🎁个人主页:我们的五年
🔍系列专栏:数据结构课程学习
🌷追光的人,终会万丈光芒
🎉欢迎大家点赞👍评论📝收藏⭐文章


目录
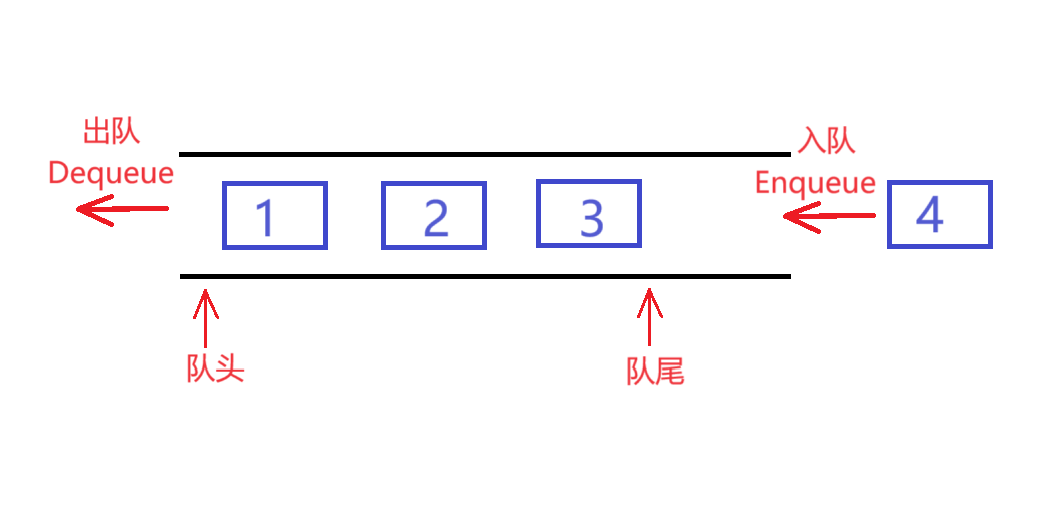
🚗 1.队列的基本概念:
🚗2.判断队列使用哪种数据结构实现:
🚗3.队列的结构:
🚗4.队列初始化:
🚗5.队列销毁:
🚗6.队列尾插:
🚗7.队列头部删数据:
🚗8.取队头,队尾元素:
🚗9.队列判空:
🚗10.整体函数:
🚗 1.队列的基本概念:
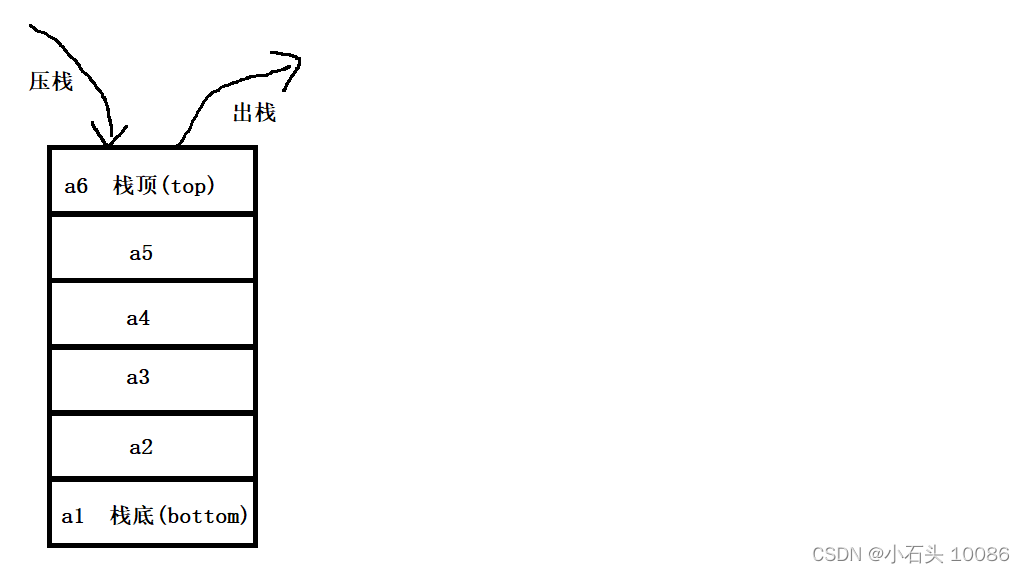
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
🚗2.判断队列使用哪种数据结构实现:
像栈一样,我们只要在栈顶插入数据,在栈顶删除数据,取栈顶的元素。这些过程中,用数组实现不需要去整体移动数,这样我们就选择数组实现。
但是,如果我们用数组实现队列,当出队列的时候,我们就要把剩下的数据整体往前面移动一位,这样就会很麻烦。如果我们使用链表,就会不需要去移动数据。
注意:
其实,栈和队列都可以用数组和链表实现,栈也可以用链表,队列也可以用数组。只是实现栈的时候用数组更好,实现队列的时候用链表更好。
🚗3.队列的结构:
typedef struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType x;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue {
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;⛷QueueNode表示一个节点,里面存着数据,和下个节点的指针,多个节点也就形成了链表。
⛷因为我们要进行头删和尾插,所以我们必须要有头节点,但是如果没有尾节点,我们每次尾插都要遍历链表,这样时间复杂度就变成了O(N),如果我们在队列里加入尾节点,这样时间复杂度就是O(1)。
⛷头删过程中,头节点会改变,我们就得使用二级指针,但是我们如果用结构体,就可以避免了使用二级指针。
⛷另外,我们增加size表示节点个数,也可以降低队列函数实现得难度。
🚗4.队列初始化:
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps); //队列判空
ps->phead =ps->ptail= NULL;
ps->size = 0; //队列个数
}
🚗5.队列销毁:
//队列销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
while (ps->phead)
{
QNode* next = ps->phead->next;
free(ps->phead);
ps->phead = next;
ps->size--;
}
}
🚗6.队列尾插:
//队列尾部插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
QNode* node = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(node);
node->x = x;
node->next = NULL;
if (ps->size == 0)
{
ps->phead = ps->ptail = node;
ps->size++;
}
else
{
ps->ptail->next = node;
ps->ptail = node;
ps->size++;
}
}
🚗7.队列头部删数据:
void QueuePop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == 0) //队列为空的情况
return;
else if (ps->size == 1) //队列只有一个数据的时候,删除数据以后,要把phead和ptail同时置为空,不然只把一个置为NULL,那么另外一个就变成野指针了。
{
free(ps->phead);
ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;
ps->size--;
}
else
{
QNode* next = ps->phead->next;
free(ps->phead);
ps->phead = next;
ps->size--;
}
}❗️注意:
队列为空,队列只有一个元素,队列有多个元素三种情况要分开考虑,因为如果把队列只有一个元素的情况放在多个元素的情况下一起处理,那么只有ps->phead变成了NULL,ps->ptail还没有置为NULL,这样ps->ptail就变成了野指针。
