next 的边,故 next 的入度减 1
inDegree[next]--;
//将入度为 0 的节点再次加入队列种
if (inDegree[next] == 0) {
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
}
if (cnt != n) {
//图中存在环,拓扑排序不存在
return new int[]{};
} else {
return order;
}
}
}
(2)当使用邻接表来表示图时,其代码实现如下:
class Solution {
/**
* @param1: 邻接表,adjList[i] 中存储节点 i 指向的节点
* @param2: 图的节点数
* @return: 拓扑序列
* @description: 对用邻接表 adjList 表示的图进行拓扑排序
*/
public static int[] topologicalSort(List<Integer>[] adjList, int n) {
//计算图中每个节点的入度,inDegree[i] = j 表示节点 i 的入度为 j
int[] inDegree = new int[n];
for (List<Integer> list : adjList) {
for (Integer node : list) {
inDegree[node]++;
}
}
//将入度为 0 的节点加入到队列中
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
//记录拓扑序列
int[] order = new int[n];
//记录遍历节点的顺序
int cnt = 0;
//通过 BFS 算法完成拓扑排序
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队首节点
int cur = queue.poll();
//取出的节点顺序即为拓扑排序的结果
order[cnt] = cur;
cnt++;
//遍历当前节点所指向的所有节点
for (int next : adjList[cur]) {
//去掉 cur 指向 next 的边,故 next 的入度减 1
inDegree[next]--;
//将入度为 0 的节点再次加入队列中
if (inDegree[next] == 0) {
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
if (cnt != n) {
//图中存在环,拓扑排序不存在
return new int[]{};
} else {
return order;
}
}
}
3.应用
(1)拓扑排序常用来确定一个依赖关系集中事物发生的顺序。例如,在日常工作中,可能会将项目拆分成 A、B、C、D 四个子部分来完成,但 A 依赖于 B 和 D,C 依赖于 D。为了计算这个项目进行的顺序,可对这个关系集进行拓扑排序,得出一个线性的序列,则排在前面的任务就是需要先完成的任务。
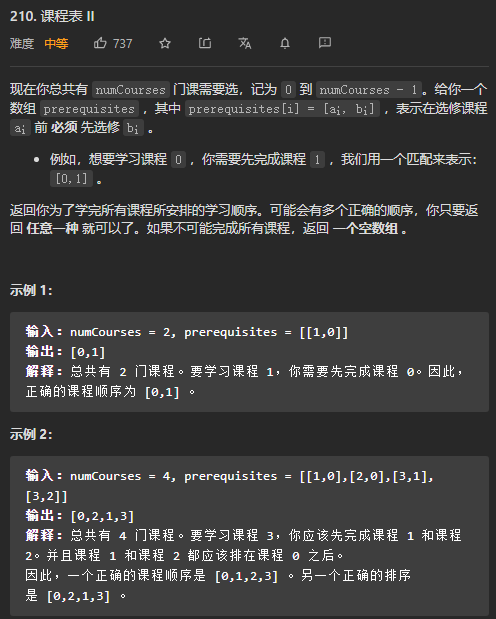
(2)例如 LeetCode 中的210. 课程表 II这题,就是对拓扑排序的应用:
此题只需要在上述代码的基础上加一个构建邻接表的方法即可,代码实现如下:
//思路1————拓扑排序_BFS
class Solution {
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
//通过题目信息创建有向图,使用邻接表存储
List<Integer>[] graph = buildGraph(numCourses, prerequisites);
//计算图中每个节点的入度,inDegree[i] = j 表示节点 i 的入度为 j
int[] inDegree = new int[numCourses];
for (int[] edge : prerequisites) {
//修完课程 from 才能修课程 to,即在图中节点 from 指向节点 to
int to = edge[0];
inDegree[to]++;
}
//将入度为 0 的节点加入到队列中
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
//记录拓扑排序的结果(即课程安排的学习顺序)
int[] res = new int[numCourses];
//记录遍历节点的顺序
int cnt = 0;
//通过BFS算法完成拓扑排序
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队首节点
int cur = queue.poll();
//取出的节点顺序即为拓扑排序的结果
res[cnt] = cur;
cnt++;
//遍历当前节点所指向的所有节点
for (int next : graph[cur]) {
//去掉cur指向next的边,故next的入度减 1
inDegree[next]--;
//将入度为 0 的节点再次加入队列种
if (inDegree[next] == 0) {
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
if (cnt != numCourses) {
//图中存在环,拓扑排序不存在,即课程安排有冲突
return new int[]{};
} else {
return res;
}
}
/*
利用题目所给信息构建有向图,通过邻接表存储
其中 numCourses 表示节点个数,prerequisites 存储节点之间的关系
*/
public List<Integer>[] buildGraph(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
//图中共有 numCourses 个节点
List<Integer>[] graph = new LinkedList[numCourses];
//创建 numCourses 个节点
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
//创建节点之间的关系(即有向边)
for (int[] edge : prerequisites) {
int from = edge[1];
int to = edge[0];
//修完课程 from 才能修课程 to,即在图中添加一条从 from 指向 to 的有向边
graph[from].add(to);
}
return graph;
}
}
(3)大家可以去 LeetCode 上找相关的拓扑排序的题目来练习,或者也可以直接查看LeetCode算法刷题目录(Java)这篇文章中的拓扑排序章节。如果大家发现文章中的错误之处,可在评论区中指出。