文章目录
- 📝为什么学习string类?
- 🌉 C语言中的字符串
- 🌉string考察
- 🌠标准库中的string类
- 🌉string类的常用接口说明
- 🌠string类对象的常见构造
- 🚩总结
📝为什么学习string类?
🌉 C语言中的字符串
C语言中,字符串是以'\0'结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。
🌉string考察
在OJ中,有关字符串的题目基本以string类的形式出现,而且在常规工作中,为了简单、方便、快捷,基本都使用string类,很少有人去使用C库中的字符串操作函数。
- 字符串相加
- 把字符串转换成整数 (atoi)
🌠标准库中的string类
官方通用网站:https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/
string类的文档介绍
std::string
typedef basic_string<char> string;
注意:在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
文档内容:
String类:
- 字符串是表示字符序列的对象。
- 标准字符串类通过类似于标准字节容器的接口为此类对象提供支持,但添加了专门设计用于处理单字节字符字符串的功能。
string类是basic_string类模板的实例化,该模板使用char(即字节)作为其字符类型,具有默认的char_traits和allocator类型(有关模板的详细信息,请参阅basic_string)。- 请注意,此类独立于所使用的编码处理字节:如果用于处理多字节或可变长度字符(如
UTF-8)的序列,则此类的所有成员(如长度或大小)及其迭代器仍将以字节(而不是实际编码字符)为单位进行操作。
总结:
string是表示字符串的字符串类- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string;- 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
🌉string类的常用接口说明
🌠string类对象的常见构造
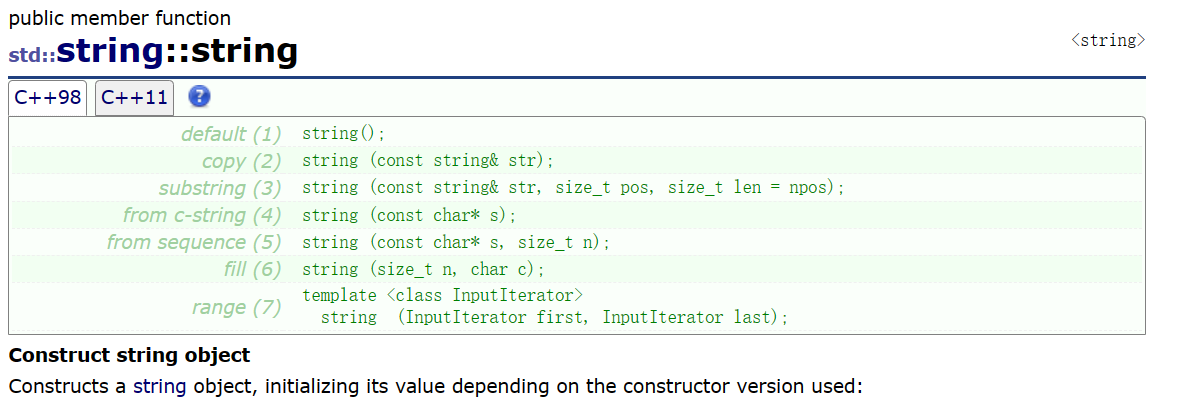

string():构造空的string类对象,即空字符串
使用:
string s1; // 构造空的string类对象s1
string(const char* s)--> 用C-string来构造string类对象
使用:
string s2("hello C++");
string(const string&s)----> 拷贝构造
使用:
