✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
智能优化算法 神经网络预测 雷达通信 无线传感器
信号处理 图像处理 路径规划 元胞自动机 无人机 电力系统
⛄ 内容介绍
局部均值分解是一种信号处理方法,旨在从信号中提取出一组纯调频信号和包络信号的“最佳拟合”乘积函数( product functions,PF) ,通过数学迭代循环可以得到所有的 PF 分量,进而进行信号分析。对于信号 x( t) ,其分解过程如下。





⛄ 完整代码
function [pfs, ams, fms, ort, fvs, iterNum] = RLMD(x,varargin)
% Robust Local Mean Decomposition (RLMD)
% ERPHM Code
% 2017-06-11 Created by Dr.Zhiliang Liu, Deng Pan and Yaqiang Jin.
%
% If you have any questions, please contact us via Zhiliang_Liu@uestc.edu.cn
% This funcion perform the local mean decompose(LMD) on the input signal, and
% return the product function (pfs), and their corresponding instantaneous
% amplitude(ams) and frequency modulation signal(fms).
%
% SYNTAX:
% pfs = lmd_liu(x);
% [pfs, ams, fms, ort] = lmd_liu(x);
% [pfs, ams, fms, ort] = lmd_liu(x,options);
% [pfs, ams, fms, ort] = lmd_liu(x,'option_name1',option_value1,....);
%
% INPUTS:
% [1] x: a row signal vecter which you want to perform LMD.
% [2] option: a struct contains options' name(option_name) and
% corresponding values(option_value).
% [2.1] 'display'
% plot PFs, AMs and FMs or not,1 plot,0 do not.
% default: 0
% [2.2] 'max_iter'
% max number of iterations in one pf sift procedure.
% default: 30
% [2.3] 'max_pfs'
% max number of pfs obtained in lmd procedure.
% default: 10
% OUTPUTS
% [1] pfs
% Product Function(PF) Matrix of which each row is a PF and the last
% row is the residual signal.
% [2] ams
% amplitude modulation signal of each PF.
% [3] fms
% frequency modulation signal of each PF.
% [4] iterNum
% iteration times for each PF.
% [5] fvs
% objective funciton values
% [6] ort
% index of orthogonality
%
% REFERENCE
% [1] Zhiliang Liu, Yaqiang Jin, Ming J. Zuo, and Zhipeng Feng. Time-frequency
% representation based on robust local mean decomposition for multi-component
% AM-FM signal analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. 95: 468-487, 2017.
% [2] Smith J S. The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG
% perception data[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2005,
% 2(5): 443-454.
% [3] G. Rilling, P. Flandrin and P. Goncalves. On empirical mode
% decomposition and its algorithms. IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear
% Signal and Image Processing NSIP-03, Grado (I), June 2003
%
% % EXAMPLE:
% clc;close all;clear;
% fs = 10000; % sampling frequency
% N = 30000; % data amount
% t = (1:N)/fs; % time vector
% x1 = (2+cos(2*pi*0.5*t)).*cos(2*pi*5*t+15*t.^2);
% x2 = cos(2*pi*2*t);
% x = x1+x2;
% options.display = 1;
% options.max_iter = 30;
% options.max_pfs = 10;
% [pf3, ams3, fms3, ort3] = lmd_public(x,options);
% figure;
% subplot(2,1,1),plot(t,x1);
% subplot(2,1,2),plot(t,x2);
% Input arguments initialization
[x, display, stop_thre, sifting_stopping_mode, max_iter, max_pfs, smooth_mode,...
ma_span, ma_iter_mode, extd_r, x_energy, pfs, ams, fms, iterNum, fvs]...
