【Java寒假打卡】Java基础-多线程
- 概述
- 读线程实现方式-继承Thread
- 多线程实现方式-Callable
- 三种实现方式的对比
- Thread方法
- 守护线程
- 线程的优先级
概述
-
并发和并行

-
进程和线程

读线程实现方式-继承Thread

- 继承Thread类进行实现

package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
// 重写run方法
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("线程开启了" + i);
}
}
}
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread m1 = new MyThread();
m1.start();// 开启一个线程
MyThread m2 = new MyThread();
m2.start();
// 线程交替执行
}
}
run方法与start方法的区别:run方法表示的仅仅是创建对象,使用对象去调用方法,并没有开启线程,使用start方法开启线程

start方法启动线程;然后使用JVM调用此线程的run()方法
- 开启多线程实现方式-runable接口

实现Runable 接口
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class MyRunable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("第二种多线程的实现" + i);
}
}
}
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class tewts2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个参数对象
MyRunable mr = new MyRunable();
// 创建线程对象 将参数传递给这个线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr);
t1.start();
MyRunable mr1 = new MyRunable();
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr1);
t2.start();
// 线程交替执行
}
}
多线程实现方式-Callable

package com.hfut.edu.test11;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
// 实现call 方法
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("hhhhhhhh" + i);
}
return "xxxx";
}
}
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallable mc = new MyCallable();
FutureTask<String> ft = new FutureTask<>(mc);// 可以获取线程执行完毕之后的结果
Thread t1 = new Thread(ft);
t1.start();
String s = ft.get();// 获取线程执行之后的结果
System.out.println(s);
}
}
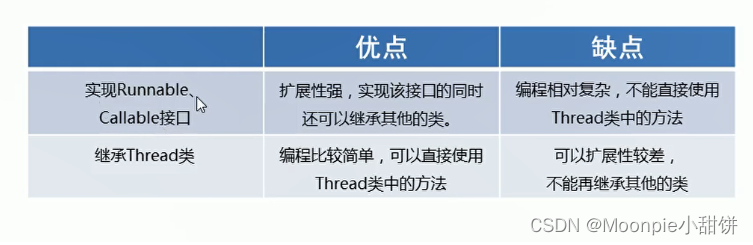
三种实现方式的对比
Thread方法
- 获取线程名称
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
// 重写run方法
@Override
public void run() {
// 获取线程的名称
String name = getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
- 获取当前线程
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
// 重写run方法
@Override
public void run() {
// 获取线程的名称
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();// 静态方法调用
System.out.println(t);
}
}
- 多线程的带参数构造方法
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread(){}
public MyThread(String name){
super(name);// 设置线程的名称
}
// 重写run方法
@Override
public void run() {
// 获取线程的名称
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();// 静态方法调用
System.out.println(t.getName());// 打印线程的名字
}
}
- Sleep方法
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 1; i < 61; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
Thread.sleep(1000);// 程序休眠1s
}
}
}
守护线程
- 当守护线程执行完毕,其他线程也就没有执行下去的必要

package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 m1 = new MyThread1();
MyThread2 m2 = new MyThread2();
m1.setName("主线程");
m2.setName("其他线程");
m1.setDaemon(true);// 主线程执行完毕 其他线程直接结束
m1.start();
m2.start();
}
}
线程的优先级

- 优先级更高 抢到CPU的几率更高
package com.hfut.edu.test11;
public class test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 m1 = new MyThread1();
MyThread2 m2 = new MyThread2();
m1.setName("主线程");
m2.setName("其他线程");
m1.setDaemon(true);// 主线程执行完毕 其他线程直接结束
m1.start();
m2.start();
System.out.println(m1.getPriority());// 打印线程的优先级 默认优先级5
System.out.println(m2.getPriority());//
m1.setPriority(6);
m2.setPriority(7);// 设置线程的优先级
}
}













![Android 设备自动重启分析[低内存]——MTK平台 debuglogger](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2b3cf088fd9240c1b4706a432864d5db.png)