🚗8.取队头,队尾元素:
//取队头元素
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->phead);
return ps->phead->x;
}//取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->phead);
return ps->ptail->x;
}
🚗9.队列判空:
//队列判空,为空返回true,不为空返回false
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size == 0;
}
🚗10.整体函数:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType x;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue {
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* ps);
//摧毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps);
//先进后出,尾插数据
void QueuePush(Queue* ps, QDataType x);
//头部删除数据
void QueuePop(Queue* ps);
//取队头元素
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps);
//取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps);
//队列判空,为空返回true,不为空返回false
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps);
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->phead =ps->ptail= NULL;
ps->size = 0; //队列个数
}
//队列销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
while (ps->phead)
{
QNode* next = ps->phead->next;
free(ps->phead);
ps->phead = next;
ps->size--;
}
}
//队列尾部插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
QNode* node = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(node);
node->x = x;
node->next = NULL;
if (ps->size == 0)
{
ps->phead = ps->ptail = node;
ps->size++;
}
else
{
ps->ptail->next = node;
ps->ptail = node;
ps->size++;
}
}
//删除队头元素
void QueuePop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == 0)
return;
else if (ps->size == 1)
{
free(ps->phead);
ps->phead = ps->ptail = NULL;
ps->size--;
}
else
{
QNode* next = ps->phead->next;
free(ps->phead);
ps->phead = next;
ps->size--;
}
}
//取队头元素
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->phead);
return ps->phead->x;
}
//取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->phead);
return ps->ptail->x;
}
//队列判空,为空返回true,不为空返回false
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size == 0;
}



![[数据集][图像分类]抽烟打电话分类数据集6150张3类别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fa27467c878a4d02b1bd07e8da39d484.png)