= initial(x,varargin{:});
% Initialize main loop
i = 0;
xs = x; % copy x to xs for sifting process, reserve original input as x.
nx = length(x);
while i < max_pfs && ~stoplmd(xs, x_energy) % outer loop for PF selection
i = i+1;
% initialize variables used in PF sifting loop
a_i = ones(1,nx);
s_j = zeros(max_iter,nx);
a_ij = zeros(max_iter, nx);
% PF sifting iteration loop
j = 0;
stop_sifting = 0;
s = xs;
while j < max_iter && ~stop_sifting % inner loop for sifting process
j = j+1;
[m_j, a_j, n_extr] = lmd_mean_amp(s, smooth_mode, ma_span, ma_iter_mode,...
extd_r);
% force to stop iter if number of extrema of s is smaller than 3.
if n_extr < 3
break;
end
h_j = s-m_j; % remove mean.
s = h_j./a_j; % demodulate amplitude.
a_i = a_i .* a_j; % mulitiply every ai
a_ij(j, :) = a_i;
s_j(j, :) = s;
[stop_sifting,fvs(i,:)] = is_sifting_stopping(a_j, j, fvs(i,:), sifting_stopping_mode, stop_thre);
end % sift iteration loop
switch sifting_stopping_mode
case {'liu'}
[~, opt0] = min(fvs(i,1:j)); % ***Critical Step***
opt_IterNum = min(j, opt0); % in case iteration stop for n_extr<3
% opt_IterNum = min(j-2, opt0);
otherwise
error('No specifications for sifting_stopping_mode.');
end
ams(i, :) = a_ij(opt_IterNum, :); % save each amplitude modulation function in ams.
fms(i, :) = s_j(opt_IterNum, :); % save each pure frequency modulation function in fms.
pfs(i, :) = ams(i, :).*fms(i, :); % gain Product Funcion.
xs = xs-pfs(i, :); % remove PF just obtained from input signal;
iterNum(i) = opt_IterNum; % record the iteration times taken by of each PF sifing.
end % main loop
pfs(i+1, :) = xs; % save residual in the last row of PFs matrix.
ams(i+1:end,:) = []; fms(i+1:end,:) = []; pfs(i+2:end,:) = []; fvs(i+1:end,:) = [];
ort = io(x, pfs);
% Output visualization
if display == 1
lmdplot(pfs, ams, fms, smooth_mode);
end
end
%--------------------------- built-in functions ---------------------------
% initialize signal and options
function [x, display, stop_thre, sifting_stopping_mode, max_iter, max_pfs, smooth_mode,...
ma_span, ma_iter_mode, extd_r, x_energy, pfs, ams, fms, iterNum, fvs]...
= initial(x,varargin)
% option fields(i.e. name)
optn_fields = {'display', 'stop_thre', 'sifting_stopping_mode', 'max_iter',...
'max_pfs', 'smooth_mode', 'ma_span', 'ma_iter_mode','extd_r', 'fix','fix_h'};
% set default options(def_opts)
def_optns.display = 0; % plot PFs.
def_optns.stop_thre = [0.005,0.7,0.05]; % sifting stopping thresholds for Rilling's criterion
def_optns.sifting_stopping_mode = 'liu'; % sifting stoppling optimizaion
def_optns.max_iter = 30; % max iteration number in a PF sifting process.
def_optns.max_pfs = 10; % max number of PFs.
def_optns.smooth_mode = 'ma'; % ma - moving average, spline - pchip.
def_optns.ma_span = 'liu'; % pdmax span method, see function ma_span.
def_optns.ma_iter_mode = 'fixed'; % fixed or dynamic span for iterate ma.
def_optns.extd_r = 0.2; % end extension length to original data.
optns = def_optns; % opts stores the final options.
% get user input options(in_opts)
if nargin == 1 % use default options(see above).
in_optns = def_optns;
elseif nargin == 2 && isstruct(varargin{1})
% 1st argument is x, 2nd is options in a struct.
in_optns = varargin{1};
elseif nargin > 2 % input options seperately.
try
in_optns = struct(varargin{:});
catch
error('wrong argmument syntax')
end
else
error('arguments error: maybe not enough or wrong syntax')
end
names = fieldnames(in_optns);% get input options' name and value
for k = names'
if ~any(strcmpi(char(k), optn_fields))
% find any wrong argument in syntax.
error(['bad option field name: ',char(k)])
end
if ~isempty(eval(['in_optns.',char(k)]))
% alter default option values with input, and empty input keep default.
eval(['optns.',lower(char(k)),' = in_optns.',char(k),';'])
end
end
display = optns.display;
stop_thre = optns.stop_thre;
sifting_stopping_mode = optns.sifting_stopping_mode;
max_iter = optns.max_iter;
max_pfs = optns.max_pfs;
smooth_mode = optns.smooth_mode;
ma_span = optns.ma_span;
ma_iter_mode = optns.ma_iter_mode;
extd_r = optns.extd_r;
% initialize x(input signal), x_energy, pf, ams, fms.