string s2("hello C++");
string s3(s2);
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);---->复制从字符位置pos开始向后len长度的str部分
如果长度
len比字符串长度str大,则复制字符串的末尾
当len= 缺省值npos时,也是遍历复制到字符串尾部
此常量使用值-1定义,由于size_t是无符号整数类型,因此它是此类型的最大可能表示值:对于unsigned int类型,-1会被解释为4294967295(2^32 - 1)
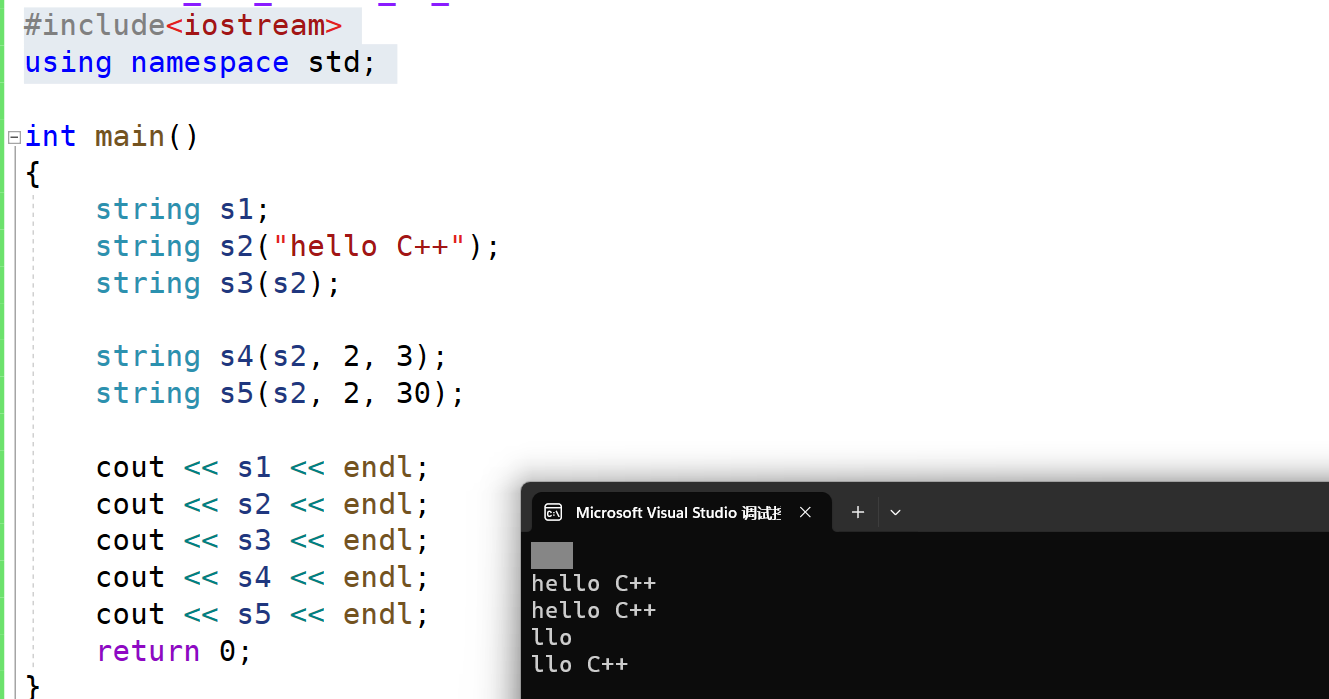
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello C++");
string s3(s2);
string s4(s2, 2, 3);
string s5(s2, 2, 30);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << s5 << endl;
return 0;
}
string (const char* s, size_t n);—>从s指向的字符数组中复制前n个字符。
使用:
string s6("hello C++", 4);
cout << s6 << endl;
输出:
hell
string (size_t n, char c);—>用字符c的n个连续副本填充字符串。
使用:
string s7(4, 'x');
cout << s7 << endl;
输出:
xxxx
注意:string类已经有了流运算符重载,可以直接使用<<和>>进行输出,无需再另外实现operator等重载函数
🚩总结
string():构造空的string类对象,即空字符串
string(const char* s)--> 用C-string来构造string类对象
string(const string&s)----> 拷贝构造
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);---->复制从字符位置pos开始向后len长度的str部分
string (const char* s, size_t n);—>从s指向的字符数组中复制前n个字符。
string (size_t n, char c);—>用字符c的n个连续副本填充字符串。




![[NSSRound#1 Basic]basic_check](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/e44781c2d6f7112cb158501699d2e10d.png)