x = x(:)'; % make x a row vector.
nx = length(x);
x_energy = sum(x.^2); % energy = square summation.
ams = zeros(max_pfs,nx);
fms = zeros(max_pfs,nx);
pfs = zeros(max_pfs,nx);
iterNum = zeros(1,max_pfs);
fvs = zeros(max_pfs,max_iter);
% fix = opts.fix;
% fix_h = opts.fix_h;
% mask = opts.mask;
% ndirs = opts.ndirs;
% complex_version = opts.complex_version;
end
% Check if there are enough (3) extrema to continue the decomposition
function stop = stoplmd(x, x_energy)
[indmin,indmax] = extr(x);
peak = length(indmin) + length(indmax);
ratio = sum(x.^2)/x_energy;
stop = peak < 3 | ratio < 0.001;
end
% Compute mean function and amplitude function of x in LMD
function [m, a, n_extr] = lmd_mean_amp(x,smooth_mode,ma_span,ma_iter_mode,extd_r)
% find extremum indices
[indmin, indmax, ~] = extr(x);
% total amount of extrema
n_extr = length(indmin)+length(indmax);
if n_extr < 3
m = [];
a = [];
return
end
% extend original data to refrain end effect
% ext_indmin(max) contains the end point's index
[ext_indmin,ext_indmax,ext_x,cut_index] = extend(x, indmin, indmax, extd_r);
% preparation
m0 = zeros(1,length(ext_x));
a0 = zeros(1,length(ext_x));
ind_extextr = sort([ext_indmin, ext_indmax]);
% compute local mean and amplititude sequence
switch smooth_mode
case 'ma'
for k = 1:length(ind_extextr)-1
subm1 = ind_extextr(k);
subm2 = ind_extextr(k+1);
m0(subm1:subm2) = 0.5*(ext_x(subm1)+ext_x(subm2));
a0(subm1:subm2) = 0.5*abs(ext_x(subm1)-ext_x(subm2));
end
[span, smax] = getBestSpan(ind_extextr, ext_x, ma_span);
% iterative moving average
m = itrma(m0, ma_iter_mode, span, smax, ma_span);
a = itrma(a0, ma_iter_mode, span, smax, ma_span);
m = m(:)'; % make m a row vector
a = a(:)';
% cut extension
m = m(1, cut_index(1):cut_index(2));
a = a(1, cut_index(1):cut_index(2));
otherwise
error('No specifications for smooth_mode.');
end
end
% Moving average span selection
% return the best span of moving average
function [span, smax] = getBestSpan(ind_extr, x, ma_span)
% ind_extr - indices of extremum of x
% x - data;
x_extr = x(ind_extr);
% 0 elements' indices of eql_extr are the first indices of identical
% maximum ,or minimum, pairs
eql_extr = x_extr(3:end)-x_extr(1:end-2);
% delete the extremum indecies between two identical maximum(minimum)
ind_extr(find(eql_extr == 0)+1) = [];
% vector contains all steps of local mean
step_vec = ind_extr(2:end)-ind_extr(1:end-1)+1;
smax = max(step_vec);
smean = mean(step_vec);
switch ma_span
case 'liu'
[density,xmesh] = histcounts(step_vec,'Normalization','probability');
xmesh = xmesh(1:end-1)+diff(xmesh)/2;
span_c = sum(xmesh.*density);
span_std = sqrt(sum((xmesh-span_c).^2.*density));
span = ceil(span_c + 3*span_std);
otherwise
error('No specifications for ma_span.');
end
span = ceil(span);
span = span+1-mod(span,2); % force span to be odd
end
% Iterative moving average dynamic step
function x = itrma(x, ma_iter_mode, span, smax, ma_span)
x = smooth(x, span);
nm = length(x);
switch ma_iter_mode
case 'fixed' % stick step
cntr = 0; % count times of moving average
max_c = ceil(smax/span)*15; % theoretic
% max_c = ceil(smax/(span-1));
% nm = length(x);
k = (span+1)/2;
kmax = nm - (span-1)/2;
while (k < kmax) && (cntr < max_c) % find flat step
if x(k) == x(k+1);
x = smooth(x, span);
cntr = cntr+1;
k = k-1;
end
k = k+1;
end
% while ~isempty(find(diff(x)==0)) && (cntr < max_c)
% % find(diff(x)==0)
% x = smooth(x, span);
% cntr = cntr+1;
% end
otherwise
error('No specifications for ma_iter_mode.');
end
end
% Extend original data to refrain end effect
% ** Modified on emd by G.Rilling and P.Flandrin
% ** http://perso.ens-lyon.fr/patrick.flandrin/emd.html
function [ext_indmin, ext_indmax, ext_x, cut_index] = extend(x, indmin,...
indmax, extd_r)
if extd_r == 0 % do not extend x
ext_indmin = indmin;
ext_indmax = indmax;
ext_x = x;
cut_index = [1,length(x)];
return
end
nbsym = ceil(extd_r*length(indmax)); % number of extrema in extending end
xlen = length(x);
t = 1:xlen;
% boundary conditions for interpolations :
% left end extend
if indmax(1) < indmin(1) % first extremum is maximum
if x(1) > x(indmin(1)) % first point > first min extremum
lmax = fliplr(indmax(2:min(end,nbsym+1)));
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lsym = indmax(1);
else % first point < first min extremum
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lmin = [fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1];
lsym = 1;
end
else % first extremum is minimum
if x(1) < x(indmax(1)) % first point < first maximum
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lmin = fliplr(indmin(2:min(end,nbsym+1)));
lsym = indmin(1);
else % first point > first minimum
lmax = [fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1];
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
lsym = 1;
end
end
% right end extension
if indmax(end) < indmin(end) % last extremum is minimum
if x(end) < x(indmax(end)) % last point < last maximum
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1));
rsym = indmin(end);
else % last point > last maximum
rmax = [xlen, fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))];
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rsym = xlen;
end
else % last extremum is maximum
if x(end) > x(indmin(end)) % last point > last minimum
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1));
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rsym = indmax(end);
else % last point < last minimum
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
rmin = [xlen, fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))];
rsym = xlen;
end
end
tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin);
tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax);
trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin);
trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax);
% in case symmetrized parts do not extend enough
if tlmin(1) > t(1) || tlmax(1) > t(1)
if lsym == indmax(1)
lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym)));
else
lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym)));
end
if lsym == 1
error('bug')
end
lsym = 1;
% tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin);
% tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax);
end
if trmin(end) < t(xlen) || trmax(end) < t(xlen)
if rsym == indmax(end)
rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
else
rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end));
end
if rsym == xlen
error('bug')
end
rsym = xlen;
% trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin);
% trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax);
end
l_end = max(max(lmax, lmin));
r_end = min(min(rmax, rmin));
new_lmax = l_end+1-lmax;
new_lmin = l_end+1-lmin;
new_rmax = rsym-rmax;
new_rmin = rsym-rmin;
lx_length = l_end-lsym;
lx = fliplr(x(lsym+1:l_end));
rx = fliplr(x(r_end:rsym-1));
ext_x = [lx, x(lsym:rsym), rx];
ext_indmin = [new_lmin,indmin+lx_length-lsym+1,new_rmin+lx_length-lsym+1+...
rsym];
ext_indmax = [new_lmax,indmax+lx_length-lsym+1,new_rmax+lx_length-lsym+1+...
rsym];
% Index for cutting extension of x
cut_index = [lx_length-lsym+2, length(x)+lx_length-lsym+1];
end
% sifting stopping criterion
function [stop_sifting,fv_i] = is_sifting_stopping(a_j, j, fv_i, sifting_stopping_mode, stop_thre)
base = ones(size(a_j)); % base line is y = 1.
% df = abs(a_j - base); % difference between a_i and baseline.
df = (a_j - base);
switch sifting_stopping_mode
case 'liu' % local optimal iteration.
fv_i(j) = rms(df)+abs(kurtosis(df)-3);
% fv_i(j) = rms(df)+(kurtosis(df)-3);
% global temp;
% temp(j,:) = [rms(df),kurtosis(df)];
if j >= 3
if ((fv_i(j) >= fv_i(j-1)) && (fv_i(j-1) >= fv_i(j-2)))
stop_sifting = 1;
return;
end
end
otherwise
error('No specifications for sifting_stopping_mode.');
end
stop_sifting = 0;
end
% Extracts the indices of extrema
% ** Copied from emd toolbox by G.Rilling and P.Flandrin
% ** http://perso.ens-lyon.fr/patrick.flandrin/emd.html
function [indmin, indmax, indzer] = extr(x)
m = length(x);
if nargout > 2
x1 = x(1:m-1);
x2 = x(2:m);
indzer = find(x1.*x2<0);
if any(x == 0)
iz = find( x==0 );
% indz = [];
if any(diff(iz)==1)
zer = x == 0;
dz = diff([0 zer 0]);
debz = find(dz == 1);
finz = find(dz == -1)-1;
indz = round((debz+finz)/2);
else
indz = iz;
end
indzer = sort([indzer indz]);
end
end
d = diff(x);
n = length(d);
d1 = d(1:n-1);
d2 = d(2:n);
indmin = find(d1.*d2<0 & d1<0)+1;
indmax = find(d1.*d2<0 & d1>0)+1;
% when two or more successive points have the same value we consider only
% one extremum in the middle of the constant area (only works if the signal
% is uniformly sampled)
if any(d==0)
imax = [];
imin = [];
bad = (d==0);
dd = diff([0 bad 0]);
debs = find(dd == 1);
fins = find(dd == -1);
if debs(1) == 1
if length(debs) > 1
debs = debs(2:end);
fins = fins(2:end);
else
debs = [];
fins = [];
end
end
if ~isempty(debs)
if fins(end) == m
if length(debs) > 1
debs = debs(1:(end-1));
fins = fins(1:(end-1));
else
debs = [];
fins = [];
end
end
end
lc = length(debs);
if lc > 0
for k = 1:lc
if d(debs(k)-1) > 0
if d(fins(k)) < 0
% imax = [imax round((fins(k)+debs(k))/2)];
end
else
if d(fins(k)) > 0
% imin = [imin round((fins(k)+debs(k))/2)];
end
end
end
end
if ~isempty(imax)
indmax = sort([indmax imax]);
end
if ~isempty(imin)
indmin = sort([indmin imin]);
end
end
end
% Compute the index of orthogonality
% ** Copied from emd toolbox by G.Rilling and P.Flandrin
% ** http://perso.ens-lyon.fr/patrick.flandrin/emd.html
function ort = io(x,pfs)
% ort = IO(x,pfs) computes the index of orthogonality
%
% inputs : - x : analyzed signal
% - pfs : production function
n = size(pfs,1);
s = 0;
for i = 1:n
for j =1:n
if i~=j
s = s + abs(sum(pfs(i,:).*conj(pfs(j,:)))/sum(x.^2));
end
end
end
ort = 0.5*s;
end
% Plot PF, Amplititude Signal and FM Signal
function lmdplot(pfs, ams, fms, smooth_mode)
t = 1:size(pfs,2);
pfn = size(pfs,1);
figure
for pfi = 1:pfn
subplot(pfn,1,pfi);
plot(t,pfs(pfi,:));
if pfi < pfn
title(['PF',num2str(pfi),' (',smooth_mode,')']);
else
title(['Residual',' (',smooth_mode,')']);
end
end
figure
for ai = 1:pfn-1
subplot(pfn-1,1,ai);
plot(t,ams(ai,:));
title(['Amplitude Signal',num2str(ai),' (',smooth_mode,')']);
end
figure
for fsi = 1:pfn-1
subplot(pfn-1,1,fsi);
plot(t,fms(fsi,:));
title(['FM Signal',num2str(fsi),' (',smooth_mode,')']);
end
end
% 主函数
% EXAMPLE:
clc;
clear;
close all;
fs = 10000; % sampling frequency
N = 30000; % data amount
t = (1:N)/fs; % time vector
x1 = (2+cos(2*pi*0.5*t)).*cos(2*pi*5*t+15*t.^2);
x2 = cos(2*pi*2*t);
x = x1+x2;
options.display = 1;
options.max_iter = 30;
options.max_pfs = 10;
[pf3, ams3, fms3, ort3] = RLMD(x,options);
figure;
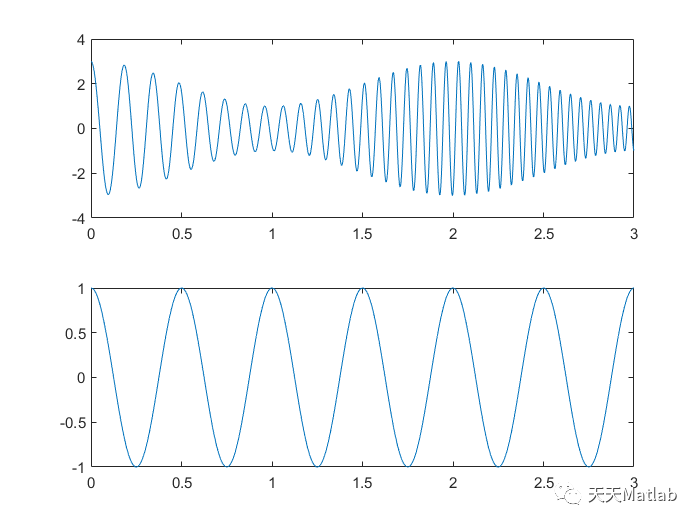
subplot(2,1,1),plot(t,x1);
subplot(2,1,2),plot(t,x2);
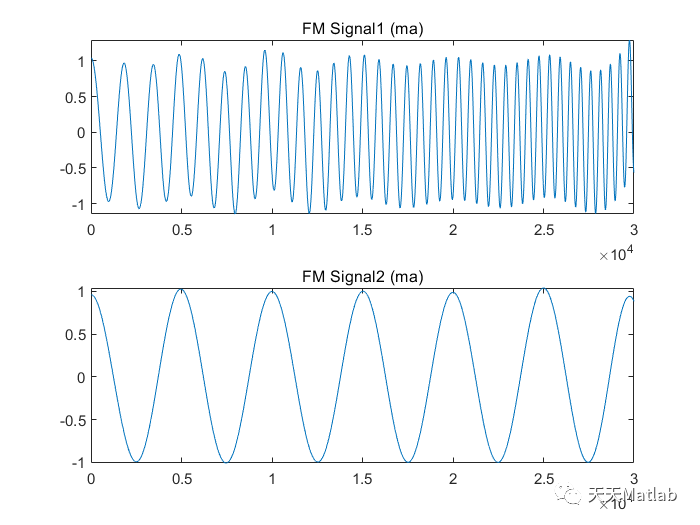
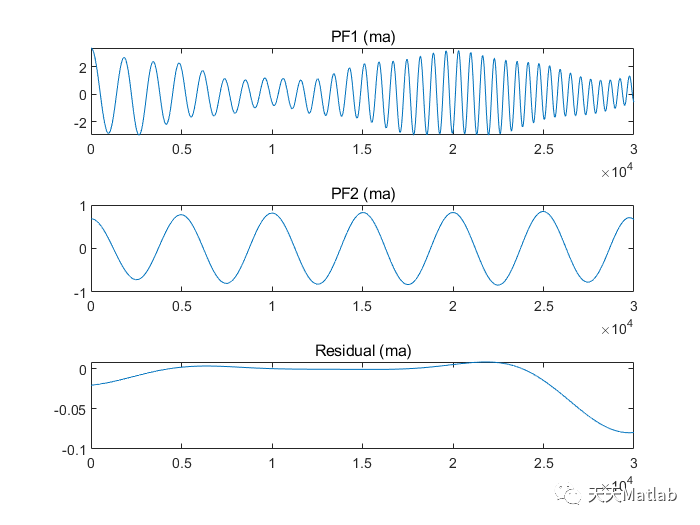
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
[1]林近山, 窦春红. 一种基于局部均值分解滤波的包络分析方法:, CN106198010B[P]. 2018.
[1]陈志刚, 赵志川, 钟新荣,等. 基于鲁棒局部均值分解与二阶瞬态提取变换的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(1):157-165.
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除






![5.python 列表切片双冒号[: :]和[:,j]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a3b30489590646a1b66dd6b7483dbb60.png)

![[附源码]java毕业设计农村电商平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cca9b046d67841e68a1b78f7d5aa4d66.png)